Tipo de Pregunta Calculada Simple
- Gestionando preguntas
- Comportamientos de preguntas
- Permisos de pregunta
- Tipos de preguntas
- Arrastrar y soltar al texto
- Arrastrar y soltar marcadores
- Arrastrar y soltar sobre imagen
- Calculada
- Calculada simple
- Calculada de opción múltiple
- Descripción
- Ensayo
- Relacionar columnas
- Respuestas incrustadas (Cloze)
- Opción Múltiple
- Ordenamiento
- Numérica
- Respuesta corta
- Relacionar columnas de respuesta corta aleatoria
- Seleccionar palabras faltantes
- Verdadero/Falso
- Preguntas de terceros
- Preguntas FAQ
Vea también:
| Nota del traductor: La palabra inglesa quiz se tradujo al Español internacional como Cuestionario y al Español de México como Examen. |
Las preguntas calculadas simples ofrecen una forma para crear preguntas numéricas individuales cuyas respuestas son el resultado de una fórmula numérica, que contiene valores numéricos variables, mediante el uso de comodines (por ejemplo, {x} , {y}), que son sustituídos con valores aleatorios cuando el estudiante toma el examen (cuestionario).
Las preguntas calculadas simples ofrecen las características más usadas de las preguntas calculadas , pero con una interfase mucho más simple.
Advertencia
Por lo que sería prudente que primero experimente antes de generar muchas preguntas Calculadas simples, especialmente si planea editarlas, lo que sería muy probable.
Hasta que la situación haya siod investigada y corregido lo necesario, usted puede usar como reemplazo para la pregunta calculada simple, ya sea el Tipo de Pregunta Calculada o la pregunta (adicional) Formulas para preguntas levemente más elaboradas.
Mi primera pregunta calculada simple
Como un primer ejemplo, Usted creará una pregunta que pide la superficie de un rectángulo. Aquí están los pasos rápidos que veremos con detalle después:
- Cree el contenido de la pregunta con las variables mostradas en {}
- Escriba la fórmula usando las variables y configure la tolerancia
- Determine el rango del conjunto de variables generadas que aparecerá en el contenido de la pregunta
- Revise el conjunto generado de contenidos de la pregunta
- Como éste es su primer ejemplo, revise su trabajo desde laperspectiva de un alumno
Iniciando el proceso de creación
Vaya al Banco de preguntas, seleccione "crear una nueva pregunta" y elija calculada simple en la ventana emergente. Aparecerá la interfase de pregunta calculada simple. Póngale un nombre razonable a su pregunta donde dice título.
El texto de la pregunta
LLene el texto de la pregunta (tome nota de que los nombres {param} pueden elegirse a voluntad.
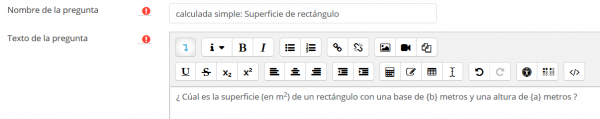
La fórmula para la respuesta correcta
LLene la Fórmula para la Respuesta Correcta usando los nombres de {param} empleados en el texto de la pregunta.
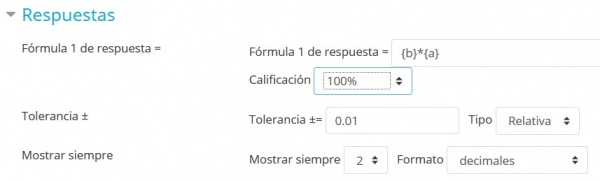
Parámetros para otra respuesta y solución
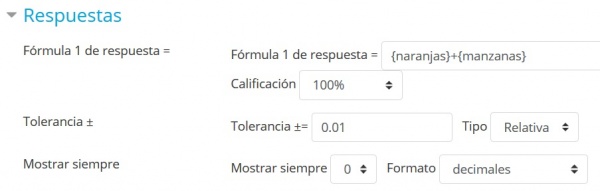
Configure la calificación a 100%, adado que es la única respuesta correcta posible en esta pregunta.
Deje los demás parámetros como están ( 0.01 relativo significa ±1% de tolerancia).
Encuentra el {param} en la fórmula
En simple calculada únicamente los {param} que estén dentro de la fórmula serán empleados.
En el texto de la pregunta , los {param} que estén en la fórmula
aparecerán con los valores numéricos tales como 6.7 .
Cualquier otro {texto incluído} aparecerá cual es, por ejemplo {texto incluído}.
Elije el botón
Al recargar, ambos {b} y {h} se mostrarán.
