Creating a web service client: Difference between revisions
(→REST) |
No edit summary |
||
| (53 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Moodle_2.0}} | {{Moodle_2.0}} | ||
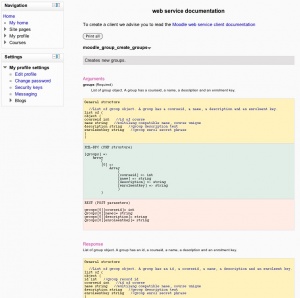
[[Image:Moodle web service function documentation.jpg|thumb]]You need to | [[Image:Moodle web service function documentation.jpg|thumb]]You need to know how to [https://docs.moodle.org/en/How_to_create_and_enable_a_web_service setup a web service] first. | ||
To see the API Documentation, connect as Admin and go to '''Administration > Plugins > Web services > API Documentation''' | |||
== Simple REST request example == | |||
To quickly test the web service works you can visit the end point from the browser or via curl. For example to call a function via REST protocol: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | |||
$ curl "https://your.site.com/webservice/rest/server.php?wstoken=...&wsfunction=...&moodlewsrestformat=json" | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Customise the parameters <tt>wstoken</tt> and <tt>wsfunction</tt> to match the server side setup. Append additional parameters for the function call as needed with "¶meter_name=param", or if your parameter is an array then use "&array_name[index][parameter_name]=param". With the core_user_create_users function's (required) parameters for example: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | |||
$ curl "...&moodlewsrestformat=json&wsfunction=core_user_create_users&moodlewsrestformat=json&users[0][username]=testuser&users[0][firstname]=Anne&users[0][lastname]=Example..." | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
The <tt>moodlewsrestformat</tt> parameter affects the response format and can be either <tt>xml</tt> (default) or <tt>json</tt>. | |||
== Officially supported protocols == | |||
; REST : The Moodle REST server accepts GET/POST parameters and return XML/JSON values. This server is not RESTfull. | |||
; SOAP : The Moodle SOAP server is based on the Zend SOAP server (itself based on the PHP SOAP server). Zend publishes [http://framework.zend.com/manual/en/zend.soap.client.html a Zend SOAP client]. The current server implementation doesn't fully work with Java/.Net because we didn't generated a fully describe WSDL yet. If you are working on a Java/.Net client, follow or participate to the tracker issues MDL-28988 / MDL-28989 | |||
; XML-RPC : The Moodle XML-RPC server is based on Zend XML-RPC server. Zend also publishes [http://framework.zend.com/manual/en/zend.xmlrpc.client.html a Zend XML-RPC client]. | |||
; AMF (Versions < Moodle 3.0) : the Moodle AMF server is based on the Zend AMF server. The test client can be found in ''Settings blocks > Site Administration > Development > Web service test client > AMF Test client''. | |||
== Demo client examples == | |||
Demo client sample codes can be downloaded on [https://github.com/moodlehq/sample-ws-clients Github]. | |||
= | For HTML5 app creators, you can also find: | ||
* a nice [https://github.com/jleyva/umm phonegap / Jquery mobile template] | |||
* a proof of concept of [http://moodle.org/mod/forum/discuss.php?d=189882 javascript cross-domain with Sencha Touch 1.1] | |||
Node.js apps can use the [https://github.com/mudrd8mz/node-moodle-client moodle-client] module. | |||
A [http://moodle.org/mod/forum/discuss.php?d=199453 Java Library for REST] can be found on [http://sourceforge.net/projects/moodlerestjava/ Sourceforge]. | |||
A [https://github.com/llagerlof/MoodleRest PHP Library for REST] can be found on GitHub. | |||
A [https://github.com/zaddok/moodle Go Library for REST] can be found on GitHub. | |||
A [https://github.com/smartcommunitylab/moodle_import Python Library for REST] can be found on GitHub. | |||
== How to get a user token == | |||
// | {{Moodle_2.2}} | ||
Your client can call the script located in /login/token.php with a simple HTTP request. We highly recommend to do it securely with HTTPS. | |||
The required parameters are: | |||
* username | |||
* password | |||
* service shortname - The service shortname is usually hardcoded in the pre-build service (db/service.php files). Moodle administrator will be able to edit shortnames for service created on the fly: MDL-29807. If you want to use the Mobile service, its shortname is <tt>moodle_mobile_app</tt>. Also useful to know, the database shortname field can be found in the table named external_services. | |||
