Cron
This page really needs improving. Please see the page comments for suggestions of what to include, then remove this template when you're done.
Cron is the name of a Unix program that runs predefined tasks on a computer at regular intervals. It assists some of Moodle's modules to perform tasks on a scheduled basis. For example, the cron process might tell Moodle to check all discussion forums so it can mail out copies of new posts to people who have subscribed to that forum.
The primary Moodle script that does all this is located in the admin directory, and is called cron.php. However, it can not tell itself to run, so you need to set up a mechanism where this script is run regularly (eg every five or ten minutes). This provides a "heartbeat" so that the script can perform functions at periods defined by each module. This kind of regular mechanism is known as a cron service. The service can be part of a webhost or can be something run from a different server or computer.
Overview of cron
Script overview
The cron.php script basically finds and determines if certain functions need to run. These functions are defined in code associated with specific activities and processes. Usually the function looks for new activity that has occurred since cron was last run. Some of the functions may use a timestamp to determine if they should look for new activity. A few functions are run on a random basis.
Moodle's cron processes include:
- updating reports such as quiz, admin, gradebook
- updating course and activity completion (if enabled in advanced settings)
- updating portfolio
- plagiarism checks
- updates activity modules. It looks through the mod directory for lib.php files that contain the function activity-name_cron and will call it. In a standard install this includes assignment, chat, forum, and SCROM.
- updates blocks. It looks for blocks for their cron methods (object functions) to be run. It then, for each such block, runs the cron method for a new object associated with that block (for more details read admin/cron.php). These files (the lib.php files and the files where the block classes are defined) can contain cleanup functions, email functions or anything that needs to be run on a regular basis.
- create the backups of courses at the time specified in the administration settings.
- updating messaging module or forum email notifications.
- unenroll students - this is done on a random basis about 20% of the time Moodle's cron process is triggered.
- deleting users who have not filled out their profile via the 20% random trigger
- deleting old logs are also checked 20% of the time via the 20% random trigger
- deletes old cached text
- generates new passwords for new users and notifies users
- runs authentication enrolments processes
- updates stats if enabled.
- runs blog cleanups
- updates registrations
The code in lib/cronlib.php shows the places that are being checked when the admin/cron.php is run and the report which is displayed on the screen after it has run.
Starting cron
There are a number of way to invoke cron.php. Cron can be started from the address bar in a browser (URL usually ending in admin/cron.php), via a Daemon, or wq1et, curl or some other code.
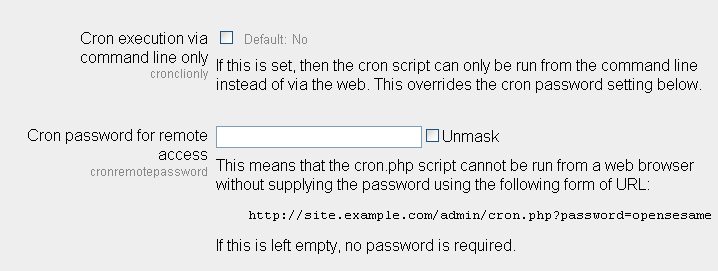
Site administeration >Security > Site Policies See the image below.
The cronclionly setting will stop the browser URL trigger. This sets Moodle so that cron.php cannot be invoked by the Moodle URL.
The cron process can be protected by a password with the cronremotepassword setting.
- TIP: While this is identified as CLI (command line interface) this is a bit misleading in that it does not mean that you have to be sitting at a shell account entering the command. If you enable this switch you can invoke cron.php through any set of batch or script files you wish, but it must be invoked via its correct location in the operating systems file structure. This can be especially frustrating for those not used to scripting in that environment is not typically provided.
Cron service location and timing
Note that the machine performing the cron does not need to be the same machine that is running Moodle. For example, if you have a limited web hosting service that does not have a cron service, then you might choose to run cron on another server or on your home computer. All that matters is that the cron.php file is called regularly.
The load of this script is not very high, so 5 minutes is usually reasonable, but if you're worried about it you can reduce the time period to something like 15 minutes or even 30 minutes. It's best not to make the time period too long, as delaying mail-outs can slow down activity within the course. Remember that mail-outs also wait for the editing time to expire before being queued for sending.
Testing cron and manual trigger
First, test that the script works by running it directly from your browser: http://example.com/moodle/admin/cron.php
If cron is called from the command line by any user logged in to your Moodle it will create a temporary admin environment in order to run and then log the user out. You can disable command line running of cron by disabling the appropriate section in the cron.php file.
Now, you need to set up some of way of running the script automatically and regularly.