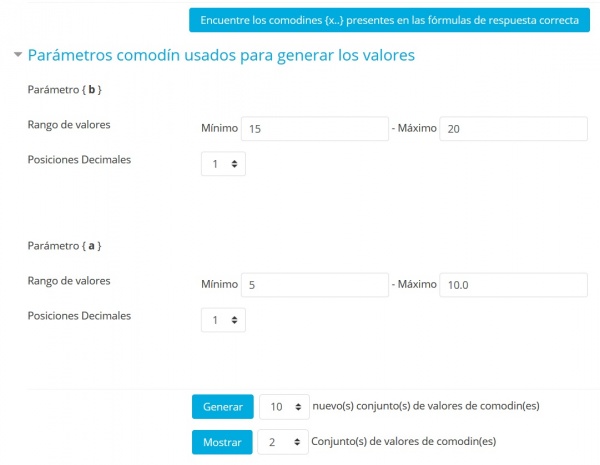
Configura los valores mínimo y máximo
Aquí el rango {b} se ha configurado a un rango de 15-20 y
el rango {a} se configurá a 5-10
dado que queremos un rectángulo con una base más ancha que su altura.
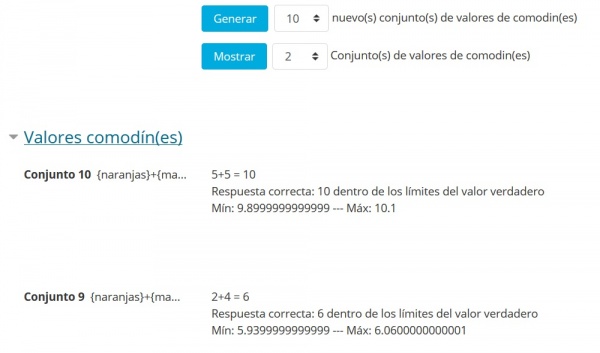
Seleccione el número de conjuntos a generar (aquí son 10) y a mostrar (aquí 2)
Solamente para ilustrar que Usted puede controlar el número de valores mostrados, lo que resulta útil si crea 100 conjuntos. También tome nota de que habrá una advertencia encolor rojo si una pregunta válida necesita al menos un conjunto de valores {comodines}. A Usted no se le permitirá guardar la pregunta hasta que realice el paso siguiente
Haga click en el botón para generar
Note que los conjuntos se muestran en órden inverso de forma que el número indica cuantos conjuntos se crearon.
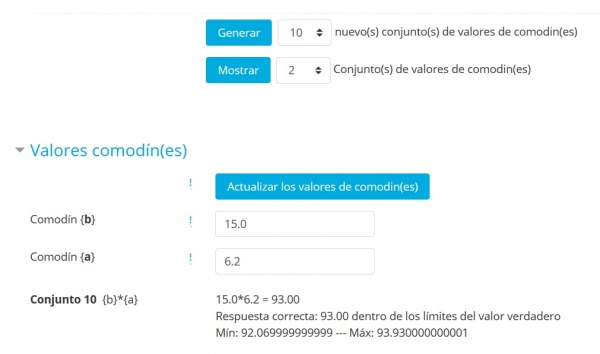
Los dos conjuntos ilustarn la variabilidad definida por los valores Min y Max.
Tome nota de que el resultado de la fórmula es analizado y
se muestra el límite de tolerancia (1% relativo aquí)
La respuesta correcta que se mostrará al alumno también se observa
Los 2 decimales, donde se definen, son los valores definidos por defecto como el último parámetro bajo la fórmula correcta.
