Administration via command line: Difference between revisions
Mary Cooch (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
(Added information on how to list and uninstall Moodle plugins from the command line.) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
To avoid problems with access control, you should run them as the owner of the web server process. It is especially important for CLI installation and upgrade as they create new files in moodledata directory and the web server has to have write access to them. In Linux distributions, the user that runs the web server is usually apache or www-data or httpd or something similar. As a root, you will probably want to execute Moodle CLI scripts like this: | To avoid problems with access control, you should run them as the owner of the web server process. It is especially important for CLI installation and upgrade as they create new files in moodledata directory and the web server has to have write access to them. In Linux distributions, the user that runs the web server is usually apache or www-data or httpd or something similar. As a root, you will probably want to execute Moodle CLI scripts like this: | ||
$ cd /path/to/your/moodle/dir | $ cd /path/to/your/moodle/dir | ||
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/somescript.php --params | $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/somescript.php --params | ||
Most of the scripts accept common --help (or -h) parameter to display the full usage information, for example: | Most of the scripts accept common --help (or -h) parameter to display the full usage information, for example: | ||
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/install.php --help | $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/install.php --help | ||
{{Note|These scripts are supposed to be run under the identity of the web server user. Examples on this page use the <tt>apache</tt> user for illustration. The particular value depends on your OS distribution and local set-up. Typical values may be <tt>apache</tt>, <tt>www-data</tt> or <tt>httpd</tt>.}} | {{Note|These scripts are supposed to be run under the identity of the web server user. Examples on this page use the <tt>apache</tt> user for illustration. The particular value depends on your OS distribution and local set-up. Typical values may be <tt>apache</tt>, <tt>www-data</tt> or <tt>httpd</tt>.}} | ||
== Upgrading == | == Upgrading == | ||
Moodle can be upgraded from the command line. As with the installation script, there is either interactive or non-interactive mode of the upgrade. The script itself does not put the site into the maintenance mode, you have to do it on your own. Also, the script does not backup any data (if you read this page, you probably have some own scripts to backup your moodledata and the database, right?) | Moodle can be upgraded from the command line. As with the installation script, there is either interactive or non-interactive mode of the upgrade. The script itself does not put the site into the maintenance mode, you have to do it on your own. Also, the script does not backup any data (if you read this page, you probably have some own scripts to backup your moodledata and the database, right?) | ||
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/upgrade.php | $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/upgrade.php | ||
Upgrading via command line is a very comfortable way of Moodle upgrade if you use Git checkout of the Moodle source code (see [[Git for Administrators]]). See the following procedure how to upgrade your site within several seconds to the most recent version while preserving your eventual local customizations tracked in git repository: | Upgrading via command line is a very comfortable way of Moodle upgrade if you use Git checkout of the Moodle source code (see [[Git for Administrators]]). See the following procedure how to upgrade your site within several seconds to the most recent version while preserving your eventual local customizations tracked in git repository: | ||
$ cd /var/www/sites/moodle/htdocs/ | $ cd /var/www/sites/moodle/htdocs/ | ||
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --enable | $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --enable | ||
| Line 28: | Line 19: | ||
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/upgrade.php | $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/upgrade.php | ||
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --disable | $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --disable | ||
== Installation == | == Installation == | ||
There are two modes of installing Moodle from the command line. In interactive mode, the install script asks you for all data needed to properly set up new Moodle site. In non-interactive mode, you must provide all required data as the script parameters and then the new site is installed silently. The parameters can be passed in the interactive mode, too. The provided values are then used as the default values during the interactive session. | There are two modes of installing Moodle from the command line. In interactive mode, the install script asks you for all data needed to properly set up new Moodle site. In non-interactive mode, you must provide all required data as the script parameters and then the new site is installed silently. The parameters can be passed in the interactive mode, too. The provided values are then used as the default values during the interactive session. | ||
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/install.php --lang=cs | $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/install.php --lang=cs | ||
If your arguments contain some specials characters for Linux-based systems, don't forget to ''escape'' them with a backslash. For example, if you want to create an admin with ''pa$sword'' as password you should wrote ''pa\$sword'' instead! | If your arguments contain some specials characters for Linux-based systems, don't forget to ''escape'' them with a backslash. For example, if you want to create an admin with ''pa$sword'' as password you should wrote ''pa\$sword'' instead! | ||