Request: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | |||
https://www.yourmoodle.com/login/token.php?username=USERNAME&password=PASSWORD&service=SERVICESHORTNAME | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Response: (HTTP) | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | |||
/ | {token:4ed876sd87g6d8f7g89fsg6987dfh78d} | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Response: (HTTPS) - Since at least M3.9 | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | |||
{ | |||
"token": "9859148a89546f0efe716a58e340849b", | |||
"privatetoken": "8RpHJevJ42W7QN23OMkeYcdOYw3YfWgWGKsak7WB3Z88wcApSCVZ9TgY6M5fEO1m" | |||
/ | |||
/ | |||
} | } | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
=== Difference between Moodle versions === | |||
== | * Moodle 2.2 and later: the script can generate user tokens for any service shortname (of course users must be allowed on the service, see [[:en:How to create and enable a web service|How to create and enable a web service]]). | ||
* Moodle 2.1: the script can only generate tokens for the official built-in mobile service. However the script can returns tokens for other services, they just need to have been previously generated. | |||
=== About service shortname === | |||
At the moment a service can have a shortname if you: | |||
== | * create the service as a built-in service (in db/services.php files) | ||
* add the shortname manually in the DB. Note: we'll add the admin UI for shortname later (MDL-30229) | |||
== Text formats == | |||
=== Moodle 2.0 to 2.2 === | |||
{{Moodle_2.0}} | |||
HTML is the format sent/received by web service functions. All returned file urls are converted to 'http://xxxx/webservice/pluginfile.php/yyyyyyyy' | |||
=== Moodle 2.3 and later === | |||
{{Moodle_2.3}} | |||
Since Moodle 2.3 you can add few GET/POST parameters to your request (for devs who have a good knowledge of File API and format_text()): | |||
* ''moodlewssettingraw'' => false by default. If true, the function will not apply format_text() to description/summary/textarea. The function will return the raw content from the DB. | |||
* ''moodlewssettingfileurl'' => true by default, returned file urls are converted to 'http://xxxx/webservice/pluginfile.php/yyyyyyyy'. If false the raw file url content from the DB is returned (e.g. @@PLUGINFILE@@) | |||
* ''moodlewssettingfilter'' => false by default. If true, the function will filter during format_text() | |||
=== Moodle 3.5 and later === | |||
{{Moodle_3.5}} | |||
* ''moodlewssettinglang'' => to force a session language for when retrieving information (same behaviour than using the language selector in the site) | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[Web services|Web services developer documentation]] | |||
* [[:en:Web_services|Web services user documentation]] | |||
* [[Creating a web service and a web service function | Implement a web service and a web service function]] | |||
* [[Web_services_Roadmap|Web service Roadmap]] | |||
* [https://moodle.org/plugins/webservice_restful A RESTful webservice plugin] by Catalyst Moodle partner. | |||
[[Category:Web Services]] | [[Category:Web Services]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:15, 7 February 2022
Moodle 2.0
You need to know how to setup a web service first.
To see the API Documentation, connect as Admin and go to Administration > Plugins > Web services > API Documentation
Simple REST request example
To quickly test the web service works you can visit the end point from the browser or via curl. For example to call a function via REST protocol:
$ curl "https://your.site.com/webservice/rest/server.php?wstoken=...&wsfunction=...&moodlewsrestformat=json"
Customise the parameters wstoken and wsfunction to match the server side setup. Append additional parameters for the function call as needed with "¶meter_name=param", or if your parameter is an array then use "&array_name[index][parameter_name]=param". With the core_user_create_users function's (required) parameters for example:
$ curl "...&moodlewsrestformat=json&wsfunction=core_user_create_users&moodlewsrestformat=json&users[0][username]=testuser&users[0][firstname]=Anne&users[0][lastname]=Example..."