Hacer click en el botón para Guardar
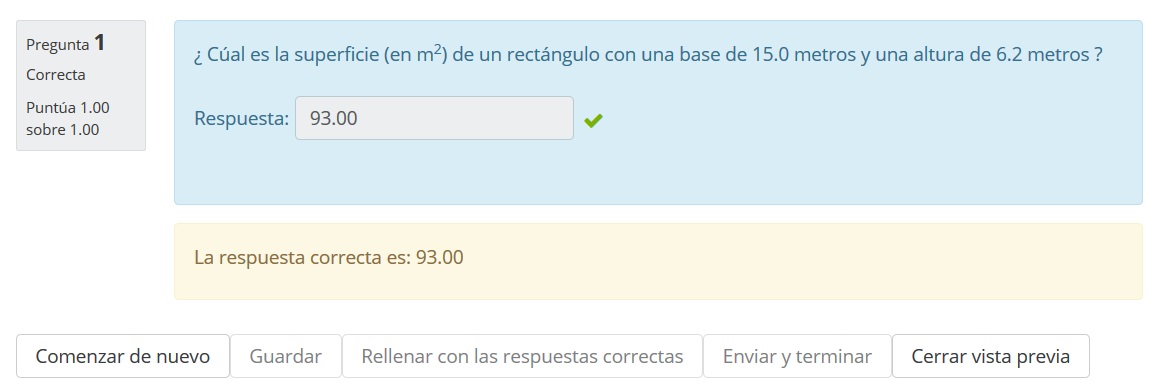
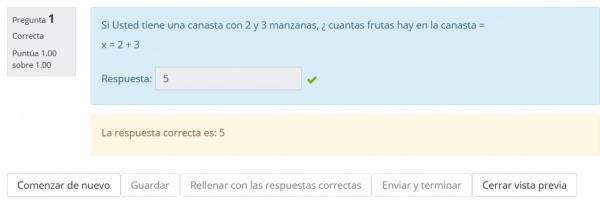
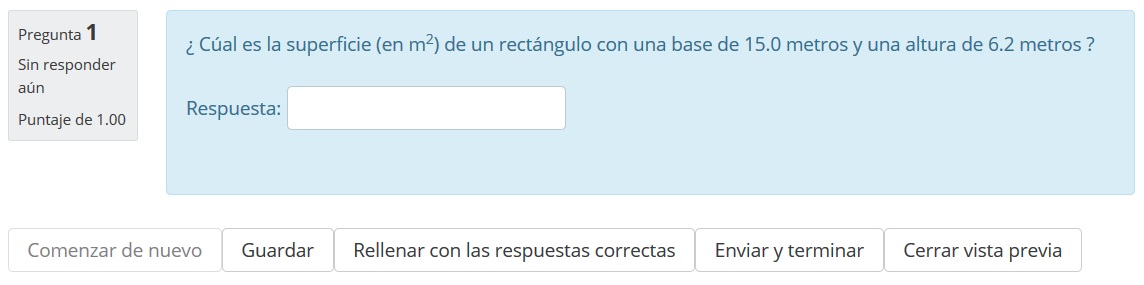
Prueba tu primera pregunta simple calculada
En el Banco de preguntas haga click en el ícono de vista previa.
Escriba el resultado que Usted mismo ha calculado o elija el botón para LLenar correctamente".
Los valores deberían de ser idénticos...
Elija el botón para enviar
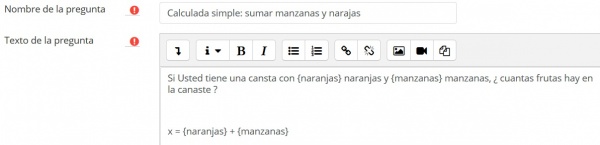
M i segunda pregunta Simple Calculada: sumar naranjas y manzanas
Texto de la pregunta
Fórmula de la pregunta
Valores calculados
La pregunta en acción
Editar una pregunta Simple Calculada: Comentarios adicionales
Nota: Pendiente de Traducir. ¡Anímese a traducir esta página!. ( y otras páginas pendientes)
- Set the default question grade (i.e. the maximum number of marks for this question).
- Set the Penalty factor (see Factor de penalización below).
Sintaxis de la fórmula para la respuesta correcta for further details.
- Choose the grade that the student will get for this question if they give this answer. This should be a percentage of the total marks available. For example, you could give 100% for a correct answer, and 50% for an answer that is nearly right. One of the answers must have a 100% grade.
- Determine the tolerance for error that you will accept in the answer. The tolerance and tolerance type settings combine to give a range of acceptable scores. So, if tolerance = t, correct answer = x and the difference between the user's answer and the correct answer is dx, then the tolerance types are as follows:
- Nominal - mark correct if dx <= t
- Relative - mark correct if dx / x <= t
- The next 2 settings, "Correct answer shows" and "Format" determine the precision of the Correct answer shown. They are not used for grading.
- Add some feedback which the student will see if they enter this answer.
- You can specify as many answer formulae as you like - click "Add another answer blank" to add more.
- You can also specify units for the answers. For example, if you enter a unit of 'cm' here, and the accepted answer is 15, then the answers '15cm' and '15' are both accepted as correct. If you add more than one unit, you can also specify a multiplier. So, if your main answer was 5500 with unit W, you can also add the unit kW with a multiplier of 0.001. This means that the answers '5500', '5500W' or '5.5kW' would all be marked correct. Note that the accepted error is also multiplied, so an allowed error of 100W would become an error of 0.1kW.
