Pattern-match question type: Difference between revisions
- Managing questions
- Question behaviours
- Question types
- Calculated
- Simple Calculated
- Drag and drop into text
- Drag and drop markers
- Drag and drop onto image
- Calculated Multichoice
- Description
- Essay
- Matching
- Embedded Answers (Cloze)
- Multiple Choice
- Random Short Answer Matching
- Select missing words
- Short-Answer
- Numerical
- True/False
- Third-party question types
- Questions FAQ
Phil Butcher (talk | contribs) |
(Added lots of info about pmatch (from OU site)) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== More documentation == | == More documentation == | ||
More [http://www.open.edu/openlearnworks/course/view.php?id=1581 documentation is available] in the [http://www.open.edu/openlearnworks/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=52747 Open University's reference manual]. That includes a description of the pmatch syntax. There another page that explains [[:dev:The_OU_PMatch_algorithm|The OU PMatch algorithm]], but that was written before development started, and may not be a 100% accurate description of what was finally implemented. | More [http://www.open.edu/openlearnworks/course/view.php?id=1581 documentation is available] in the [http://www.open.edu/openlearnworks/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=52747 Open University's reference manual]. That includes a description of the pmatch syntax. There is another page that explains [[:dev:The_OU_PMatch_algorithm|The OU PMatch algorithm]], but that was written before development started, and may not be a 100% accurate description of what was finally implemented. | ||
==Overview== | |||
The Pattern match question type is used to test if a short free-text student response matches a specified response pattern. | |||
Pattern match is a more sophisticated alternative to the ''Short answer question'' type and offers: | |||
* the ability to cater for misspellings, with and without an English dictionary | |||
* specification of synonyms and alternative phrases | |||
* flexible word order | |||
* checks on the proximity of words. | |||
For certain types of response it has been shown to provide an accuracy of marking that is on a par with, or better than, that provided by a cohort of human markers. | |||
Pattern match works on the basis that you have a student response which you wish to match against any number of response matching patterns. Each pattern is compared in turn until a match is found and feedback and marks are assigned. | |||
The key to using ''Pattern match'' is in asking questions that you have a reasonable hope of marking accurately. Hence writing the question stem is the most important part of writing these questions. | |||
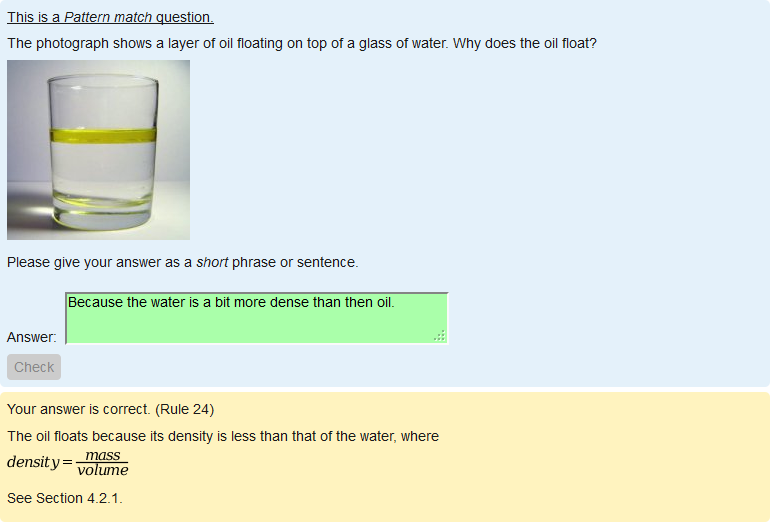
[[File:The Question text, Grade and General feedback for a Pattern match question.png]] | |||
==Components of the question== | |||
'''Question name''': A descriptive name is sensible. This name will not be shown to students. | |||
'''Question text''': You may use the full functionality of the editor to state the question. | |||
===Placing the response box=== | |||
The response box may be placed within the question rubric by including a sequence of underscores e.g. _____. At runtime the response box will replace the underscores. The minimum number of underscores required to trigger this action is 5. The size of the input box may also be specified by __XxY__ e.g. __20x1__ will produce a box 20 columns wide and 1 row high. If no underscores are present the response box will be placed after the question. | |||
'''Default mark''': Decide on how to score your questions and be consistent. | |||
'''General feedback''': We recommend that all questions should have this box completed with the correct answer and a fully worked explanation. The contents of this box will be shown to all students irrespective of whether their response was correct or incorrect. For the Pattern match question type you cannot rely on using the machine generated 'Right answer' (from the iCMA definition form). | |||
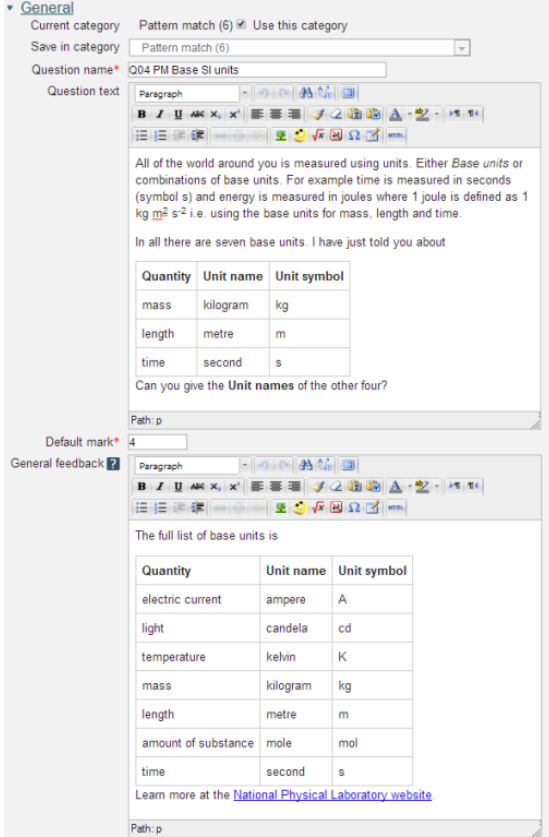
[[File:Options for entering answers.png]] | |||
'''Case sensitivity''': No or yes. | |||
