Dataform building: Difference between revisions
- Overview
- Activity administration
- Building an activity
- CSS tips and tricks
- JS tips and tricks
- Activating RSS
- Activity workflow
- Grading
(Created page with "{{Dataform}} {{Dataform Docs Note 1}} ==Views== Dataform views allow you to control the way entries and other information is displayed in the activity. Views management is don...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Fields== | ==Fields== | ||
Dataform fields are used to enter, edit and store unit of information in an entry. | Dataform fields are used to enter, edit and store unit of information in an entry. | ||
[[File:df-fields-index.png|700px]] | |||
==Filters== | ==Filters== | ||
Dataform filters are used for sorting and filtering the activity entries in browse mode. | Dataform filters are used for sorting and filtering the activity entries in browse mode. | ||
[[File:df-filters-index.png|700px]] | |||
==Access rules== | ==Access rules== | ||
Dataform access rules can be used for controlling access to various areas/components of a Dataform activity. | Dataform access rules can be used for controlling access to various areas/components of a Dataform activity. | ||
[[File:df-access-rules-index.png|700px]] | |||
==Notification rules== | ==Notification rules== | ||
Dataform notification rules can used for defining and sending custom notifications to the activity participants. | Dataform notification rules can used for defining and sending custom notifications to the activity participants. | ||
[[File:df-notifiction-rules-index.png|700px]] | |||
==CSS== | ==CSS== | ||
You can use CSS to manipulate the layout and styles of entries and content in any of the Dataform views. Any html element in the designated view, that has an id or a CSS class can be assigned specialized styles by including the style definitions in the CSS tab. | You can use CSS to manipulate the layout and styles of entries and content in any of the Dataform views. Any html element in the designated view, that has an id or a CSS class can be assigned specialized styles by including the style definitions in the CSS tab. | ||
[[File:df-css-tab.png|700px]] | |||
The Dataform allows you to add CSS in the CSS tab in three ways: | The Dataform allows you to add CSS in the CSS tab in three ways: | ||
| Line 46: | Line 61: | ||
* '''Upload CSS files''' - You can upload CSS files into the Dataform files area in Moodle's file system. These files become part of the Dataform instance to which they are uploaded and are included in Dataform presets and backups. | * '''Upload CSS files''' - You can upload CSS files into the Dataform files area in Moodle's file system. These files become part of the Dataform instance to which they are uploaded and are included in Dataform presets and backups. | ||
==Javascript== | ==Javascript== | ||
You can use javascript to manipulate the way entries are displayed and behave in any of the Dataform views. Any html element in the designated view, that has an id or a css class can be accessed and manipulated by javascript. | You can use javascript to manipulate the way entries are displayed and behave in any of the Dataform views. Any html element in the designated view, that has an id or a css class can be accessed and manipulated by javascript. | ||
[[File:df-js-tab.png|700px]] | |||
The Dataform allows you to add javascript in three ways: | The Dataform allows you to add javascript in three ways: | ||
| Line 55: | Line 71: | ||
* '''Upload javascript files''' - You can upload javascript files into the Dataform files area in Moodle's file system. These files become part of the Dataform instance to which they are uploaded and are included in Dataform presets and backups. | * '''Upload javascript files''' - You can upload javascript files into the Dataform files area in Moodle's file system. These files become part of the Dataform instance to which they are uploaded and are included in Dataform presets and backups. | ||
==Tools== | ==Tools== | ||
TBC | TBC | ||
[[File:df-tools-index.png|700px]] | |||
==Setting permissions== | ==Setting permissions== | ||
TBC | TBC | ||
Revision as of 17:10, 26 February 2014
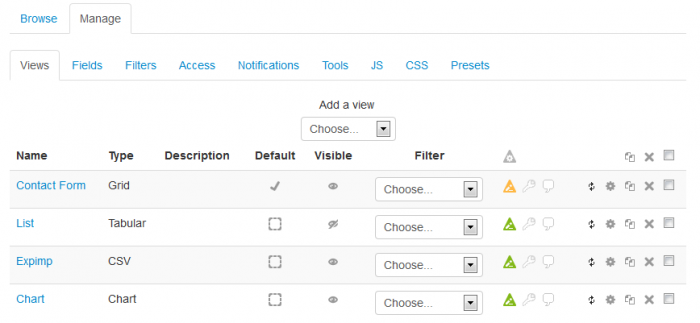
Views
Dataform views allow you to control the way entries and other information is displayed in the activity. Views management is done under the Manage | Views tab and requires Manage Dataform templates capability.
Adding a view
To add a view select the view type from the 'Add a view' dropdown. This will open the view configuration form where you can configure the view templates and behaviour. Typically, views have default configuration and if this default configuration serves your purpose you can simply enter a name for the view and save.