If required, the database install may be skipped, with just config.php populated. | If required, the database install may be skipped, with just config.php populated. | ||
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/install.php --skip-database | $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/install.php --skip-database | ||
== Maintenance mode == | == Maintenance mode == | ||
To switch your site into the maintenance mode via CLI, you can use | To switch your site into the maintenance mode via CLI, you can use | ||
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --enable | $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --enable | ||
To turn maintenance mode off, execute the same script with the --disable parameter: | To turn maintenance mode off, execute the same script with the --disable parameter: | ||
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --disable | $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --disable | ||
If you don't want to enable maintenance mode immediately, but show a countdown to your users, execute the same script with the --enablelater parameter and the number of minutes which the countdown should run: | If you don't want to enable maintenance mode immediately, but show a countdown to your users, execute the same script with the --enablelater parameter and the number of minutes which the countdown should run: | ||
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --enablelater=10 | $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --enablelater=10 | ||
This script will also create and remove the climaintenance.html file for "Offline" mode. | This script will also create and remove the climaintenance.html file for "Offline" mode. | ||
== Offline mode == | == Offline mode == | ||
In some situations, you may want to switch your Moodle site into offline mode so that it is not accessible via the web but you can not stop the web server completely (typically because there are other web pages and applications running there). If a file called <code>climaintenance.html</code> exists in the root folder of moodledata directory, Moodle will automatically display the contents of that file instead of any other page. | In some situations, you may want to switch your Moodle site into offline mode so that it is not accessible via the web but you can not stop the web server completely (typically because there are other web pages and applications running there). If a file called <code>climaintenance.html</code> exists in the root folder of moodledata directory, Moodle will automatically display the contents of that file instead of any other page. | ||
$ cd /var/www/sites/moodle/moodledata/ | $ cd /var/www/sites/moodle/moodledata/ | ||
$ echo '<h1>Sorry, maintenance in progress</h1>' > climaintenance.html | $ echo '<h1>Sorry, maintenance in progress</h1>' > climaintenance.html | ||
You can prepare a nice formatted HTML page to inform your users about the server being down and keep in the moodledata directory under a name like <code>climaintenance.off</code> and rename it to the <code>climaintenance.html</code> if needed. | You can prepare a nice formatted HTML page to inform your users about the server being down and keep in the moodledata directory under a name like <code>climaintenance.off</code> and rename it to the <code>climaintenance.html</code> if needed. | ||
== Custom site defaults == | == Custom site defaults == | ||
During the install and upgrade via CLI, Moodle sets the administration variables to the default values. You can use different defaults. See MDL-17850 for details. Shortly, all you need to do is to add a file <code>local/defaults.php</code> into your Moodle installation. The format of the file is like | During the install and upgrade via CLI, Moodle sets the administration variables to the default values. You can use different defaults. See MDL-17850 for details. Shortly, all you need to do is to add a file <code>local/defaults.php</code> into your Moodle installation. The format of the file is like | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | ||
<?php | <?php | ||
| Line 75: | Line 46: | ||
$defaults['moodle']['settingname'] = 'settingvalue'; // for core settings | $defaults['moodle']['settingname'] = 'settingvalue'; // for core settings | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
These defaults are used during install, upgrade and are also displayed as defaults on Site administration pages. | These defaults are used during install, upgrade and are also displayed as defaults on Site administration pages. | ||
== Reset user password == | == Reset user password == | ||
If you happen to forget your admin password (or you want to set a password for any other user on the site), you can use reset_password.php script. The script sets the correctly salted password for the given user. | If you happen to forget your admin password (or you want to set a password for any other user on the site), you can use reset_password.php script. The script sets the correctly salted password for the given user. | ||
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/reset_password.php | $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/reset_password.php | ||
==Converting InnoDB to Barracuda== | ==Converting InnoDB to Barracuda== | ||
Newer versions of MySQL and MariaDB have an improved file format called Barracuda. To take advantage of this: | Newer versions of MySQL and MariaDB have an improved file format called Barracuda. To take advantage of this: | ||
# Ensure your version of MySQL/MariaDB is using Barracuda with the large index key prefix (innodb_large_prefix). See below for details. | # Ensure your version of MySQL/MariaDB is using Barracuda with the large index key prefix (innodb_large_prefix). See below for details. | ||
# Change to the compressed row format (see [[#Changing_tables_to_compressed_row_format|Changing tables to compressed row format]]) | # Change to the compressed row format (see [[#Changing_tables_to_compressed_row_format|Changing tables to compressed row format]]) | ||
| Line 93: | Line 57: | ||