The moodlewsrestformat parameter affects the response format and can be either xml (default) or json.
Officially supported protocols
- REST
- The Moodle REST server accepts GET/POST parameters and return XML/JSON values. This server is not RESTfull.
- SOAP
- The Moodle SOAP server is based on the Zend SOAP server (itself based on the PHP SOAP server). Zend publishes a Zend SOAP client. The current server implementation doesn't fully work with Java/.Net because we didn't generated a fully describe WSDL yet. If you are working on a Java/.Net client, follow or participate to the tracker issues MDL-28988 / MDL-28989
- XML-RPC
- The Moodle XML-RPC server is based on Zend XML-RPC server. Zend also publishes a Zend XML-RPC client.
- AMF (Versions < Moodle 3.0)
- the Moodle AMF server is based on the Zend AMF server. The test client can be found in Settings blocks > Site Administration > Development > Web service test client > AMF Test client.
Demo client examples
Demo client sample codes can be downloaded on Github.
For HTML5 app creators, you can also find:
- a nice phonegap / Jquery mobile template
- a proof of concept of javascript cross-domain with Sencha Touch 1.1
Node.js apps can use the moodle-client module.
A Java Library for REST can be found on Sourceforge.
A PHP Library for REST can be found on GitHub.
A Go Library for REST can be found on GitHub.
A Python Library for REST can be found on GitHub.
How to get a user token
Moodle 2.2
Your client can call the script located in /login/token.php with a simple HTTP request. We highly recommend to do it securely with HTTPS. The required parameters are:
- username
- password
- service shortname - The service shortname is usually hardcoded in the pre-build service (db/service.php files). Moodle administrator will be able to edit shortnames for service created on the fly: MDL-29807. If you want to use the Mobile service, its shortname is moodle_mobile_app. Also useful to know, the database shortname field can be found in the table named external_services.
Request:
https://www.yourmoodle.com/login/token.php?username=USERNAME&password=PASSWORD&service=SERVICESHORTNAME
Response: (HTTP)
{token:4ed876sd87g6d8f7g89fsg6987dfh78d}
Response: (HTTPS) - Since at least M3.9
{
"token": "9859148a89546f0efe716a58e340849b",
"privatetoken": "8RpHJevJ42W7QN23OMkeYcdOYw3YfWgWGKsak7WB3Z88wcApSCVZ9TgY6M5fEO1m"
}
Difference between Moodle versions
- Moodle 2.2 and later: the script can generate user tokens for any service shortname (of course users must be allowed on the service, see How to create and enable a web service).
- Moodle 2.1: the script can only generate tokens for the official built-in mobile service. However the script can returns tokens for other services, they just need to have been previously generated.
About service shortname
At the moment a service can have a shortname if you:
- create the service as a built-in service (in db/services.php files)
- add the shortname manually in the DB. Note: we'll add the admin UI for shortname later (MDL-30229)
Text formats
Moodle 2.0 to 2.2
Moodle 2.0
HTML is the format sent/received by web service functions. All returned file urls are converted to 'http://xxxx/webservice/pluginfile.php/yyyyyyyy'
Moodle 2.3 and later
Moodle 2.3
Since Moodle 2.3 you can add few GET/POST parameters to your request (for devs who have a good knowledge of File API and format_text()):
- moodlewssettingraw => false by default. If true, the function will not apply format_text() to description/summary/textarea. The function will return the raw content from the DB.
- moodlewssettingfileurl => true by default, returned file urls are converted to 'http://xxxx/webservice/pluginfile.php/yyyyyyyy'. If false the raw file url content from the DB is returned (e.g. @@PLUGINFILE@@)
- moodlewssettingfilter => false by default. If true, the function will filter during format_text()
Moodle 3.5 and later
Moodle 3.5
- moodlewssettinglang => to force a session language for when retrieving information (same behaviour than using the language selector in the site)