Managing Cron on Windows systems
There are two different ways for setting-up Moodle cron.php on Windows systems:
- Use the Moodle Cron package. The simplest way is to use this little package MoodleCron-Setup.exe, which makes this whole thing very easy by installing a small Windows service. Run it and forget about it! :-)
- Use a Scheduled Task. If you prefer to use the built-in Windows Scheduler or are having trouble with moodle-cron-for-windows package, you can use wget for windows or php from the command line and setup a scheduled task. Just follow these steps:
- Choose either the php.exe/php-win.exe (command line binary) or wget
- The php.exe or php-win.exe binary (for PHP version 5 or later) is installed in your php folder (e.g. c:\php) will give you better performance when running the cron script.
- If you want to use wget, download a compiled version of wget for windows from the native GNU Win32 ports (http://unxutils.sourceforge.net/), from Heiko Herold's wget for windows page (http://xoomer.virgilio.it/hherold/) or Bart Puype's wget for windows page (http://users.ugent.be/~bpuype/wget/). If you use Heiko Herold's package, copy all of the .DLL files to your C:\Windows\system32 directory. Copy the wget.exe file to c:\windows (this makes sure wget is always in the search path).
- Setup a Scheduled Task.
- - Go to Start >> Control Panel >> Scheduled Tasks >> Add Scheduled Task.
- - Click "Next" to start the wizard:
- - Click in the "Browse..." button and browse to c:\php\php.exe or c:\windows\wget.exe and click "Open"
- - Type "Moodle Cron" as the name of the task and select "Daily" as the schedule. Click "Next".
- - Select "12:00 AM" as the start time, perform the task "Every Day" and choose today's date as the starting date. Click "Next".
- - Enter the username and password of the user the task will run under (it doesn't have to be a priviledged account at all). Make sure you type the password correctly. Click "Next".
- - Mark the checkbox titled "Open advanced properties for this task when I click Finish" and click "Finish".
- - In the new dialog box, type the following in the "Run:" text box:
c:\windows\wget.exe -q -O NUL http://my.moodle.site/moodle/admin/cron.php
orc:\php\php-win.exe -f c:\moodle\admin\cron.php
Replace "c:\moodle" with the path to your moodle directory or "my.moode.site" with the name of your site. - - Click on the "Schedule" tab and there in the "Advanced..." button.
- - Mark the "Repeat task" checkbox and set "Every:" to 5 minutes, and set "Until:" to "Duration" and type "23" hours and "59" minutes.
- - Click "OK" and you are done.
- Test your scheduled task. You can test that your scheduled task can run successfully by clicking it with the right button and chosing "Run". If everything is correctly setup, you will briefly see a DOS command window while wget/php executes and fetches the cron page and then it disappears. If you refresh the scheduled tasks folder, you will see the Last Run Time column (in detailed folder view) reflects the current time, and that the Last Result column displays "0x0" (everything went OK). If either of these is different, then you should recheck your setup.
- Logging cron output. You may want to log the output of the cron script as it executes, in case you see the job is producing errors, backups are not being completed or users are experiencing delays in receiving forum emails. To do this, adjust the command so that it uses the php.exe and stores the output in a file called (for example c:\moodle\admin\cron.log). Here is an example of the php.exe command:
c:\php\php.exe -f c:\moodle\admin\cron.php > c:\moodle\admin\cron.log
If you experience problems logging the output of cron.php to a text file using the above command then read this message by Iñaki Arenaza for an alternative way to log the output of Cron.
Note: In version 2.0 and later the path for running cron.php from the commandline has changed. Use c:\moodle\admin\cli\cron.php
Managing the cron job on Mac OS X with launchd
It's really important to start the cron job every 5 minutes. The cron job assists most of Moodle's modules to perform tasks on a scheduled basis. For example, the discussion forums can only mail out copies of new posts to all subscribers if the cron job tells Moodle to do this.
In Mac OS X 10.5 you will find the system daemon launchd for this service. This daemon offers a standardized interface to any user and all programs started automatically by the system. Please look at http://developer.apple.com/macosx/launchd.html for more informations about the configurations and all parameters.
In our case the service should get the web page http://your-server-address/moodle19/admin/cron.php every 5 minutes. The configuration will be done by the file named moodle4mac.cron.plist which must be placed in the system folder /Library/LaunchDaemons/ ... surely you can use any other file name but it should say something about the function of the service. The extension must be .plist. After any reboot of your Mac server the cron service will start automaticly because the file is placed in the correct system folder.