If you have MySQL 8.0.0 or later, or MariaDB 10.3.0 or later, then these versions only support | If you have MySQL 8.0.0 or later, or MariaDB 10.3.0 or later, then these versions only support Barracuda with the large index key prefix. For earlier versions to check if MySQL/MariaDB is using Barracuda run the following statement in the MySQL/MariaDB client or phpMyAdmin SQL tab: | ||
SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES WHERE variable_name IN ('innodb_file_format', 'innodb_large_prefix', 'innodb_file_per_table'); | SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES WHERE variable_name IN ('innodb_file_format', 'innodb_large_prefix', 'innodb_file_per_table'); | ||
If your settings do not match any of the tables below, see [[MySQL#Configure_full_UTF-8_support|Configure full UTF-8 support]] for how to change these settings: | If your settings do not match any of the tables below, see [[MySQL#Configure_full_UTF-8_support|Configure full UTF-8 support]] for how to change these settings: | ||
| Line 102: | Line 64: | ||
If your settings match one of these tables then MySQL/MariaDB is using Barracuda with the large index key prefix. | If your settings match one of these tables then MySQL/MariaDB is using Barracuda with the large index key prefix. | ||
===Changing tables to compressed row format=== | ===Changing tables to compressed row format=== | ||
This script changes tables with many text columns to use ROW_FORMAT=COMPRESSED. This change isn’t required but is recommended. If the database error ''Row size too large (> 8126)'' occurs when using Moodle then run this script to fix this. | This script changes tables with many text columns to use ROW_FORMAT=COMPRESSED. This change isn’t required but is recommended. If the database error ''Row size too large (> 8126)'' occurs when using Moodle then run this script to fix this. | ||
| Line 110: | Line 70: | ||
To view tables requiring conversion, use the --list option: | To view tables requiring conversion, use the --list option: | ||
$ php admin/cli/mysql_compressed_rows.php --list | $ php admin/cli/mysql_compressed_rows.php --list | ||
Here is an example output: | Here is an example output: | ||
mdl_data Compact (needs fixing) | mdl_data Compact (needs fixing) | ||
mdl_data_fields Compact (needs fixing) | mdl_data_fields Compact (needs fixing) | ||
mdl_enrol_paypal Compact (needs fixing) | mdl_enrol_paypal Compact (needs fixing) | ||
To proceed with the conversion, run the command using the fix option: | To proceed with the conversion, run the command using the fix option: | ||
$ php admin/cli/mysql_compressed_rows.php --fix | $ php admin/cli/mysql_compressed_rows.php --fix | ||
Successful table conversion will be reported in the output, for example: | Successful table conversion will be reported in the output, for example: | ||
mdl_data ... Compressed | mdl_data ... Compressed | ||
mdl_data_fields ... Compressed | mdl_data_fields ... Compressed | ||
mdl_enrol_paypal ... Compressed | mdl_enrol_paypal ... Compressed | ||
If you get errors due to having insufficient privileges to run these commands use --showsql to generate the required SQL commands: | If you get errors due to having insufficient privileges to run these commands use --showsql to generate the required SQL commands: | ||
$ php admin/cli/mysql_compressed_rows.php --showsql | $ php admin/cli/mysql_compressed_rows.php --showsql | ||
You can then copy the generated SQL into your MySQL/MariaDB client running as the 'root' user. | You can then copy the generated SQL into your MySQL/MariaDB client running as the 'root' user. | ||
===Converting character set and collation=== | ===Converting character set and collation=== | ||
This script changes the Moodle database tables to enable full Unicode support. | This script changes the Moodle database tables to enable full Unicode support. | ||
$ php admin/cli/mysql_collation.php --collation=utf8mb4_unicode_ci | $ php admin/cli/mysql_collation.php --collation=utf8mb4_unicode_ci | ||
After making this change edit config.php and change the 'dbcollation' to 'utf8mb4_unicode_ci' in the $CFG->dboptions array. | After making this change edit config.php and change the 'dbcollation' to 'utf8mb4_unicode_ci' in the $CFG->dboptions array. | ||
For further details see: [[MySQL_full_unicode_support|MySQL full unicode support]] | For further details see: [[MySQL_full_unicode_support|MySQL full unicode support]] | ||
== Running cron via command line == | == Running cron via command line == | ||
In versions 1.x, you could execute admin/cron.php either from command line or via the web. Since Moodle 2.0, only admin/cli/cron.php script can be run via command line. | In versions 1.x, you could execute admin/cron.php either from command line or via the web. Since Moodle 2.0, only admin/cli/cron.php script can be run via command line. | ||
== Scheduled tasks == | == Scheduled tasks == | ||
Scheduled tasks are automatically run by the cron script, but the specific tasks which run on each cron iteration are determined by the scheduled tasks configuration. It is possible to override the scheduled tasks configuration and run a single scheduled task immediately using the admin/cli/scheduled_task.php script. | Scheduled tasks are automatically run by the cron script, but the specific tasks which run on each cron iteration are determined by the scheduled tasks configuration. It is possible to override the scheduled tasks configuration and run a single scheduled task immediately using the admin/cli/scheduled_task.php script. | ||
This script accepts the following arguments: | This script accepts the following arguments: | ||
