Workshop module
Moodle 2.0
![]() Workshop is a peer assessment activity with many options. Students submit their work via an on line text tool and attachments. There are two grades for a student: their own work and their peer assessments of other students' work. These instructions are for the completely redesigned version for Moodle 2.0.
Workshop is a peer assessment activity with many options. Students submit their work via an on line text tool and attachments. There are two grades for a student: their own work and their peer assessments of other students' work. These instructions are for the completely redesigned version for Moodle 2.0.
For more information on using Workshop in Moodle 1.x, please refer to the "See also" section.
Workshop in Moodle 2.0 video:
<mediaplayer>http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8QypkOcAEaE</mediaplayer>
Key features
Workshop is similar to the Assignment module and extends its functionality in many ways. However, it is recommended that both course facilitator (teacher) and course participants (students) have at least some experience with the Assignment module before the Workshop is used in the course.
- As in the Assignment, course participants submit their work during the Workshop activity. Every course participant submits their own work. The submission may consist of a text and attachments. Therefore, Workshop submission merges both Online text and Upload file types of the Assignment module. Support for team work (in the sense of one submission per group of participants) is out of scope of Workshop module.
- The submissions are assessed using a structured assessment form defined by the course facilitator (teacher). Workshop supports several types of assessment forms. All of them allows multi-criteria assessment - on the contrary to the Assignment module where only one grade is given to a submission.
- Workshop supports peer assessment process. Course participants may be asked to assess selected set of their peers' submissions. The module coordinates the collection and distribution of these assessments.
- Course participants get actually two grades in a single Workshop activity - grade for their submission (that is how good their submitted work is) and grade for assessment (that is how well they assessed their peers). Workshop activity creates two grade items in the course Gradebook and they can be aggregated there as needed (in Moodle 1.x, Workshop automatically summed up these grades and sent the total into Gradebook as a single item).
- The process of peer assessment and understanding the assessment form can be trained in advance on so called example submissions. These examples are provided by the facilitator together with a reference assessment. Workshop participants can assess these examples and compare their assessment with the reference one.
- The course facilitator can select some submissions and publish them so they are available to the others at the end of Workshop activity (on contrary to the Assignment module where submitted work is available only to the author and the facilitator).
Workshop phases
Typical Workshop is not a short-term activity and it takes up to several days or even weeks to complete. The Workshop work flow can be divided into five phases. The teacher controls which phase the workshop activity is in at any time.
- Setup phase - Teacher create and determine workshop, students can not do anything
- Submission phase - Students turn in work within a time frame
- Assessment phase - Peer assessment by students
- Grading/evaluation phase - Teacher grades submissions and peer assessments
- Closed phase - Final grade is calculated. Students may see grades and their work
In Moodle 2.0, teachers switch from one phase to the next manually by clicking on the light-bulb icon in the Workshop planner tool. There is no support for automatic or scheduled phase switching yet.
Grading strategies
Grading strategy determines how the assessment form may look like and how the final grade for submission is calculated from all the filled assessment forms for the given submission. Workshop ships with four standard grading strategies. More strategies can be developed as pluggable extensions.
- Accumulative grading strategy - a set of criteria is graded separately.
- Comments - similar to above but always given a 100% grade. Useful for initial feedback to authors
- Number of errors - an assessment method that counts errors in specific criteria (for example, spelling, formatting, creative ideas, lack of examples).
- Rubric - a set of descriptions that are associated with a specific criteria (outome). Each criteria has unique word scale.
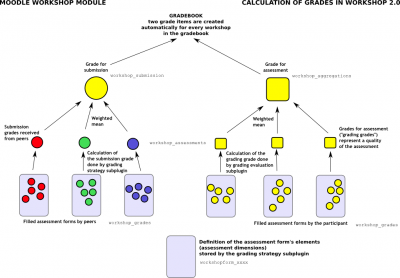
Calculation of final grades
The final grades for a Workshop activity are obtained gradually at several stages. The following scheme illustrates the process and also provides the information in what database tables the grade values are stored.
As you can see, every participant gets two numerical grades into the course Gradebook. During the Grading evaluation phase, course facilitator can let Workshop module to calculate these final grades. Note that they are stored in Workshop module only until the activity is switched to the final (Closed) phase. Therefore it is pretty safe to play with grades unless you are happy with them and then close the Workshop and push the grades into the Gradebook. You can even switch the phase back, recalculate or override the grades and close the Workshop again so the grades are updated in the Gradebook again (should be noted that you can override the grades in the Gradebook, too).
During the grading evaluation, Workshop grades report provides you with a comprehensive overview of all individual grades. The report uses various symbols and syntax:
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| - (-) < Alice | The is an assessment allocated to be done by Alice, but it has been neither assessed nor evaluated yet |
| 68 (-) < Alice | Alice assessed the submission, giving the grade for submission 68. The grade for assessment (grading grade) has not been evaluated yet. |
| 23 (-) > Bob | Bob's submission was assessed by a peer, receiving the grade for submission 23. The grade for this assessment has not been evaluated yet. |
| 76 (12) < Cindy | Cindy assessed the submission, giving the grade 76. The grade for this assessment has been evaluated 12. |
| 67 (8) @ 4 < David | David assessed the submission, giving the grade for submission 67, receiving the grade for this assessment 8. His assessment has weight 4 |
| 80 ( |
Eve's submission was assessed by a peer. Eve's submission received 80 and the grade for this assessment was calculated to 20. Teacher has overridden the grading grade to 17, probably with an explanation for the reviewer. |
Grade for submission
The final grade for every submission is calculated as weighted mean of particular assessment grades given by all reviewers of this submission. The value is rounded to a number of decimal places set in the Workshop settings form.
