Testing strategy/Test Environments: Difference between revisions
Tim Barker (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Tim Barker (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
<P>A master hub VM is required for Jenkins and the hub for the Selenium | <P>A master hub VM is required for Jenkins and the hub for the Selenium | ||
grid.</P> | grid.</P> | ||
Revision as of 03:02, 13 March 2012
Test Environments
Test environments for automation will be hosted on the VM server. These will include a CI server (the build machine), database servers, web servers and client PCs.
Requirements Gathering
As a task while provisioning the VM Server, two surveys have been run to determine popular Test Platforms. Survey 1 gathered metrics from the Moodle Community and Survey 2 gathered metrics from Moodle Partners. Limiting factors of these surveys are that both samples are relatively small. The results of the surveys are as follows:
Survey 1 The Moodle Community:
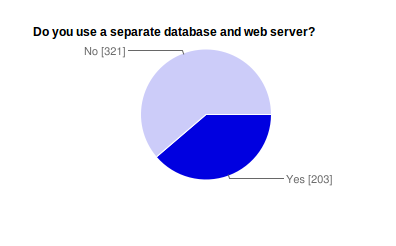
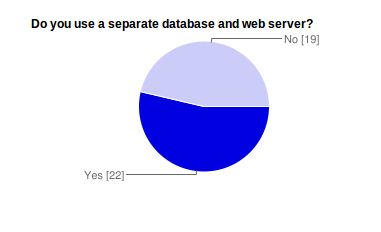
Fig. 4 Separate Database and Web Server Yes/No:
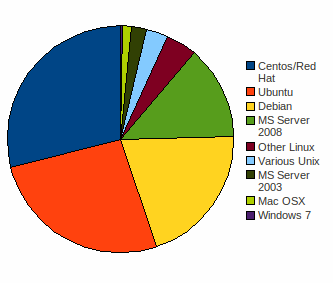
Fig. 5 Operating System of Separate Web Server:
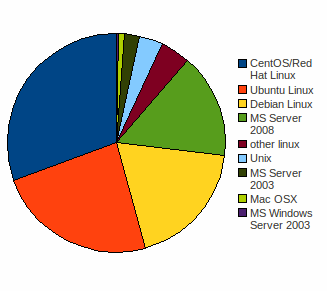
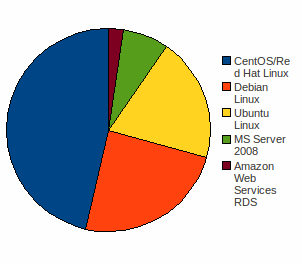
Fig. 6 Operating System of Separate Database Server:
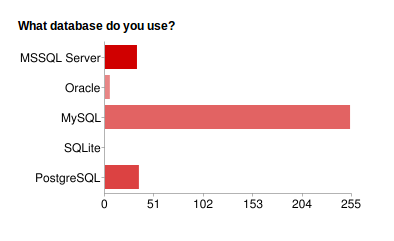
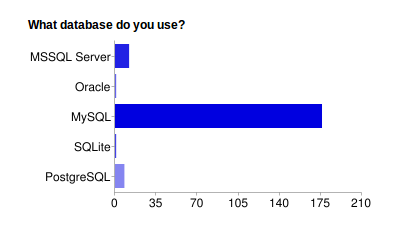
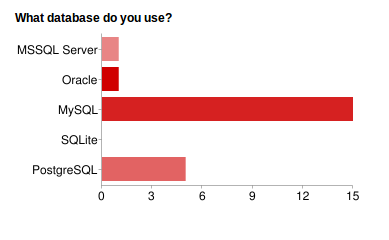
Fig. 7 What Databases are Used on a Split System:
Fig. 8 What Databases are Used on an all in one Database Server and Webserver:
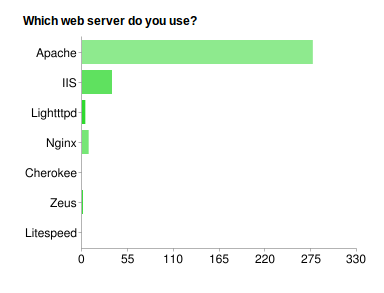
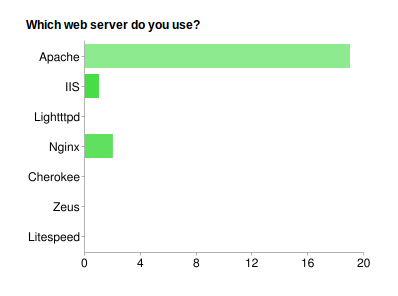
Fig. 9 What Web Server is Used on a Split System:
Fig. 10 What Web Server is Used on an all in one Database Server and Webserver:
As Debian and Ubuntu are similar and Red Hat and Centos are similar that,based upon our sample data, our three main operating used by the Moodle community Debian/Ubuntu, Red Hat/Centos and MS Server 2008 with a weighting of almost 75% towards the two Linux operating systems.
Of the five supported databases, the majority of community users prefer MySQL with PostgreSQL and MSSQL a fairly equal but distant second and third.
The Majority of community users also use Apache with IIS a very distant second.
7.1.1Survey 2 The Moodle Partners:
Fig. 11 Separate Database and Web Server Yes/No:
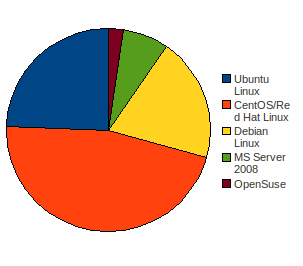
Fig. 12 Partner OS Database Server (combining answers for fig 11):
Fig. 13 Partner OS Web Server (combining answers for fig 8):
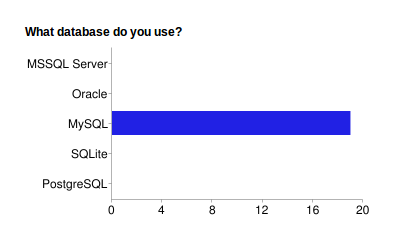
Fig. 14 What Databases are Used on a Split System:
Fig. 15 What Databases are Used on a Combined System:
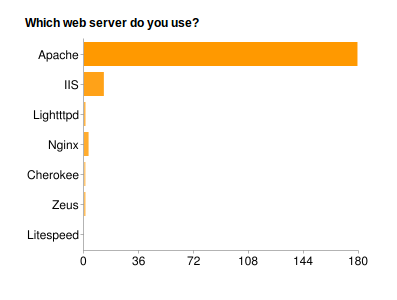
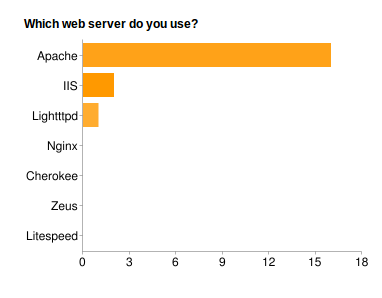
Fig. 16 What Web Servers are used on a Split System:
Fig. 17 What Web Servers are used on a Combined System:
This suggests that the majority of partners use Debian/Ubuntu or Centos/Rad Hat Linux, Apache and either a MySQL or PostgreSQL database.
VM Requirements
In true agile fashion and to promote flexibility, VM's for test environments will be modular i.e. they will be separate database servers and web servers. This will allow the mixing and matching of databases and their host OS to the web servers and their host OS as requirements change. At any time, any Web Server can connect to any Database Server. It should also reduce potential numbers of running VMs required for a particular platform.
A master hub VM is required for Jenkins and the hub for the Selenium grid.