'''Allow use of subscript/superscript''': No or Yes. Any subscripts entered by the student are contained in their response between the standard tags of <sub> and </sub> or <sup> and </sup>. For example: | |||
* The formula for water is H<sub>2</sub>O | |||
* The speed of light is approximately 3x10<sup>8</sup> m s<sup>-1</sup> | |||
At run time keyboard users may move between normal, subscript and superscript by using the up-arrow and down-arrow keys. You may wish to include this information within your question. If you do please note that the up-arrow and down-arrow provided in the HTML editor’s ‘insert custom characters’ list are not spoken by a screen reader and you should also include the words ‘up-arrow’ and ‘down-arrow’. | |||
'''If answer is more than 20 words''': We strongly recommend that you limit responses to 20 words. Allowing unconstrained responses often results in responses that are both right and wrong – which are difficult to mark consistently one way or the other. | |||
'''Check spelling of student''': How many ways do you know of to spell ‘temperature’? We’ve seen 14! You will improve the marking accuracy by insisting on words that are in Moodle system dictionary. | |||
'''Add these words to dictionary''': When dealing with specialised scientific, technical and medical terms that are not in a standard dictionary it is most likely that you will have to add them by using this field. Enter your words leaving a space between them. | |||
'''Convert the following characters to space''': In ''Pattern match'' words are defined as sequences of characters between spaces. The exclamation mark and question mark are also taken to mark the end of a word. The period is a special case; as a full stop it is also a word delimiter but as the decimal point it is not. All other punctuation is considered to be part of the response but this option lets you remove it. | |||
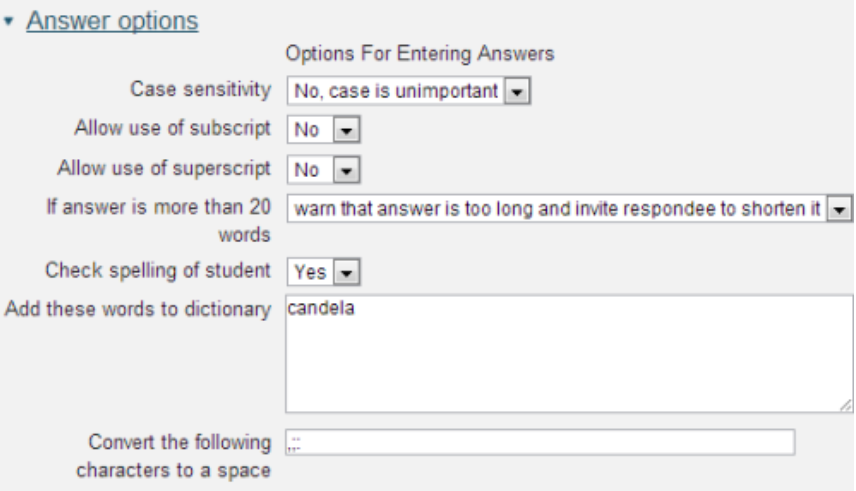
[[File:Fields for entering synonyms (not associated with the SI units question).png]] | |||
'''Words and synonyms''': All words and synonyms are specified as they are to be applied by the response matching. They do not have to be full words but can be stems with a wildcard. | |||
Synonyms may only be single words i.e. the ability to specify alternate phrases in synonym lists is not allowed. | |||
From the example above any occurrence of the word oil in the response match will be replaced by '''oil|glycer*|paraf*''' before the match is carried out. | |||
[[File:A response match.png]] | |||
'''Answer''': This example shows that Pattern match will support complex response matching. | |||
Take the first answer field '''match_o(ampere candela kelvin mole)''' is the exact match for the four words with the additional feature that the matching option 'o' allows the words to be given in any order. | |||
The answer field '''match_ow(ampere candela kelvin mole)''' requires the same four words, again in any order, but also allows other words. | |||
The third answer field match_mow(ampere candela kelvin mole) allows for misspellings which are still in the dictionary e.g. mule instead of mole. | |||
Please see the section on ''Pattern match syntax'' for a full description. | |||
'''Grade''': Between ‘none’ and 100%. At least one response must have a mark of 100%. | |||
'''Feedback''': Specific feedback that is provided to anyone whose response is matched by the response matching rule in Answer. | |||
[[File:Feedback to all non-matched responses.png]] | |||
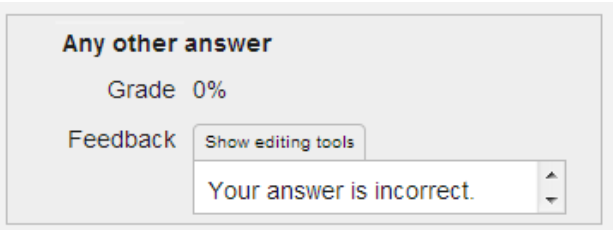
The feedback for all non-matched responses should go into the ‘Any other answer’ field. | |||
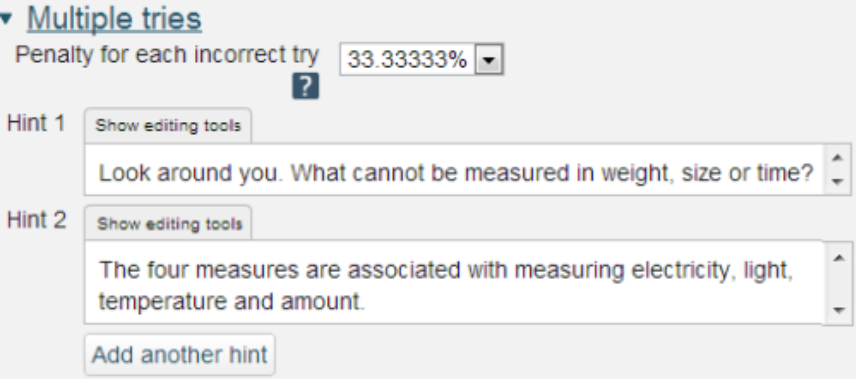
[[File:The multiple tries section.png]] | |||
==How the response is handled== | |||
The basic unit of the student response that Pattern match operates on is the word, where a word is defined as a sequence of characters between spaces. The full stop (but not the decimal point), exclamation mark and question mark are also treated as ending a word. | |||
Numbers are special instances of words and are matched by value and not by the form in which they are given. '''match_w(25 ms<sup>-1</sup>)''' will match the following correct responses; 25 ms-1, 2.5e1 ms-1, 2.5x10-1 ms-1 | |||