Course facilitator can influence the grade for a given submission in two ways:
- by providing their own assessment, possibly with a higher weight than usual peer reviewers have
- by overriding the grade to a fixed value
Grade for assessment
Grade for assessment tries to estimate the quality of assessments that the participant gave to the peers. This grade (also known as grading grade) is calculated by the artificial intelligence hidden within the Workshop module as it tries to do typical teacher's job.
During the grading evaluation phase, you use a Workshop subplugin to calculate grades for assessment. At the moment, only one subplugin is available called Comparison with the best assessment. The following text describes the method used by this subplugin. Note that more grading evaluation subplugins can be developed as Workshop extensions.
Grades for assessment are displayed in the braces () in the Workshop grades report. The final grade for assessment is calculated as the average of particular grading grades.
There is not a single formula to describe the calculation. However the process is deterministic. Workshop picks one of the assessments as the best one - that is closest to the mean of all assessments - and gives it 100% grade. Then it measures a 'distance' of all other assessments from this best one and gives them the lower grade, the more different they are from the best (given that the best one represents a consensus of the majority of assessors). The parameter of the calculation is how strict we should be, that is how quickly the grades fall down if they differ from the best one.
If there are just two assessments per submission, Workshop can not decide which of them is 'correct'. Imagine you have two reviewers - Alice and Bob. They both assess Cindy's submission. Alice says it is a rubbish and Bob says it is excellent. There is no way how to decide who is right. So Workshop simply says - ok, you both are right and I will give you both 100% grade for this assessment. To prevent it, you have two options:
- Either you have to provide an additional assessment so the number of assessors (reviewers) is odd and workshop will be able to pick the best one. Typically, the teacher comes and provide their own assessment of the submission to judge it
- Or you may decide that you trust one of the reviewers more. For example you know that Alice is much better in assessing than Bob is. In that case, you can increase the weight of Alice's assessment, let us say to "2" (instead of default "1"). For the purposes of calculation, Alice's assessment will be considered as if there were two reviewers having the exactly same opinion and therefore it is likely to be picked as the best one.
Backward compatibility note: In Workshop 1.x this case of exactly two assessors with the same weight is not handled properly and leads to wrong results as only the one of them is lucky to get 100% and the second get lower grade.
It is very important to know that the grading evaluation subplugin Comparison with the best assessment does not compare the final grades. Regardless the grading strategy used, every filled assessment form can be seen as n-dimensional vector or normalized values. So the subplugin compares responses to all assessment form dimensions (criteria, assertions, ...). Then it calculates the distance of two assessments, using the variance statistics.
To demonstrate it on example, let us say you use grading strategy Number of errors to peer-assess research essays. This strategy uses a simple list of assertions and the reviewer (assessor) just checks if the given assertion is passed or failed. Let us say you define the assessment form using three criteria:
- Does the author state the goal of the research clearly? (yes/no)
- Is the research methodology described? (yes/no)
- Are references properly cited? (yes/no)
Let us say the author gets 100% grade if all criteria are passed (that is answered "yes" by the assessor), 75% if only two criteria are passed, 25% if only one criterion is passed and 0% if the reviewer gives 'no' for all three statements.
Now imagine the work by Daniel is assessed by three colleagues - Alice, Bob and Cindy. They all give individual responses to the criteria in order:
- Alice: yes / yes / no
- Bob: yes / yes / no
- Cindy: no / yes / yes
As you can see, they all gave 75% grade to the submission. But Alice and Bob agree in individual responses, too, while the responses in Cindy's assessment are different. The evaluation method Comparison with the best assessment tries to imagine, how a hypothetical absolutely fair assessment would look like. In the Development:Workshop 2.0 specification, David refers to it as "how would Zeus assess this submission?" and we estimate it would be something like this (we have no other way):
- Zeus 66% yes / 100% yes / 33% yes
Then we try to find those assessments that are closest to this theoretically objective assessment. We realize that Alice and Bob are the best ones and give 100% grade for assessment to them. Then we calculate how much far Cindy's assessment is from the best one. As you can see, Cindy's response matches the best one in only one criterion of the three so Cindy's grade for assessment will not be much high.
The same logic applies to all other grading strategies, adequately. The conclusion is that the grade given by the best assessor does not need to be the one closest to the average as the assessment are compared at the level of individual responses, not the final grades.
More explanations
- Thread at moodle.org where David explains a particular Workshop results
- Presentation by Mark Drechsler
Research papers dealing with Workshop module
- Peer assessments using the moodle workshop tool by John F. Dooley
- Easy-to-use Workshop Module by Álvaro Figueira and Elisabete Cunha
For developers
Please see Development:Workshop for more information on the module infrastructure and ways how to extend provided functionality by developing own Workshop subplugins.
Earlier versions
Workshop was the very first contributed code module and was unmaintained for a long time except for emergency fixes by various developers to keep it operational. By default, it is hidden in Moodle 1.9 in the Site administration > Modules > Manage activities. Users are discouraged from using it in Moodle 1.x versions due to a number of known problem in these versions.
See also
- A Brief Journey into the Moodle 2.0 Workshop at moodlefairy's posterous
- Workshop module/Tutorial
- Using Moodle Chapter 6: Workshops
- Moodle Workshop Guide by Laura M. Christensen © 2007
- Using Moodle New Workshop Module forum discussion
- Promoting Peer Assessment: Moodle Workshop by Nitin Parmar, 2006
- Exercise module allows student self assessment and teacher to separately grade the quality of the assignment and the self assessment.