--list - list all the known scheduled tasks. The tasks are listed by the class name used to run the task. This class name is required as the argument to the next option in order to run a specific task immediately. | --list - list all the known scheduled tasks. The tasks are listed by the class name used to run the task. This class name is required as the argument to the next option in order to run a specific task immediately. | ||
| Line 162: | Line 103: | ||
--showdebugging - Shows developer debugging info | --showdebugging - Shows developer debugging info | ||
'''Note:''' You must escape the "\" with an extra \ when using the --execute command. Take the following for example: | '''Note:''' You must escape the "\" with an extra \ when using the --execute command. Take the following for example: | ||
<pre>php admin/cli/scheduled_task.php --list</pre> | <pre>php admin/cli/scheduled_task.php --list</pre> | ||
will return something like: | will return something like: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
== List of scheduled tasks (http://yourserver.com/moodle) == | == List of scheduled tasks (http://yourserver.com/moodle) == | ||
| Line 178: | Line 116: | ||
... | ... | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
To run the first task in that list, you would execute | To run the first task in that list, you would execute | ||
php admin/cli/scheduled_task.php --execute='\enrol_imsenterprise\task\cron_task' | php admin/cli/scheduled_task.php --execute='\enrol_imsenterprise\task\cron_task' | ||
Be aware of the single quotes. Without them, you would need to use double backlashes to avoid escaping by the shell. | Be aware of the single quotes. Without them, you would need to use double backlashes to avoid escaping by the shell. | ||
=== Ad hoc tasks === | === Ad hoc tasks === | ||
[[Cron#Low_latency_adhoc_tasks|Ad hoc tasks]] are low-latency tasks that are normally run by the cron. You can run just the queued ad hoc tasks with admin/cli/adhoc_task.php. | [[Cron#Low_latency_adhoc_tasks|Ad hoc tasks]] are low-latency tasks that are normally run by the cron. You can run just the queued ad hoc tasks with admin/cli/adhoc_task.php. | ||
This script accepts the following options and arguments: | This script accepts the following options and arguments: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
-h, --help Print out this help | -h, --help Print out this help | ||
| Line 199: | Line 132: | ||
-f, --force Run even if cron is disabled | -f, --force Run even if cron is disabled | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
For example to run the currently queued ad hoc tasks: | For example to run the currently queued ad hoc tasks: | ||
sudo -u apache php admin/cli/adhoc_task.php -e | sudo -u apache php admin/cli/adhoc_task.php -e | ||
==Database transfer== | ==Database transfer== | ||
A command line script for [[Database transfer]] may be found in ''admin/tool/dbtransfer/cli/migrate.php''. | A command line script for [[Database transfer]] may be found in ''admin/tool/dbtransfer/cli/migrate.php''. | ||
==Purge caches== | ==Purge caches== | ||
You can purge caches using this script: | You can purge caches using this script: | ||
php admin/cli/purge_caches.php | php admin/cli/purge_caches.php | ||
==Kill all sessions== | ==Kill all sessions== | ||
If needed for administrative reasons, you can kill all user sessions using this script: | If needed for administrative reasons, you can kill all user sessions using this script: | ||
php admin/cli/kill_all_sessions.php | php admin/cli/kill_all_sessions.php | ||
As a result, all users will be logged out from Moodle. | As a result, all users will be logged out from Moodle. | ||
==Backup and restore of large courses== | ==Backup and restore of large courses== | ||
See Backup via CLI in [[Course backup]] and Restore via CLI in [[Course restore]] (new in 3.10 onwards). | See Backup via CLI in [[Course backup]] and Restore via CLI in [[Course restore]] (new in 3.10 onwards). | ||
==Fix course / module sequences== | ==Fix course / module sequences== | ||
In rare cases (such as after upgrading from a very old version of Moodle), the course / section / module sequence data can be out of sync. This can cause various problems for affected courses, such as sections not appearing, backups failing, pages not displaying etc. There is a specific check to check for errors caused by this problem, and to fix the data in the database if they are found. To run this script please use the command below: | In rare cases (such as after upgrading from a very old version of Moodle), the course / section / module sequence data can be out of sync. This can cause various problems for affected courses, such as sections not appearing, backups failing, pages not displaying etc. There is a specific check to check for errors caused by this problem, and to fix the data in the database if they are found. To run this script please use the command below: | ||
php admin/cli/fix_course_sequence.php -c=* --fix | php admin/cli/fix_course_sequence.php -c=* --fix | ||
This will check every course in Moodle and report which ones had errors and were fixed. | This will check every course in Moodle and report which ones had errors and were fixed. | ||
==Fix orphaned question categories== | ==Fix orphaned question categories== | ||
When a quiz is created, a new question category for the quiz is automatically created. In versions of Moodle prior to 2.9.1, if the quiz is deleted, the question category and any questions in the category remain in database. These orphaned question categories may be fixed by running the admin/cli/fix_orphaned_question_categories.php script with the --fix option. | When a quiz is created, a new question category for the quiz is automatically created. In versions of Moodle prior to 2.9.1, if the quiz is deleted, the question category and any questions in the category remain in database. These orphaned question categories may be fixed by running the admin/cli/fix_orphaned_question_categories.php script with the --fix option. | ||