With the exception of numbers and the word terminators (<space><full stop>? and !) ''Pattern match'' matches what it is given. Whether case does or does not matter is left to the author to decide as is the significance of punctuation such as ,;: and others. | |||
The response is treated as a whole with the exception that words that are required to be in proximity must also be in the same sentence. | |||
==Pattern match syntax== | |||
The match syntax can be considered in three parts. | |||
# the matching options e.g. '''mow''' | |||
# the words to be matched e.g.'''tom dick harry''' together with the in-word special characters. | |||
# and, or and not combinations of matches e.g. '''match_any()''' | |||
==Matching options== | |||
Matching option Symbol Description | |||
allowExtraChars c Extra characters can be anywhere within the word. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using the misspelling options below. | |||
allowAnyWordOrder o Where multiple words are to be matched they can be in any order. | |||
allowExtraWords w Extra words beyond those being searched for are accepted. | |||
misspelling: allowReplaceChar mr Will match a word where one character is different to those specified in the pattern. The pattern word must be 4 characters or greater, excluding wildcards, for replacement to kick in. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using this option. | |||
misspelling: allowTransposeTwoChars mt Will match a word where two characters are transposed. The pattern word must be 4 characters or greater, excluding wildcards, for transposition to kick in. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using this option. | |||
misspelling: allowExtraChar mx Will match a word where one character is extra to those specified in the pattern. The pattern word must be 3 characters or greater, excluding wildcards, for extra to kick in. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using this option. | |||
misspelling: allowFewerChar mf Will match a word where one character is missing from those specified in the pattern. The pattern word must be 4 characters or greater, excluding wildcards, for fewer to kick in. Without this 'no' would be reduced to just matching 'n' or 'o'. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using this option. | |||
misspelling m This combines the four ways of misspelling a word described above i.e. m is equivalent to mxfrt. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using this option. | |||
misspellings m2 Allows two misspellings, as defined by option 'm', in pattern words of 8 characters or more, excluding wildcards. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using this option. N.b. use this option sparely. It introduces a huge number of possible acceptable spellings all of which have to be checked and the time taken for the match to complete goes up and up. | |||
allowProximityOf0 p0 No words, or full stops, are allowed in between any words specified in the proximity sequence. | |||
allowProximityOf1 p1 One word is allowed in between any two words specified in the proximity sequence. The words must not span sentences. | |||
allowProximityOf2 p2 (Default value) Two words are allowed in between any two words specified in the proximity sequence. The words must not span sentences. | |||
allowProximityOf3 p3 Three words are allowed in between any two words specified in the proximity sequence. The words must not span sentences. | |||
allowProximityOf4 p4 Four words are allowed in between any two words specified in the proximity sequence. The words must not span sentences. | |||
The matching options are appended to the word match with an intervening underscore and may be combined. A typical match combines the options ‘mow’ to allow for | |||
# misspellings | |||
# any word order | |||
# any extra words | |||
and is written match_mow(words to be matched). | |||
==Special characters== | |||
Special character Symbol Description | |||
Word AND space 'space' delimits words and acts as the logical AND. | |||
Word OR | | between words indicates that either word will be matched. | delimits words and acts as the logical OR. | |||
