Creating a web service client: Difference between revisions
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{token:4ed876sd87g6d8f7g89fsg6987dfh78d} | {token:4ed876sd87g6d8f7g89fsg6987dfh78d} | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
== Difference between Moodle versions == | |||
* Moodle 2.2 and later: the script can generate user tokens for any service shortname (of course users must be allowed on the service, see [[:en:How to create and enable a web service|How to create and enable a web service]]). | |||
* Moodle 2.1: the script can only generate tokens for the official built-in mobile service. However the script can returns tokens for other services, they just need to have been previously generated. | |||
== About service shortname == | |||
At the moment a service can have a shortname if you: | |||
* create the service as a built-in service (in db/services.php files) | |||
* add the shortname manually in the DB. Note: we'll add the admin UI for shortname later (MDL-30229) | |||
= See also = | = See also = | ||
Revision as of 05:55, 23 November 2011
Moodle 2.0
You need to know how to setup a web service first.
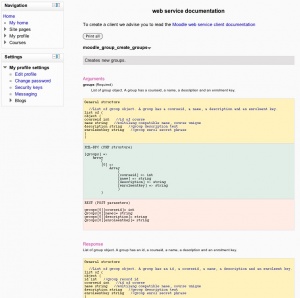
To see the API Documentation, connect as Admin and go to Administration > Plugins > Web services > API Documentation
Officially supported protocols
- REST: the Moodle REST server accepts GET/POST parameters and return XML/JSON values. This server is not RESTfull.
- SOAP: the Moodle SOAP server is based on the Zend SOAP server (itself based on the PHP SOAP server). Zend publishes a Zend SOAP client. The current server implementation doesn't fully work with Java/.Net because we didn't generated a fully describe WSDL yet. If you are working on a Java/.Net client, follow or participate to the tracker issues MDL-28988 / MDL-28989
- XML-RPC: the Moodle XML-RPC server is based on Zend XML-RPC server. Zend also publishes a Zend XML-RPC client.
- AMF: the Moodle AMF server is based on the Zend AMF server. The test client can be found in Settings blocks > Site Administration > Development > Web service test client > AMF Test client.
Demo client examples
Demo client sample codes can be downloaded on Github.
How to get a user token
Moodle 2.2
Your client can call the script located in /login/token.php with a simple HTTP request. We highly recommend to do it securely with HTTPS. The required parameters are:
- username
- password
- service shortname - The service shortname is usually hardcoded in the pre-build service (db/service.php files). Moodle administrator will be able to edit shortnames for service created on the fly: MDL-29807. If you want to use the Mobile service, its shortname is moodle_mobile_app. Also useful to know, the database shortname field can be found in the table named external_services.
Call:
https://www.yourmoodle.com/login/token.php?username=USERNAME&password=PASSWORD&service=SERVICESHORTNAME //Moodle mobile service shortname => moodle_mobile_app
Get in return:
{token:4ed876sd87g6d8f7g89fsg6987dfh78d}
Difference between Moodle versions
- Moodle 2.2 and later: the script can generate user tokens for any service shortname (of course users must be allowed on the service, see How to create and enable a web service).
- Moodle 2.1: the script can only generate tokens for the official built-in mobile service. However the script can returns tokens for other services, they just need to have been previously generated.
About service shortname
At the moment a service can have a shortname if you:
- create the service as a built-in service (in db/services.php files)
- add the shortname manually in the DB. Note: we'll add the admin UI for shortname later (MDL-30229)