==Search and replace text== | ==Search and replace text== | ||
This script can be used to search and replace text throughout the whole database. Use carefully and backup first always. More info in [[Search and replace tool]]. | This script can be used to search and replace text throughout the whole database. Use carefully and backup first always. More info in [[Search and replace tool]]. | ||
php admin/tool/replace/cli/replace.php --search=//oldsitehost --replace=//newsitehost | php admin/tool/replace/cli/replace.php --search=//oldsitehost --replace=//newsitehost | ||
==Build theme CSS cache== | ==Build theme CSS cache== | ||
If Moodle is not running in theme designer mode it will keep a copy of the compiled CSS on local disk and serve that to the browser when it requests a page. If there isn't a copy on local disk then a copy will be built the first time a page within Moodle is requested. | If Moodle is not running in theme designer mode it will keep a copy of the compiled CSS on local disk and serve that to the browser when it requests a page. If there isn't a copy on local disk then a copy will be built the first time a page within Moodle is requested. | ||
With this script you can pre-compile the cached CSS files for themes within Moodle to avoid having a user wait for the theme to compile during the first page request. | With this script you can pre-compile the cached CSS files for themes within Moodle to avoid having a user wait for the theme to compile during the first page request. | ||
php admin/cli/build_theme_css.php --themes=boost | php admin/cli/build_theme_css.php --themes=boost | ||
==Get and set configuration values== | ==Get and set configuration values== | ||
Displays the current value of the given setting, or set the given setting to the specified value. | Displays the current value of the given setting, or set the given setting to the specified value. | ||
$ php admin/cli/cfg.php [--component=<componentname>] [--json] [--shell-arg] | $ php admin/cli/cfg.php [--component=<componentname>] [--json] [--shell-arg] | ||
$ php admin/cli/cfg.php --name=<configname> [--component=<componentname>] [--shell-arg] [--no-eol] | $ php admin/cli/cfg.php --name=<configname> [--component=<componentname>] [--shell-arg] [--no-eol] | ||
| Line 260: | Line 166: | ||
$ php admin/cli/cfg.php --name=<configname> [--component=<componentname>] --unset | $ php admin/cli/cfg.php --name=<configname> [--component=<componentname>] --unset | ||
$ php admin/cli/cfg.php [--help|-h] | $ php admin/cli/cfg.php [--help|-h] | ||
Examples: | Examples: | ||
$ php admin/cli/cfg.php --name=langmenu | $ php admin/cli/cfg.php --name=langmenu | ||
| Line 268: | Line 173: | ||
$ php admin/cli/cfg.php --name=langmenu --set=0 | $ php admin/cli/cfg.php --name=langmenu --set=0 | ||
will disable the ''Language menu''. | will disable the ''Language menu''. | ||
== Managing plugins == | |||
=== List and uninstall Moodle plugins === | |||
Moodle includes a handy command-line tool to display a list of plugins and remove plugins. | |||
$ php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php | |||
This command line tool accepts the following arguments. | |||
Options: | |||
-h --help Print this help. | |||
--show-all Displays a list of all installed plugins. | |||
--show-contrib Displays a list of all third-party installed plugins. | |||
--show-missing Displays a list of plugins missing from disk. | |||
--purge-missing Uninstall all missing from disk plugins. | |||
--plugins=<plugin name> A comma separated list of plugins to be uninstalled. E.g. mod_assign,mod_forum | |||
--run Execute uninstall. If this option is not set, then the script will be run in a dry mode. | |||
--showsql Show sql queries before they are executed. | |||
--showdebugging Show developer level debugging information. | |||
Dry Mode does everything the script would normally do except for actually making any changes. This is useful when you want to test the validity of your command. | |||
Run this command from the Moodle wwwroot directory. Here are some examples: | |||
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --show-all | |||
Prints tab-separated list of all installed plugins. | |||
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --show-contrib | |||
Prints tab-separated list of all third-party installed plugins. | |||
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --show-missing | |||
<blockquote> Prints tab-separated list of all missing from disk plugins.</blockquote> | |||
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --purge-missing | |||
A dry run of uninstalling all missing plugins. This will NOT uninstall the plugin. To actually uninstall, you need to add the '--run' arguments. | |||
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --purge-missing --run | |||
Run uninstall of all missing plugins. | |||
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --plugins=mod_assign,mod_forum | |||
A dry run of uninstalling mod_assign and mod_forum plugins. This will NOT uninstall the plugin. To actually uninstall, you need to add the '--run' arguments. | |||
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --plugins=mod_assign,mod_forum --run | |||
Run uninstall for mod_assign and mod_forum plugins. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* MDL-35736 - Manage plugins via command-line | |||
* MDL-35736 - Manage plugins via command line | |||
* MDL-36237 - Resort course list via CLI | * MDL-36237 - Resort course list via CLI | ||
* [http://moosh-online.com/ MOOSH] - MOOdle SHell. It is a | * [http://moosh-online.com/ MOOSH] - MOOdle SHell. It is a command-line tool that will allow you to perform many of the most common Moodle tasks. | ||
[[fr:Administration en ligne de commande]] | [[fr:Administration en ligne de commande]] | ||
[[de:Administration über Kommandozeile]] | [[de:Administration über Kommandozeile]] | ||
Revision as of 14:49, 15 January 2023
This page requires updating. Please do so and remove this template when finished.