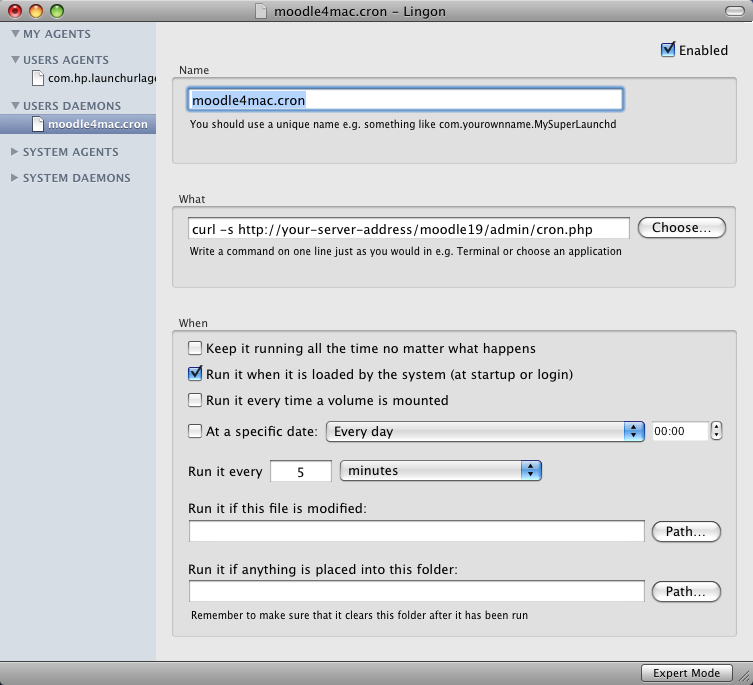
Use the graphical way
You can use Lingon to add a new daemon plist or to edit one. It produces the same text as you can write in your text editor. http://sourceforge.net/projects/lingon/files/
Use a text editor
Please use a text editor to write the needed file. You can open the Terminal and use the system editors vi or pico. But you can also write the text file with any GUI text editor ... I mostly use TextWrangler ... but do NOT take an editor for formatted texts like Microsoft Word or OpenOffice Writer. You must get pure text!
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple Computer//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN"
"http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>KeepAlive</key><false/>
<key>Label</key><string>moodle4mac.cron</string>
<key>ProgramArguments</key>
<array>
<string>curl</string>
<string>-s</string>
<string>http://your-server-address/moodle19/admin/cron.php</string>
</array>
<key>RunAtLoad</key><true />
<key>StartInterval</key><integer>300</integer>
<key>StandardErrorPath</key><string>/dev/null</string>
<key>StandardOutPath</key><string>/dev/null</string>
</dict>
</plist>
The label string must be the same as the file name is but without the extension .plist. Save the text file /Library/LaunchDaemons/moodle4mac.cron.plist. The owner of the file must be set to the system user root. If you use a site with SSL (ie: it has an https:// protocol) you either need to have your SSL certificates listed for use by the CURL utility (see these docs for more details) OR you must use the '-k' switch in addition to the '-s' switch used above; your arguments line would then read: `<string>-s -k</string>`.
That's all, really!
How to start and stop the cron service
You can start the new cron service in the Terminal.
sudo launchctl load /Library/LaunchDaemons/moodle4mac.cron.plist
The following command would stop the service. If you want to activate changes in the cron service you need to unload and then to load the daemon again.
sudo launchctl unload /Library/LaunchDaemons/moodle4mac.cron.plist
Only one service for two servers?
For my server I needed to have a cron service for to instances moodle19 and moodle20 ... no problem ... with the typo moodle[19-20] I will get a cron service for both.
curl -s http://your-server-address/moodle[19-20]/admin/cron.php
To see if the cron service works correctly you should look at the access.log of your web server. The cron.php should be accessed every 5 minutes ... on my server for both Moodle instances moodle19 and moodle20 ... oh yes, it works!!
192.168.0.220 - - [30/Jul/2009:22:10:56 +0200] "GET /moodle19/admin/cron.php HTTP/1.1" 200 1136 192.168.0.220 - - [30/Jul/2009:22:10:57 +0200] "GET /moodle20/admin/cron.php HTTP/1.1" 200 1403 192.168.0.220 - - [30/Jul/2009:22:11:18 +0200] "OPTIONS * HTTP/1.0" 200 - 192.168.0.220 - - [30/Jul/2009:22:15:56 +0200] "GET /moodle19/admin/cron.php HTTP/1.1" 200 735 192.168.0.220 - - [30/Jul/2009:22:15:57 +0200] "GET /moodle20/admin/cron.php HTTP/1.1" 200 964 192.168.0.220 - - [30/Jul/2009:22:20:56 +0200] "GET /moodle19/admin/cron.php HTTP/1.1" 200 1136 192.168.0.220 - - [30/Jul/2009:22:20:57 +0200] "GET /moodle20/admin/cron.php HTTP/1.1" 200 1365
Managing cron on web hosting services
Your web-based control panel may have a web page that allows you to set up a cron service process.
