Grade calculations: Difference between revisions
m (Improved wording and correction of some typos) |
m (fix small typo) |
||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
==Calculations when user language is not English== | ==Calculations when user language is not English== | ||
Calculations and formulas use decimal and list separators as defined in the [https://docs.moodle.org/dev/Translation_langconfig langconfig.php] file of each [[Language packs|language pack]]. | |||
The [[Decimal separator|decimal separator]] (the symbol used to mark the boundary between the integral and the fractional parts of a decimal number) is a point (.) in English. In other languages it may be a comma (,). | The [[Decimal separator|decimal separator]] (the symbol used to mark the boundary between the integral and the fractional parts of a decimal number) is a point (.) in English. In other languages it may be a comma (,). | ||
Revision as of 15:46, 22 January 2019
A grade calculation is a formula used to determine grades, based on other grade items. Note that this is not the same as Calculated question types.
Grade calculations follow the pattern of formulas/functions in popular spreadsheet programs. They start with an equal (=) sign, and use common mathematical operators and functions to produce a single numerical output. This output is then used as the computed value for the grade item you are editing.
Setting a grade calculation
To set a grade calculation:
- Login as teacher or other user with permission to edit grades
- Click on Grades in the course administration block
- Click the 'Categories and items'
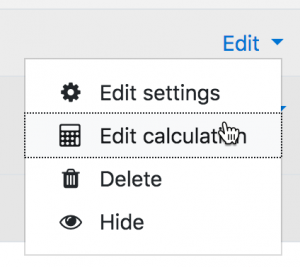
- Click the 'Edit settings' and then 'Edit calculation'. Note: if you don't see this, then it must be enabled in Site administration>Grades>Report settings>Grader report
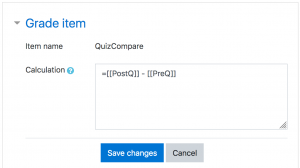
- Start with an equal sign (=)
- Type an expression using numbers, arithmetic operators, mathematical functions and ID numbers; for example =average()
- Plug in your ID numbers (see below) enclosed in double square brackets, for example =[[item1]]+[[item2]]
- Separate each function argument with a comma, as in =average([[item1]], [[item2]])+[[item3]])
- Click the "Save Changes" button
Assigning ID numbers
You can include the values of other grade items by using their ID number as references in your formulas. The ID number must be surrounded by double square brackets, for example if you have a grade item with Quiz.3 as ID number, you can refer this item using [[Quiz.3]] in your calculation.
Below the calculation field there is a list of your course grade categories and grade items. Next to each item or category's total there is the ID number you can use in your calculation (already surrounded with the required double square brackets).
However, since ID numbers are optional, some items may not yet have one. Each item without ID number have a form field that you can use to enter its ID number directly. As soon as you have assigned the ID numbers you need, you must click the "Add ID numbers" button; the page will reload and show you the same list including the ID numbers you have just assigned. Now you can use them in your grade calculation.
Note: Moodle does not allow calculations involving no ID numbers.
Calculation functions
Every grade calculation must start with an equal sign (=) followed by an expression using operators and functions supported by the system. All common arithmetic operators are supported
- addition, using the plus (+) sign
- subtraction, using the minus (-) sign
- multiplication, using the asterisk (*) character
- division, using the slash (/) character
- exponentiation, using the caret (^) character
with their usual evaluation precedence rules: exponentiations are evaluated first, then multiplications and divisions are performed, finally additions and subtraction are carried out; so, the expression =1+2-3*4/5^6 gives almost 3 (2,999232). Different precedences can be forced using round parentheses, as in the expression =((((1+2)-3)*4)/5)^6 which yields 0.
Functions can also appear in expressions, using the comma (,) character to separate their arguments listed within round brackets. (Note that the separator character could be a semicolon (;) in other languages, see below).
- average([[item1]], [[item2]]...): Returns the average of the values in a list of arguments
- max([[item1]], [[item2]]...): Returns the maximum value in a list of arguments
- min([[item1]], [[item2]]...): Returns the minimum value in a list of arguments
- mod(dividend, divisor): Calculates the remainder of a division
- pi(): Returns the value of the number Pi (3.14159265...)
- power(base, exponent): Raises a number to the exponent power (this is the same as base^exponent)
- round(number, count): Rounds number to count decimal digits
- floor(number): Maps a real number to the largest previous integer
- ceil(number): Maps a real number to the smallest following integer
- sum([[item1]], [[item2]]...): Returns the sum of all arguments (this is the same as [[item1]]+[[item2]]+...
Many other mathematical functions are also supported:
- sin()
- sinh()
- arcsin()
- asin()
- arcsinh()
- asinh()
- cos()
- cosh()
- arccos()
- acos()
- arccosh()
- acosh()
- tan()
- tanh()
- arctan()
- atan()
- arctanh()
- atanh()
- sqrt()
- abs()
- ln()
- log()
- exp()
Example calculations
- =max([[Quiz.1]], [[Quiz.4]], [[Assignment.1]]) - Returns the maximum value of the grades referred by Quiz.1, Quiz.4 and Assignment.1
- =average(max([[Quiz.1]], [[Quiz.4]], [[Assignment.1]]), min([[Quiz.1]], [[Quiz.4]], [[Assignment.1]])) - Returns the average of the maximum and the minimum values among Quiz.1, Quiz.4 and Assignment.1 (functions can be nested)
- =sum([[item1]]*0.3, [[item2]]*0.6, [[item3]]*2) - Returns a weighted grade sum where item1 is weighted 30%, item2 is weighted at 60% and item3 is weighted at 200%
Calculations when user language is not English
Calculations and formulas use decimal and list separators as defined in the langconfig.php file of each language pack.
The decimal separator (the symbol used to mark the boundary between the integral and the fractional parts of a decimal number) is a point (.) in English. In other languages it may be a comma (,).
Analogously, the list separator (the symbol used to separate the items within a list, such as the arguments of a function) is a comma (,) in English. In other languages it may be a semicolon (;).