Running CLI scripts
If you have shell access to your web server, you may find various CLI (command line interface) scripts useful during Moodle administration. Core admin CLI tools are located in the admin/cli/* folder. Other plugins may provide CLI functionality via scripts in their own cli folder.
To avoid problems with access control, you should run them as the owner of the web server process. It is especially important for CLI installation and upgrade as they create new files in moodledata directory and the web server has to have write access to them. In Linux distributions, the user that runs the web server is usually apache or www-data or httpd or something similar. As a root, you will probably want to execute Moodle CLI scripts like this:
$ cd /path/to/your/moodle/dir $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/somescript.php --params
Most of the scripts accept common --help (or -h) parameter to display the full usage information, for example:
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/install.php --help
Upgrading
Moodle can be upgraded from the command line. As with the installation script, there is either interactive or non-interactive mode of the upgrade. The script itself does not put the site into the maintenance mode, you have to do it on your own. Also, the script does not backup any data (if you read this page, you probably have some own scripts to backup your moodledata and the database, right?)
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/upgrade.php
Upgrading via command line is a very comfortable way of Moodle upgrade if you use Git checkout of the Moodle source code (see Git for Administrators). See the following procedure how to upgrade your site within several seconds to the most recent version while preserving your eventual local customizations tracked in git repository:
$ cd /var/www/sites/moodle/htdocs/ $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --enable $ git pull $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/upgrade.php $ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --disable
Installation
There are two modes of installing Moodle from the command line. In interactive mode, the install script asks you for all data needed to properly set up new Moodle site. In non-interactive mode, you must provide all required data as the script parameters and then the new site is installed silently. The parameters can be passed in the interactive mode, too. The provided values are then used as the default values during the interactive session.
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/install.php --lang=cs
If your arguments contain some specials characters for Linux-based systems, don't forget to escape them with a backslash. For example, if you want to create an admin with pa$sword as password you should wrote pa\$sword instead!
If required, the database install may be skipped, with just config.php populated.
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/install.php --skip-database
Maintenance mode
To switch your site into the maintenance mode via CLI, you can use
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --enable
To turn maintenance mode off, execute the same script with the --disable parameter:
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --disable
If you don't want to enable maintenance mode immediately, but show a countdown to your users, execute the same script with the --enablelater parameter and the number of minutes which the countdown should run:
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/maintenance.php --enablelater=10
This script will also create and remove the climaintenance.html file for "Offline" mode.
Offline mode
In some situations, you may want to switch your Moodle site into offline mode so that it is not accessible via the web but you can not stop the web server completely (typically because there are other web pages and applications running there). If a file called climaintenance.html exists in the root folder of moodledata directory, Moodle will automatically display the contents of that file instead of any other page.
$ cd /var/www/sites/moodle/moodledata/ $ echo '<h1>Sorry, maintenance in progress</h1>' > climaintenance.html
You can prepare a nice formatted HTML page to inform your users about the server being down and keep in the moodledata directory under a name like climaintenance.off and rename it to the climaintenance.html if needed.
Custom site defaults
During the install and upgrade via CLI, Moodle sets the administration variables to the default values. You can use different defaults. See MDL-17850 for details. Shortly, all you need to do is to add a file local/defaults.php into your Moodle installation. The format of the file is like
<?php
$defaults['pluginname']['settingname'] = 'settingvalue'; // for plugins
$defaults['moodle']['settingname'] = 'settingvalue'; // for core settings
These defaults are used during install, upgrade and are also displayed as defaults on Site administration pages.
Reset user password
If you happen to forget your admin password (or you want to set a password for any other user on the site), you can use reset_password.php script. The script sets the correctly salted password for the given user.