CPanel cron service
If you are using CPanel, login then look for "Advanced" category towards the bottom of the page. Click on Cron Jobs -> Advanced (Unix style). Enter the following for the cron to run every 30 minutes.
Email address for output: emailaddress@mydomain.con Minute:*/30 Hour:* Day:* Month:* Weekday:* Command: wget -q -O /dev/null http://www.mydomain.com/moodle/admin/cron.php
Click Commit Changes. Check your email for the output.
Other systems cron service
For other systems, look for a button called "Cron jobs". In there you can put the same sort of Unix commands as listed below.
If you don't have permissions to run the 'wget' command on the server, you can use this php command:
/usr/local/bin/php -q /real/path/to/script/admin/cron.php
For example:
/usr/local/bin/php -q /home/username/public_html/moodle/admin/cron.php
If you don't know what is the real path of your Moodle folder you can use the PHP command realpath.
Another alternative, if you do not have permission to run the 'wget' command, may be to use a curl command.
For example:
curl --silent --compressed http://mydomain.com/moodle/admin/cron.php
Note: In version 2.0 and later the path for running cron.php from the commandline has changed. Use c:\moodle\admin\cli\cron.php
Using a cron command line in Unix
There are different command line programs you can use to call the page from the command line. Not all of them may be available on a given server.
Note: The examples with wget, lynx, and similar are not the same as the "CLI only" cron checkbox, mentioned above (the configuration variable "cronclionly"). wget, lynx, and other similar utilities are Unix command-line HTTP clients, and thus running cron.php in this way is the same as running it in a browser, from Moodle's point of view.
For example, you can use a Unix utility like 'wget':
wget -q -O /dev/null http://example.com/moodle/admin/cron.php
Note in this example that the output is thrown away (to /dev/null).
A number of users of Moodle have found that 'wget' sometimes fails. Especially if you have trouble with email digests not being sent on a daily basis to all users, an alternative command that solves the problem is:
php http://example.com/moodle/admin/cron.php
The same thing using lynx:
lynx -dump http://example.com/moodle/admin/cron.php > /dev/null
Note in this example that the output is thrown away (to /dev/null).
Alternatively, you can use a standalone version of PHP, compiled to be run on the command line. The disadvantage is that you need to have access to a command-line version of php. The advantage is that your web server logs aren't filled with constant requests to cron.php and you can run at a lower I/O and CPU priority.
/opt/bin/php /web/moodle/admin/cli/cron.php
Example command to run at lower priority:
ionice -c3 -p$$;nice -n 10 /usr/bin/php /moodle/admin/cli/cron.php > /dev/null
Note: In version 2.0 and later the path for running cron.php from the commandline has changed. Use c:\moodle\admin\cli\cron.php
Using the crontab program on Unix
All that Cpanel does is provide a web interface to a Unix utility known as crontab. If you have a command line, you can set up crontab yourself using the command:
crontab -e
and then adding one of the above commands like:
*/30 * * * * wget -q -O /dev/null http://example.com/moodle/admin/cron.php
The first five entries are the times to run values, followed by the command to run. The asterisk is a wildcard, indicating any time. The above example means run the command wget -q -O /dev/null... every 30 minutes (*/30), every hour (*), every day of the month (*), every month (*), every day of the week (*).
The "O" of "-O" is the capital letter not zero, and refers the output file destination, in this case "/dev/null" which is a black hole and discards the output. If you want to see the output of your cron.php then enter its url in your browser.
For beginners, "EDITOR=nano crontab -e" will allow you to edit the crontab using the nano editor. Ubuntu defaults to using the nano editor.
Usually, the "crontab -e" command will put you into the 'vi' editor. You enter "insert mode" by pressing "i", then type in the line as above, then exit insert mode by pressing ESC. You save and exit by typing ":wq", or quit without saving using ":q!" (without the quotes). Here is an intro to the 'vi' editor.
See also
Using Moodle forum discussions:
- Cron - can someone give me a quick confirmation of function?
- Cronjob Question
- Slow cron : avoiding simultaneous cron
- Visibility of cron.php
- How to log the output of a Scheduled Task on Windows - this discussion explains a nice trick that can be very useful when you are experiencing problems with your Windows Scheduled Task and you need to log the output of the Scheduled Task to a log file.