Proximity control _ Words must be in the order given and with no more than n (where n is 0 - 4) intervening words. All words under the proximity control must be in the same sentence. _ delimits words and also acts as logical 'AND'. Other words included in the match that are not under proximity control must be outside the words under the proximity control in the response for them to be matched.For example: 'match(abcd_ffff ccc)'does match the response 'abcd ffff ccc' but does not match the response 'abcd ccc ffff' | |||
Word groups [ ] [ ] enables multiple words to be accepted as an alternative to other single words in OR lists. [ ] may not be nested. Single words may be OR'd inside [ ]. Where a word group is preceded or followed by the proximity control the word group is governed by the proximity control rule that the words must be in the order given. | |||
Single character wildcard ? Matches any single character. | |||
Multiple character wildcard * Matches any sequence of characters including none. | |||
It is possible to match some of the special characters by ‘escaping’ them with the ‘\’ character. So match(\|) will match ‘|’. Ditto for _, [, ], and *. And if you wish to match round brackets then match(\(\)) will match exactly ‘()’ | |||
==Combinations== | |||
match_all() All matches contained within the brackets must be true. match_all( | |||
match_mow(first) | |||
match_mow(second) | |||
) | |||
match_any() Just one of the matches contained within the brackets must be true. match_any( | |||
match_mow(first) | |||
match_mow(second) | |||
) | |||
not() The match within the brackets must be false. not ( | |||
match_any( | |||
match_mow(first) | |||
match_mow(second) | |||
) | |||
) | |||
match_all(), match_any()and not() may all be nested. | |||
==Examples== | |||
Student response Matching options Pattern match match method return | |||
tom dick harry empty tom dick harry True. This is the exact match. | |||
thomas c tom True. Extra characters are allowed anywhere within the word. | |||
tom, dick and harry w dick True. Extra words are allowed anywhere within the sentence. | |||
harry dick tom o tom dick harry True. Any order of words is allowed. | |||
rick m dick True. One character in the word can differ. | |||
rick and harry and tom mow tom dick harry True. | |||
dick and harry and thomas cow tom dick harry True. | |||
arthur, harry and sid mow tom|dick|harry True. Any of tom or dick or harry will be matched. | |||
tom, harry and sid mow tom|dick harry|sid True. The pattern requires either tom or dick AND harry or sid. Note that 'tom,' is only allowed because m allows the extra character, the comma, in 'tom,'. | |||
tom was mesmerised by maud mow [tom maud]|[sid jane] True. The pattern requires either (tom and maud) or (sid and jane). | |||
rick empty ?ick True. The first character can be anything. | |||
harold empty har* True. Any sequence of characters can follow 'har'. | |||
tom married maud, sid married jane. mow tom_maud True. Only one word is between tom and maud. | |||
maud married tom, sid married jane. mow tom_maud False. The proximity control also specifies word order and over-rides the allowAnyWordOrder matching option. | |||
tom married maud, sid married jane. mow tom_jane False. Only two words are allowed between tom and jane. | |||
tom married maud mow tom|thomas marr* maud True. | |||
maud marries thomas mow tom|thomas marr* maud True. | |||
tom is to marry maud mow tom|thomas marr* maud True. | |||
tempratur m2ow temperature True. Two characters are missing. | |||
temporatur m2ow temperature True. Two characters are incorrect; one has been replaced and one is missing. | |||
==Advice on creating matching rules== | |||
How can you possibly guess the multiplicity of phrases that your varied student cohort will use to answer a question? Of course you can’t, but you can record everything and over time you will build a bank of student responses on which you can base your response matching. And gradually you might be surprised at how well your response matching copes. | |||
Before we describe the response matching it’s worth stressing: | |||
