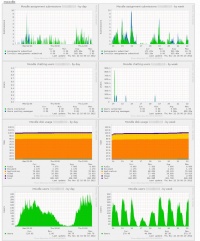
Munin plugin for Moodle
Courtesy of Lancaster University CIS, Munin plugin for generating various Moodle stats is available for download on GitHub. This is a multigraph wildcard Munin plugin, that allows you to gather some useful statistics from Moodle database and represent it in the nice graphs. Among the graphs it generates are:
- Currently logged-in users
- Assignments submission activity (with optional Turnitin assignments display if you use it)
- Disk usage
- Unique Moodle users over the period
- Chat sessions activity
The plugin can be used with Moodle 2.3 and above. It works with PostgreSQL database only at the moment.
Pre-requires
You need to have Munin installed and configured on your system. This is beyond the scope of this discussion, please use Munin documentation for more information.
Configuration
To make this work, you have to install plugin, create plugin configuration file and then create a symlink to plugin that reflects the name of the Moodle database.
Installing plugin
You can clone using git or download the plugin from GitHub, unpack (if you downloaded it) and copy to either Munin standard plugins directory (i.e. /usr/share/munin/plugins/) or custom directory if you want to keep custom plugins separate.
mv /tmp/moodle_ /usr/share/munin/plugins/moodle_
Configuring plugin
You need to create configuration file in plugin-conf.d directory, it's usually located in /etc/munin/. There is no specific requirements for configuration file name, but it is better to call it moodle for convenience. The configuration may contain standard Munin plugin configuration attributes, libpq environment variables for configuring database connection settings (e.g. PGUSER, PGHOST, etc.) and plugin-specific settings. Generally, it is easier if you run the the plugin directly on the database server as postgres user. In this case the minimum configuration will look like:
[moodle_*] user postgres
If your plugin located on the different server, it will need an additional settings to accessing Moodle database. Given that plugin is using Munin::Plugin::Pgsql library, it supports all libpq variables, the most common of them are:
- PGHOST - hostname to connect to
- PGPORT - port number to connect to
- PGUSER - username to connect as
- PGPASSWORD - password to connect with, if a password is required
For using these variables in the plugin configuration, you need to pass them as environment setting, i.e. prepend them with env.
[moodle_*] user root env.PGHOST your_db_hostname env.PGUSER your_db_username env.PGPASSWORD your_db_password
Plugin also has some own configuration variables that need to be set as environment setting as well if you wish using them:
- env.updatetime - you may configure the period for which the time-based data is calculated (e.g. used in the number of logged-in users reporting or assignments submissions). By default the value of 300 sec is used (which is 5 min Munin default update interval).
- env.mdlprefix - if you use different from 'mdl_' (mdl_tablename) prefix in Moodle database tables, pass the correct one using this parameter.
- env.modturnitintool - if you have Turnitintool module installed, you may add it to assignment monitoring by setting this variable to 1. Disabled by default.
For more information on Munin plugins configuration see corresponding Munin wiki page.
Creating a symlink
The final bit that needs to be done is to create a symlink to the plugin in /etc/munin/plugins directory. Being a wildcard plugin, Moodle plugin will attempt to determine the database name it will be using from the symlink, thus the symlink need to contain the name of the moodle database:
ln -s /usr/share/munin/plugins/moodle_ /etc/munin/plugins/moodle_yourmoodledatabasename
ls -la command run in /usr/share/munin/plugins directory will display that the symlink is correct:
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 52 Nov 21 16:29 moodle_moodle-db -> /usr/share/munin/plugins/moodle_
The database name in the example above is moodle-db
The wildcard plugin concept is especially useful for large scale systems when you have more than one Moodle database on the same database server. I this case you may create symlink for each Moodle database on the same system and have them all monitored.
Testing configuration and plugin
You will need to restart munin node on the client to make sure it picked up new plugins. Now, you may see what the plugin outputs when it is being queried by Munin service:
~# munin-run moodle_moodle-db
will output the current data values for each graph
multigraph mdlusers users.value 272 multigraph uniquemdluserssince day.value 3011 week.value 4036 month.value 5146 ...
to see the graphs configuration that plugin returns run
~# munin-run moodle_moodle-db config
You may read more about plugin debugging in Munin wiki document.
Some useful hints
You may set up warning and critical thresholds for particular services on the Munin server side. When one of the values will be above defined limits, the service will be highlighted in the Munin web interface. You may elaborate this further and set up various alerts. For more info see page.
Note for developers
This Munin Moodle plugin is using Munin::Plugin::Pgsql library, which makes it work with PostgreSQL database only at the moment. It is also a multigraph plugin which allows to keep all the graphs generation code within the same file. The wildcard plugin functionality is implemented the way that it takes database name from the symlink.
You are more than welcome to contribute to this work and create pull request for integration of your changes.
Useful Links
- moodle-munin-plugin on GitHub
- Munin system documentation
- Monitorización de Moodle con Munin - Alternative Munin plugin for Moodle found in the search, this might be regarded as complicated, as stats data is collected by Moodle plugin and recorded to the text files on cron, these text files are then being read by the Munin plugin itself. Docs is only in Spanish.