$ sudo -u apache /usr/bin/php admin/cli/reset_password.php
Converting InnoDB to Barracuda
Newer versions of MySQL and MariaDB have an improved file format called Barracuda. To take advantage of this:
- Ensure your version of MySQL/MariaDB is using Barracuda with the large index key prefix (innodb_large_prefix). See below for details.
- Change to the compressed row format (see Changing tables to compressed row format)
- Change the character set and collation for full Unicode support (see Converting character set and collation).
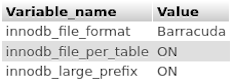
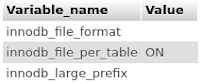
If you have MySQL 8.0.0 or later, or MariaDB 10.3.0 or later, then these versions only support Barracuda with the large index key prefix. For earlier versions to check if MySQL/MariaDB is using Barracuda run the following statement in the MySQL/MariaDB client or phpMyAdmin SQL tab:
SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES WHERE variable_name IN ('innodb_file_format', 'innodb_large_prefix', 'innodb_file_per_table');
If your settings do not match any of the tables below, see Configure full UTF-8 support for how to change these settings:
If your settings match one of these tables then MySQL/MariaDB is using Barracuda with the large index key prefix.
Changing tables to compressed row format
This script changes tables with many text columns to use ROW_FORMAT=COMPRESSED. This change isn’t required but is recommended. If the database error Row size too large (> 8126) occurs when using Moodle then run this script to fix this.
Note: If you have MariaDB version 10.6.0 to 10.6.6 or version 10.7.0 to 10.7.2 you must upgrade to a later version before running this script. See MDL-72131 for details.
To view tables requiring conversion, use the --list option:
$ php admin/cli/mysql_compressed_rows.php --list
Here is an example output:
mdl_data Compact (needs fixing) mdl_data_fields Compact (needs fixing) mdl_enrol_paypal Compact (needs fixing)
To proceed with the conversion, run the command using the fix option:
$ php admin/cli/mysql_compressed_rows.php --fix
Successful table conversion will be reported in the output, for example:
mdl_data ... Compressed mdl_data_fields ... Compressed mdl_enrol_paypal ... Compressed
If you get errors due to having insufficient privileges to run these commands use --showsql to generate the required SQL commands:
$ php admin/cli/mysql_compressed_rows.php --showsql
You can then copy the generated SQL into your MySQL/MariaDB client running as the 'root' user.
Converting character set and collation
This script changes the Moodle database tables to enable full Unicode support.
$ php admin/cli/mysql_collation.php --collation=utf8mb4_unicode_ci
After making this change edit config.php and change the 'dbcollation' to 'utf8mb4_unicode_ci' in the $CFG->dboptions array.
For further details see: MySQL full unicode support
Running cron via command line
In versions 1.x, you could execute admin/cron.php either from command line or via the web. Since Moodle 2.0, only admin/cli/cron.php script can be run via command line.
Scheduled tasks
Scheduled tasks are automatically run by the cron script, but the specific tasks which run on each cron iteration are determined by the scheduled tasks configuration. It is possible to override the scheduled tasks configuration and run a single scheduled task immediately using the admin/cli/scheduled_task.php script.
This script accepts the following arguments:
--list - list all the known scheduled tasks. The tasks are listed by the class name used to run the task. This class name is required as the argument to the next option in order to run a specific task immediately.
--execute=<task> - Runs a single scheduled task immediately - regardless of scheduling settings. This will even run disabled tasks. Tasks will still use locking to prevent concurrent execution of the same task - even on clusters. The format of the <task> argument must be the same as returned by the --list option above.
--showsql - Shows sql queries before they are execute
--showdebugging - Shows developer debugging info
Note: You must escape the "\" with an extra \ when using the --execute command. Take the following for example:
php admin/cli/scheduled_task.php --list
will return something like:
== List of scheduled tasks (http://yourserver.com/moodle) == \enrol_imsenterprise\task\cron_task 10 * * * * * ASAP \logstore_legacy\task\cleanup_task * 5 * * * * ASAP \logstore_standard\task\cleanup_task * 4 * * * * Wednesday, November 12, 2014, 4:35 AM \mod_forum\task\cron_task * * * * * * ASAP \core\task\automated_backup_task 50 * * * * * ASAP ...
To run the first task in that list, you would execute
php admin/cli/scheduled_task.php --execute='\enrol_imsenterprise\task\cron_task'
Be aware of the single quotes. Without them, you would need to use double backlashes to avoid escaping by the shell.
Ad hoc tasks
Ad hoc tasks are low-latency tasks that are normally run by the cron. You can run just the queued ad hoc tasks with admin/cli/adhoc_task.php.