# The starting point is asking a question that you believe you will be able to mark accurately. | |||
# How you phrase the question can have a significant impact. | |||
# Pattern match works best when you are asking for a single explanation that you will mark as simply right or wrong. You will find that dealing with multiple parts in a question or apportioning partial marks is a much harder task that will quickly turn into a research project. | |||
# A bank of marked responses from real students is an essential starting point for developing matching patterns. Consider using the question in a human marked essay to get your first bank of student responses. Alternatively first use the question in a deferred feedback test where marks are allocated once all responses are received. | |||
# This question type possibly more than all others demands that you monitor student responses and amend your response matching as required. There will come a point at which you believe that the response matching is ‘good enough’ and might wonder ‘how many responses might I need to check?’ Unfortunately there is no easy answer to this question. Sometimes 200 responses will be sufficient. At other times you may have to go much further than this. If you do bear in mind that | |||
## Asking students to construct their response, as opposed to choosing it from a list, asks more of the student i.e. it is worth your while to do this. | |||
## Human markers following a mark scheme are fallible too. Ditto. | |||
# Stemming is the accepted method of catering for different word endings e.g. mov* will cater for ‘moved’ and ‘moves’ and ‘moving’ etc. | |||
# Students do not type responses that are deliberately wrong. Why should they? This is in contrast to academics who try to defeat the system. Consequently you will not find students entering the right response but preceding it with ‘it is not..’ And consequently you do not have to match deliberate errors. | |||
# The proximity control enables you to link one word to another. | |||
# It is often the case that marking obvious wrong responses early in your matching scheme will improve your overall accuracy. | |||
# Dealing with responses that contain both right and wrong answers requires you to take a view. You will either mark all such responses right or wrong. The computer will carry out your instructions consistently c.f. asking a group of human markers to apply your mark scheme consistently. | |||
# You should aim for an accuracy of >95% (in our trials our human markers were in the range 92%-96%). But, of course, aim as high as is reasonable given the usual diminishing returns on continuing efforts. | |||
==History== | |||
The underlying structure of the response matching described here was developed in the Computer Based Learning Unit of Leeds University in the 1970s and was incorporated into Leeds Author Language. The basic unit of the word, the matching options of allowAnyChars, allowAnyWords, allowAnyOrder and the word OR feature all date back to Leeds Author Language. | |||
In 1976 the CALCHEM project which was hosted by the Computer Based Learning Unit, the Chemistry Department at Leeds University and the Computer Centre of Sheffield Polytechnic (now Sheffield Hallam University) produced a portable version of Leeds Author Language. | |||
A portable version for microcomputers was developed in 1982 by the Open University, the Midland Bank (as it then was; now Midland is part of HSBC) and Imperial College. The single and multiple character wildcards were added at this time. | |||
The misspelling, proximity and Word groups in 'or' lists additions were added as part of the Open University COLMSCT projects looking at free text response matching during 2006 - 2009. | |||
==References== | |||
Philip G. Butcher and Sally E. Jordan, A comparison of human and computer marking of short free-text student responses, Computers & Education 55 (2010) 489-499 | |||
This info was copied from [http://www.open.edu/openlearnworks/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=52747§ion=2.2.1 http://www.open.edu/openlearnworks/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=52747§ion=2.2.1] on september 17th 2014. | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Revision as of 23:50, 17 September 2014
Pattern-match questions allow the student to give an answer of up to about 20 words, which can then be automatically graded by matching the students response against a number of different patterns expressed in the PMatch syntax. The first matching pattern determines the score and the feedback.