Factor de penalización
The 'penalty factor' only applies when the question is used in a quiz using adaptive mode - i.e. where the student is allowed multiple attempts at a question even within the same attempt at the quiz. If the penalty factor is more than 0, then the student will lose that proportion of the maximum grade upon each successive attempt. For example, if the default question grade is 10, and the penalty factor is 0.2, then each successive attempt after the first one will incur a penalty of 0.2 x 10 = 2 points.
Sintaxis para la fórmula de la respuesta correcta
NO PONGA EL SIGNO DE = en la fórmula
- In the recent versions of the calculated question type, you could have more than one answer formula and applied a specific grading value to each of them as long as there is at least one 100% correct answer formula. If more than one correct answer formula input field are displayed when editing, your site has the multiple answer feature.
- As a general rule, write these formulas like you would in a calculator e.g.
3 + 5 * sin(3/{x})A notable exception is exponentiation, where x3 cannot be entered as{x}^3, but instead should be entered aspow(x, 3). - Each function's placeholders and other arguments should be in parentheses (brackets). For example, if you want students to calculate the sine of one angle and cosine of two times of another angle, you would enter
sin({a}) + cos({b}*2). - It's usually better to have too many parentheses (brackets) than too few. The server won't care, and the more specific you are about what you mean, the more likely it will like your complex formulas.
- There is no implicit multiplication. To you, the human editor, "5(23)" or "5x" may seem perfectly obvious. To the server doing the math, it's crazy talk and won't be understood. Always use the "*" for multiplication.
- Any special mathematical function must have parentheses around its values. Take the sine function in the first bullet point for instance. Notice that the 3 / x is wrapped in parentheses (brackets)--this is so the server can understand it properly. Without those parentheses, the server won't know if you mean "(sin 3) / x" or "sin (3 / x)" and will reject the entire formula accordingly.
Funciones disponibles
Las preguntas calculadas pueden usar mucho más que operadores aritméticos simples. Las siguientes funciones están permitidas en versiones de Moodle 1.5 y superiores:
| Function | Explanation |
|---|---|
| abs | Absolute value |
| acos | Arc cosine -- in radians!!! Convert your degree measurement to radians before you take the acos of it. |
| acosh | Inverse hyperbolic cosine -- in radians!!! Convert your degree measurement to radians before you take the acosh of it. |
| asin | Arc sine -- in radians!!! Convert your degree measurement to radians before you take the asin of it. |
| asinh | Inverse hyperbolic sine -- in radians!!! Convert your degree measurement to radians before you take the asing of it. |
| atan2 | Arc tangent of two variables -- pass in two values like (x, y), and you'll get the atah(y/x), adjusted to the proper quadrant. |
| atan | Arc tangent -- in radians!!! Convert your degree measurement to radians before you take the atan of it. |
| atanh | Inverse hyperbolic tangent |
| bindec | Binary to decimal |
| ceil | Round fractions up |
| cos | Cosine -- in radians!!! Convert your degree measurement to radians before you take the cos of it. |
| cosh | Hyperbolic cosine -- in radians!!! Convert your degree measurement to radians before you take the cosh of it. |
| decbin | Decimal to binary |
| decoct | Decimal to octal |
| deg2rad | Converts the number in degrees to the radian equivalent |
| exp | Calculates the exponent of e |
| expm1 | Returns exp(number) - 1, computed in a way that is accurate even when the value of number is close to zero |
| floor | Round fractions down |
| fmod | Returns the floating-point modulus of two numbers - i.e. the remainder when the first is divided by the second. |
| is_finite | Finds whether a value is a legal finite number |
| is_infinite | Finds whether a value is infinite |
| is_nan | Finds whether a value is not a number |
| log10 | Base-10 logarithm |
| log1p | Returns log(1 + number), computed in a way that is accurate even when the value of number is close to zero |
| log | Natural logarithm (ln) |
| max | Find highest value |
| min | Find lowest value |
| octdec | Octal to decimal |
| pi | Get value of pi |
| pow (numberToRaise, NumberRaisedTo) | Exponential expression |
| rad2deg | Converts the radian number to the equivalent number in degrees |
| rand | Generate a random integer |
| round | Rounds a float |
| sin | Sine -- in radians!!! Convert your degree measurement to radians before you take the sin of it. |
| sinh | Hyperbolic sine -- in radians!!! Convert your degree measurement to radians before you take the sinh of it. |
| sqrt | Square root |
| tan | Tangent -- in radians!!! Convert your degree measurement to radians before you take the tan of it. |
| tanh | Hyperbolic tangent -- in radians!!! Convert your degree measurement to radians before you take the tanh of it. |
Constantes predefinidas
En realidad NO hay constantes predefinidas que estén permitidas, con la excepción de pi() como una función sin parámetros.