This script accepts the following options and arguments:
-h, --help Print out this help
--showsql Show sql queries before they are executed
--showdebugging Show developer level debugging information
-e, --execute Run all queued adhoc tasks
-k, --keep-alive=N Keep this script alive for N seconds and poll for new adhoc tasks
-i --ignorelimits Ignore task_adhoc_concurrency_limit and task_adhoc_max_runtime limits
-f, --force Run even if cron is disabled
For example to run the currently queued ad hoc tasks:
sudo -u apache php admin/cli/adhoc_task.php -e
Database transfer
A command line script for Database transfer may be found in admin/tool/dbtransfer/cli/migrate.php.
Purge caches
You can purge caches using this script:
php admin/cli/purge_caches.php
Kill all sessions
If needed for administrative reasons, you can kill all user sessions using this script:
php admin/cli/kill_all_sessions.php
As a result, all users will be logged out from Moodle.
Backup and restore of large courses
See Backup via CLI in Course backup and Restore via CLI in Course restore (new in 3.10 onwards).
Fix course / module sequences
In rare cases (such as after upgrading from a very old version of Moodle), the course / section / module sequence data can be out of sync. This can cause various problems for affected courses, such as sections not appearing, backups failing, pages not displaying etc. There is a specific check to check for errors caused by this problem, and to fix the data in the database if they are found. To run this script please use the command below:
php admin/cli/fix_course_sequence.php -c=* --fix
This will check every course in Moodle and report which ones had errors and were fixed.
Fix orphaned question categories
When a quiz is created, a new question category for the quiz is automatically created. In versions of Moodle prior to 2.9.1, if the quiz is deleted, the question category and any questions in the category remain in database. These orphaned question categories may be fixed by running the admin/cli/fix_orphaned_question_categories.php script with the --fix option.
Search and replace text
This script can be used to search and replace text throughout the whole database. Use carefully and backup first always. More info in Search and replace tool.
php admin/tool/replace/cli/replace.php --search=//oldsitehost --replace=//newsitehost
Build theme CSS cache
If Moodle is not running in theme designer mode it will keep a copy of the compiled CSS on local disk and serve that to the browser when it requests a page. If there isn't a copy on local disk then a copy will be built the first time a page within Moodle is requested.
With this script you can pre-compile the cached CSS files for themes within Moodle to avoid having a user wait for the theme to compile during the first page request.
php admin/cli/build_theme_css.php --themes=boost
Get and set configuration values
Displays the current value of the given setting, or set the given setting to the specified value.
$ php admin/cli/cfg.php [--component=<componentname>] [--json] [--shell-arg] $ php admin/cli/cfg.php --name=<configname> [--component=<componentname>] [--shell-arg] [--no-eol] $ php admin/cli/cfg.php --name=<configname> [--component=<componentname>] --set=<value> $ php admin/cli/cfg.php --name=<configname> [--component=<componentname>] --unset $ php admin/cli/cfg.php [--help|-h]
Examples:
$ php admin/cli/cfg.php --name=langmenu
will display the value of Display language menu in Site administration > Language > Language settings (0 for No or 1 for Yes).
$ php cfg.php --name=maxsizetodownload --component=folder
will display the value of Maximum folder download size (MB) accessible from Site administration > Plugins > Activity modules > Folder.
$ php admin/cli/cfg.php --name=langmenu --set=0
will disable the Language menu.
Managing plugins
List and uninstall Moodle plugins
Moodle includes a handy command-line tool to display a list of plugins and remove plugins.
$ php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php
This command line tool accepts the following arguments.
Options:
-h --help Print this help. --show-all Displays a list of all installed plugins. --show-contrib Displays a list of all third-party installed plugins. --show-missing Displays a list of plugins missing from disk. --purge-missing Uninstall all missing from disk plugins. --plugins=<plugin name> A comma separated list of plugins to be uninstalled. E.g. mod_assign,mod_forum --run Execute uninstall. If this option is not set, then the script will be run in a dry mode. --showsql Show sql queries before they are executed. --showdebugging Show developer level debugging information.
Dry Mode does everything the script would normally do except for actually making any changes. This is useful when you want to test the validity of your command.
Run this command from the Moodle wwwroot directory. Here are some examples:
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --show-all
Prints tab-separated list of all installed plugins.
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --show-contrib
Prints tab-separated list of all third-party installed plugins.
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --show-missing
Prints tab-separated list of all missing from disk plugins.
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --purge-missing
A dry run of uninstalling all missing plugins. This will NOT uninstall the plugin. To actually uninstall, you need to add the '--run' arguments.
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --purge-missing --run
Run uninstall of all missing plugins.
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --plugins=mod_assign,mod_forum
A dry run of uninstalling mod_assign and mod_forum plugins. This will NOT uninstall the plugin. To actually uninstall, you need to add the '--run' arguments.
# php admin/cli/uninstall_plugins.php --plugins=mod_assign,mod_forum --run
Run uninstall for mod_assign and mod_forum plugins.