This is a question type created and maintained by the Open University.
More documentation
More documentation is available in the Open University's reference manual. That includes a description of the pmatch syntax. There is another page that explains The OU PMatch algorithm, but that was written before development started, and may not be a 100% accurate description of what was finally implemented.
Overview
The Pattern match question type is used to test if a short free-text student response matches a specified response pattern.
Pattern match is a more sophisticated alternative to the Short answer question type and offers:
- the ability to cater for misspellings, with and without an English dictionary
- specification of synonyms and alternative phrases
- flexible word order
- checks on the proximity of words.
For certain types of response it has been shown to provide an accuracy of marking that is on a par with, or better than, that provided by a cohort of human markers.
Pattern match works on the basis that you have a student response which you wish to match against any number of response matching patterns. Each pattern is compared in turn until a match is found and feedback and marks are assigned.
The key to using Pattern match is in asking questions that you have a reasonable hope of marking accurately. Hence writing the question stem is the most important part of writing these questions.
Components of the question
Question name: A descriptive name is sensible. This name will not be shown to students.
Question text: You may use the full functionality of the editor to state the question.
Placing the response box
The response box may be placed within the question rubric by including a sequence of underscores e.g. _____. At runtime the response box will replace the underscores. The minimum number of underscores required to trigger this action is 5. The size of the input box may also be specified by __XxY__ e.g. __20x1__ will produce a box 20 columns wide and 1 row high. If no underscores are present the response box will be placed after the question.
Default mark: Decide on how to score your questions and be consistent.
General feedback: We recommend that all questions should have this box completed with the correct answer and a fully worked explanation. The contents of this box will be shown to all students irrespective of whether their response was correct or incorrect. For the Pattern match question type you cannot rely on using the machine generated 'Right answer' (from the iCMA definition form).
Case sensitivity: No or yes.
Allow use of subscript/superscript: No or Yes. Any subscripts entered by the student are contained in their response between the standard tags of and or and . For example:
- The formula for water is H2O
- The speed of light is approximately 3x108 m s-1
At run time keyboard users may move between normal, subscript and superscript by using the up-arrow and down-arrow keys. You may wish to include this information within your question. If you do please note that the up-arrow and down-arrow provided in the HTML editor’s ‘insert custom characters’ list are not spoken by a screen reader and you should also include the words ‘up-arrow’ and ‘down-arrow’.
If answer is more than 20 words: We strongly recommend that you limit responses to 20 words. Allowing unconstrained responses often results in responses that are both right and wrong – which are difficult to mark consistently one way or the other.
Check spelling of student: How many ways do you know of to spell ‘temperature’? We’ve seen 14! You will improve the marking accuracy by insisting on words that are in Moodle system dictionary.
Add these words to dictionary: When dealing with specialised scientific, technical and medical terms that are not in a standard dictionary it is most likely that you will have to add them by using this field. Enter your words leaving a space between them.
Convert the following characters to space: In Pattern match words are defined as sequences of characters between spaces. The exclamation mark and question mark are also taken to mark the end of a word. The period is a special case; as a full stop it is also a word delimiter but as the decimal point it is not. All other punctuation is considered to be part of the response but this option lets you remove it.
Words and synonyms: All words and synonyms are specified as they are to be applied by the response matching. They do not have to be full words but can be stems with a wildcard.
Synonyms may only be single words i.e. the ability to specify alternate phrases in synonym lists is not allowed.
From the example above any occurrence of the word oil in the response match will be replaced by oil|glycer*|paraf* before the match is carried out.
Answer: This example shows that Pattern match will support complex response matching.
Take the first answer field match_o(ampere candela kelvin mole) is the exact match for the four words with the additional feature that the matching option 'o' allows the words to be given in any order.
The answer field match_ow(ampere candela kelvin mole) requires the same four words, again in any order, but also allows other words.
The third answer field match_mow(ampere candela kelvin mole) allows for misspellings which are still in the dictionary e.g. mule instead of mole.
Please see the section on Pattern match syntax for a full description.
Grade: Between ‘none’ and 100%. At least one response must have a mark of 100%.
Feedback: Specific feedback that is provided to anyone whose response is matched by the response matching rule in Answer.
The feedback for all non-matched responses should go into the ‘Any other answer’ field.
How the response is handled
The basic unit of the student response that Pattern match operates on is the word, where a word is defined as a sequence of characters between spaces. The full stop (but not the decimal point), exclamation mark and question mark are also treated as ending a word.
