Email processing
| Warning: This page is no longer in use. The information contained on the page should NOT be seen as relevant or reliable. |
Features
Moodle is capable of using an e-mail technique known as VERP (Variable Envelope Return Path) in order to disable e-mail for bouncing e-mail addresses. This is particularly useful on busy sites where you may generate huge volumes of e-mail, where you do not control user e-mail addresses, or where users are created with false e-mail addresses (for example in Primary education).
The Moodle VERP system:
- works on most modern Mail Transfer Agents such as Postfix, Qmail, and exim (at least MTAs on Unix systems);
- generates a processing e-mail address with HMAC (Hashed Message Authentication Code) and validation hash;
- handles receiving of e-mails sent to the Moodle noreply address ($CFG->noreplyaddress);
- handles receiving of bounce e-mails validating using the MD5 hash and validating against the site HMAC.
Moodle configuration
Edit config.php to enable bounce handling, and setup Moodle to match your MTA configuration. A full description of these configuraiton settings can be found in config-dist.php. You will need to uncomment the following lines:
// once handlebounces is true, we will be using VERP for the return address of every sent email $CFG->handlebounces = true; // minimum bounces allowed per user $CFG->minbounces = 10; // ratio of bad emails to sent emails // if we get more than 20% bounces // for a given user, his/her email is marked bad $CFG->bounceratio = .20; // Prefix to identify your site MUST BE EXACTLY 3 characters $CFG->mailprefix = 'mdl'; // Domain which acccepts email for processing $CFG->maildomain = 'bounces.my.domain';
Edit the $CFG->maildomain line and one of the $CFG->mailprefix lines (the one that matches your MTA).
Make sure your server has a command-line PHP interpreter, and that it is able to connect to mysql (or postgres if relevant). If you are able to run cron.php from the commandline or from crontab, this means PHP is ok.
Edit the process_email.php script to point to the location of your php binary. It will usually be /usr/bin/php.
Email confirmation or registration words, and how to edit them.
- Students receive a confirmation email when they create a user account. This text can be found in the lang/?/moodle.php as the emailconfirmation "variable".
- Students receive a welcome email when they enroll in a course. This text can be found in the lang/?/moodle.php file as the welcometocoursetext "variable".
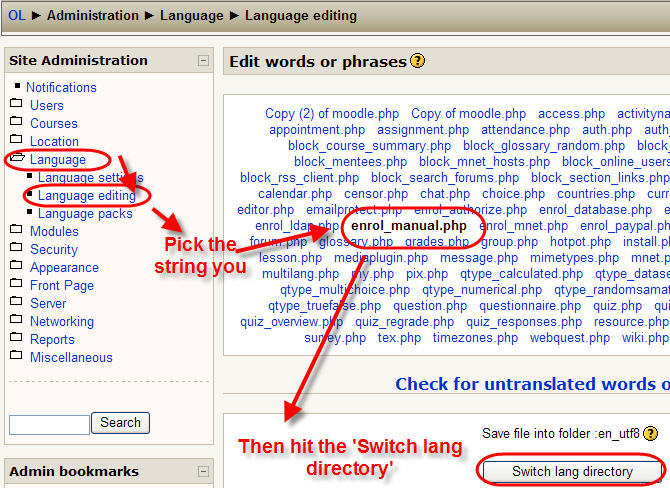
- If you feel the need to edit this text, the best way to do this is to go to Site Administration -> Language editing, and then clicking on the string that you wish to edit. Once you have done this, hit the "Switch lang directory" button, and do your editing.
- If you decide to get your hands dirty and work by editing the moodle.php directly, be careful to open the file only in a simple text editor like notepad or wordpad.
- Tip: Be careful with markup - as you edit, you must use " " for things like putting in hyperlinks, titles and targets. You MUST 'escape' them by putting a \ before each ". If you don't the resulting page will appear blank. For example, the normal way to markup a hyperlink is:-
- <a href="http://www.blah_blah">click here</a> If you do this in the moodle.php file, your edited text won't appear.
- Use <a href=\"http://www.blah_blah\">click here</a>
- Use the \ before each " when marking up things like target=\"_blank\" and title=\"Blah blah\" and other similar codes.
- If you feel you must really go the route of editing the moodle.php file directly, save a copy of the file in its own folder (copy and paste the file in the same folder). That way, if it all goes wrong for you, all you have to do is delete the botched file and rename the 'copy of moodle.php' back to 'moodle.php' and you are back to square one, no harm done!
- Having said all that, it is best to do all your editing in the web interface by going to Site Administration -> Language editing, and then clicking on the string that you wish to edit.
Setup under Postfix
Add a line to your aliases file. The line should list a 3-letter prefix, to which we'll add a '|', and the path of the script. For example for a prefix of 'mdl' and moodle installed under /var/www/moodle we have in aliases:
mdl: |/var/www/moodle/admin/process_email.php noreply: |/var/www/moodle/admin/process_email.php
If you are using virtualdomains, consult your server administrator for the correct configuration. It probably involves editing transports and mapping your address to a "pipe" transport. One such transport can be configured using the following line in "master.cf":
moodle unix - n n - - pipe
flags=FR user=www-data argv=/usr/bin/env SENDER=${sender} RECIPIENT=${recipient} /srv/www/moodle/admin/process_email.php
Because process_email.php uses environment variables to get recipient and sender adresses, you also need to make sure the $_ENV variable is available within PHP, otherwise Moodle will not process any messages. See : http://www.php.net/manual/en/reserved.variables.environment.php#98113
Setup under Qmail
Depending on your setup, your aliases will be controlled by one or more of
- /etc/aliases
- /var/qmail/alias/.qmail-PREFIX
If you edit /etc/aliases add a line like this (for a prefix of 'mdl'):
mdl: |/var/www/moodle/admin/process_email.php noreply: |/var/www/moodle/admin/process_email.php
If you create /var/qmail/alias/.qmail-PREFIX, just do
echo "|/var/www/moodle/admin/process_email.php" > /var/qmail/alias/.qmail-mdl echo "|/var/www/moodle/admin/process_email.php" > /var/qmail/alias/.qmail-noreply
To this three letter prefix, we will add a '-' when sending and receiving messages. For more info, check out the manpage for dot-qmail.
Setup under Exim
Open /etc/exim/exim.conf and add to trusted_users the user Apache and cron.php run as (usually "www-data" or "nobody").
Add a line to your aliases file. The line should list a 3-letter prefix, to which we'll add a '+', and the path of the script. For example for a prefix of 'mdl' we have in aliases:
mdl: |/var/www/moodle/admin/process_email.php noreply: |/var/www/moodle/admin/process_email.php
If you are using virtualdomains, consult your server administrator for the correct configuration. It probably involves editing transports and mapping your address to a "pipe" transport.
More documentation about Exim can be found here.
You will probably have to tell Exim not to lowercase the local-part in your exim configuration. This can be done in the router which handles the mail for your aliases file with: caseful_local_part = true