Numbers are special instances of words and are matched by value and not by the form in which they are given. match_w(25 ms-1) will match the following correct responses; 25 ms-1, 2.5e1 ms-1, 2.5x10-1 ms-1
With the exception of numbers and the word terminators (<space><full stop>? and !) Pattern match matches what it is given. Whether case does or does not matter is left to the author to decide as is the significance of punctuation such as ,;: and others.
The response is treated as a whole with the exception that words that are required to be in proximity must also be in the same sentence.
Pattern match syntax
The match syntax can be considered in three parts.
- the matching options e.g. mow
- the words to be matched e.g.tom dick harry together with the in-word special characters.
- and, or and not combinations of matches e.g. match_any()
Matching options
Matching option Symbol Description allowExtraChars c Extra characters can be anywhere within the word. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using the misspelling options below. allowAnyWordOrder o Where multiple words are to be matched they can be in any order. allowExtraWords w Extra words beyond those being searched for are accepted. misspelling: allowReplaceChar mr Will match a word where one character is different to those specified in the pattern. The pattern word must be 4 characters or greater, excluding wildcards, for replacement to kick in. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using this option. misspelling: allowTransposeTwoChars mt Will match a word where two characters are transposed. The pattern word must be 4 characters or greater, excluding wildcards, for transposition to kick in. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using this option. misspelling: allowExtraChar mx Will match a word where one character is extra to those specified in the pattern. The pattern word must be 3 characters or greater, excluding wildcards, for extra to kick in. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using this option. misspelling: allowFewerChar mf Will match a word where one character is missing from those specified in the pattern. The pattern word must be 4 characters or greater, excluding wildcards, for fewer to kick in. Without this 'no' would be reduced to just matching 'n' or 'o'. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using this option. misspelling m This combines the four ways of misspelling a word described above i.e. m is equivalent to mxfrt. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using this option. misspellings m2 Allows two misspellings, as defined by option 'm', in pattern words of 8 characters or more, excluding wildcards. Authors are expected to omit allowExtraChars when using this option. N.b. use this option sparely. It introduces a huge number of possible acceptable spellings all of which have to be checked and the time taken for the match to complete goes up and up. allowProximityOf0 p0 No words, or full stops, are allowed in between any words specified in the proximity sequence. allowProximityOf1 p1 One word is allowed in between any two words specified in the proximity sequence. The words must not span sentences. allowProximityOf2 p2 (Default value) Two words are allowed in between any two words specified in the proximity sequence. The words must not span sentences. allowProximityOf3 p3 Three words are allowed in between any two words specified in the proximity sequence. The words must not span sentences. allowProximityOf4 p4 Four words are allowed in between any two words specified in the proximity sequence. The words must not span sentences.
The matching options are appended to the word match with an intervening underscore and may be combined. A typical match combines the options ‘mow’ to allow for
- misspellings
- any word order
- any extra words
and is written match_mow(words to be matched).
Special characters
Special character Symbol Description Word AND space 'space' delimits words and acts as the logical AND. Word OR | | between words indicates that either word will be matched. | delimits words and acts as the logical OR. Proximity control _ Words must be in the order given and with no more than n (where n is 0 - 4) intervening words. All words under the proximity control must be in the same sentence. _ delimits words and also acts as logical 'AND'. Other words included in the match that are not under proximity control must be outside the words under the proximity control in the response for them to be matched.For example: 'match(abcd_ffff ccc)'does match the response 'abcd ffff ccc' but does not match the response 'abcd ccc ffff' Word groups [ ] [ ] enables multiple words to be accepted as an alternative to other single words in OR lists. [ ] may not be nested. Single words may be OR'd inside [ ]. Where a word group is preceded or followed by the proximity control the word group is governed by the proximity control rule that the words must be in the order given. Single character wildcard ? Matches any single character. Multiple character wildcard * Matches any sequence of characters including none.
It is possible to match some of the special characters by ‘escaping’ them with the ‘\’ character. So match(\|) will match ‘|’. Ditto for _, [, ], and *. And if you wish to match round brackets then match(\(\)) will match exactly ‘()’
Combinations
match_all() All matches contained within the brackets must be true. match_all(
match_mow(first) match_mow(second)
) match_any() Just one of the matches contained within the brackets must be true. match_any(
match_mow(first) match_mow(second)
) not() The match within the brackets must be false. not (
match_any(
match_mow(first)
match_mow(second)
)
)
match_all(), match_any()and not() may all be nested.
Examples
Student response Matching options Pattern match match method return tom dick harry empty tom dick harry True. This is the exact match. thomas c tom True. Extra characters are allowed anywhere within the word. tom, dick and harry w dick True. Extra words are allowed anywhere within the sentence. harry dick tom o tom dick harry True. Any order of words is allowed. rick m dick True. One character in the word can differ. rick and harry and tom mow tom dick harry True. dick and harry and thomas cow tom dick harry True. arthur, harry and sid mow tom|dick|harry True. Any of tom or dick or harry will be matched. tom, harry and sid mow tom|dick harry|sid True. The pattern requires either tom or dick AND harry or sid. Note that 'tom,' is only allowed because m allows the extra character, the comma, in 'tom,'. tom was mesmerised by maud mow [tom maud]|[sid jane] True. The pattern requires either (tom and maud) or (sid and jane). rick empty ?ick True. The first character can be anything. harold empty har* True. Any sequence of characters can follow 'har'. tom married maud, sid married jane. mow tom_maud True. Only one word is between tom and maud. maud married tom, sid married jane. mow tom_maud False. The proximity control also specifies word order and over-rides the allowAnyWordOrder matching option. tom married maud, sid married jane. mow tom_jane False. Only two words are allowed between tom and jane. tom married maud mow tom|thomas marr* maud True. maud marries thomas mow tom|thomas marr* maud True. tom is to marry maud mow tom|thomas marr* maud True. tempratur m2ow temperature True. Two characters are missing. temporatur m2ow temperature True. Two characters are incorrect; one has been replaced and one is missing.
Advice on creating matching rules
How can you possibly guess the multiplicity of phrases that your varied student cohort will use to answer a question? Of course you can’t, but you can record everything and over time you will build a bank of student responses on which you can base your response matching. And gradually you might be surprised at how well your response matching copes.
Before we describe the response matching it’s worth stressing:
- The starting point is asking a question that you believe you will be able to mark accurately.
- How you phrase the question can have a significant impact.
- Pattern match works best when you are asking for a single explanation that you will mark as simply right or wrong. You will find that dealing with multiple parts in a question or apportioning partial marks is a much harder task that will quickly turn into a research project.
- A bank of marked responses from real students is an essential starting point for developing matching patterns. Consider using the question in a human marked essay to get your first bank of student responses. Alternatively first use the question in a deferred feedback test where marks are allocated once all responses are received.
- This question type possibly more than all others demands that you monitor student responses and amend your response matching as required. There will come a point at which you believe that the response matching is ‘good enough’ and might wonder ‘how many responses might I need to check?’ Unfortunately there is no easy answer to this question. Sometimes 200 responses will be sufficient. At other times you may have to go much further than this. If you do bear in mind that
- Asking students to construct their response, as opposed to choosing it from a list, asks more of the student i.e. it is worth your while to do this.
- Human markers following a mark scheme are fallible too. Ditto.
- Stemming is the accepted method of catering for different word endings e.g. mov* will cater for ‘moved’ and ‘moves’ and ‘moving’ etc.
- Students do not type responses that are deliberately wrong. Why should they? This is in contrast to academics who try to defeat the system. Consequently you will not find students entering the right response but preceding it with ‘it is not..’ And consequently you do not have to match deliberate errors.
- The proximity control enables you to link one word to another.
- It is often the case that marking obvious wrong responses early in your matching scheme will improve your overall accuracy.
- Dealing with responses that contain both right and wrong answers requires you to take a view. You will either mark all such responses right or wrong. The computer will carry out your instructions consistently c.f. asking a group of human markers to apply your mark scheme consistently.
- You should aim for an accuracy of >95% (in our trials our human markers were in the range 92%-96%). But, of course, aim as high as is reasonable given the usual diminishing returns on continuing efforts.
History
The underlying structure of the response matching described here was developed in the Computer Based Learning Unit of Leeds University in the 1970s and was incorporated into Leeds Author Language. The basic unit of the word, the matching options of allowAnyChars, allowAnyWords, allowAnyOrder and the word OR feature all date back to Leeds Author Language.
In 1976 the CALCHEM project which was hosted by the Computer Based Learning Unit, the Chemistry Department at Leeds University and the Computer Centre of Sheffield Polytechnic (now Sheffield Hallam University) produced a portable version of Leeds Author Language.
A portable version for microcomputers was developed in 1982 by the Open University, the Midland Bank (as it then was; now Midland is part of HSBC) and Imperial College. The single and multiple character wildcards were added at this time.
The misspelling, proximity and Word groups in 'or' lists additions were added as part of the Open University COLMSCT projects looking at free text response matching during 2006 - 2009.
References
Philip G. Butcher and Sally E. Jordan, A comparison of human and computer marking of short free-text student responses, Computers & Education 55 (2010) 489-499
This info was copied from http://www.open.edu/openlearnworks/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=52747§ion=2.2.1 on september 17th 2014.