Setting the default view
The Dataform activity must have a default view to fall back on to when the activity is accessed without specifying the target view (for instance, when you access the activity from the activity link on the course page).
A Dataform activity without a default view is not ready and a message will be displayed on its front page and in the view list advising you to set a default view.
You can select the default view by clicking the 'Default' box in the view list. The selected default view is marked by a check sign. You can change the default view at any time. Since the default view must be visible, if you set a hidden view to default, this view will automatically become visible and you will not be able to hide it as long as it is the default view.
Setting view visibility
A view can be either visible or hidden. Visible views can be accessed by users with capability mod/dataform:viewaccess that is granted by default to all roles. Hidden views can be accessed by users with capability mod/dataform:viewaccesshidden that is granted by default only to the teacher role. Users without the required capability will not see views with the respective visibility setting in the standard views navigation menu (##viewsmenu##). Setting the view visibility can be done from the views index by clicking the eye icon of the designated view or from the visibility setting in the view configuration form. The default view must be visible and setting a hidden view as the default view will automatically change its visibility to visible.
Forcing a view filter
When filters are defined for the activity you can force a filter on a view by selecting the filter either from the index list or in the view configuration form. When the view forces a filter, users without capability mod/dataform:viewfilteroverride cannot apply other activity filters (the activity filters menu will not be displayed) and user advanced filters (if the option is added to the view) will be appended to the forced filter.
Resetting a view
Each view type has default templates which are generated and automatically added to the configuration form when adding a new view. The default View template typically consists of navigation menus, quick filters, add new entry link and entries display. The default Entry template (where applicable) typically adds the base pattern for each field and the edit and delete action buttons. As you build the activity you may change the templates of a view and in some cases you may wish to reset the templates to their defaults. This can be done by clicking the reset icon of the designated view in the views index or in the view configuration form.
Updating a view
Duplicating one or more views
Deleting one or more views
Access and Notifications info
Patterns validation and replacement
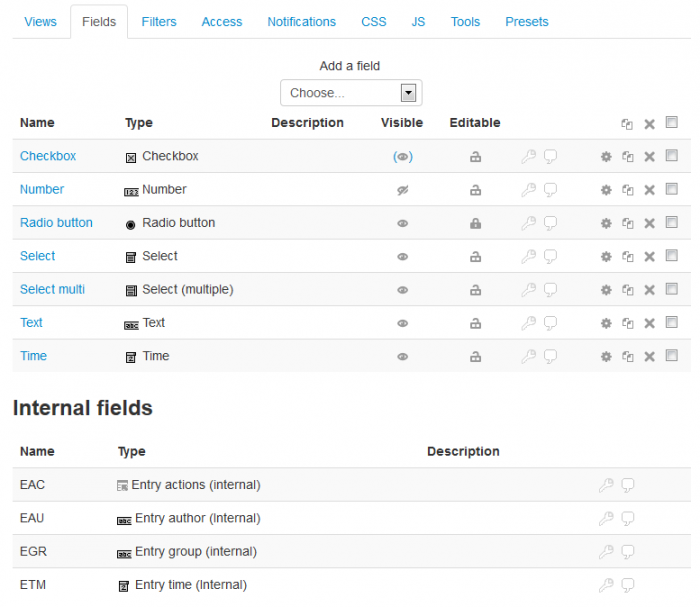
Fields
Dataform fields are used to enter, edit and store unit of information in an entry.
Filters
Dataform filters are used for sorting and filtering the activity entries in browse mode.
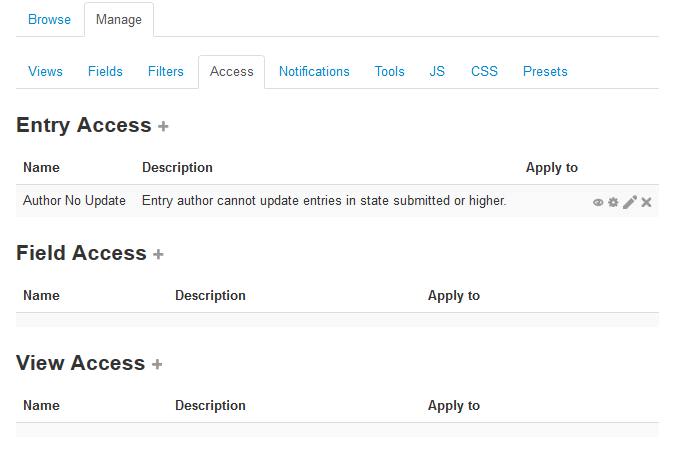
Access rules
Dataform access rules can be used for controlling access to various areas/components of a Dataform activity.
Notification rules
Dataform notification rules can used for defining and sending custom notifications to the activity participants.
File:df-notifiction-rules-index.png
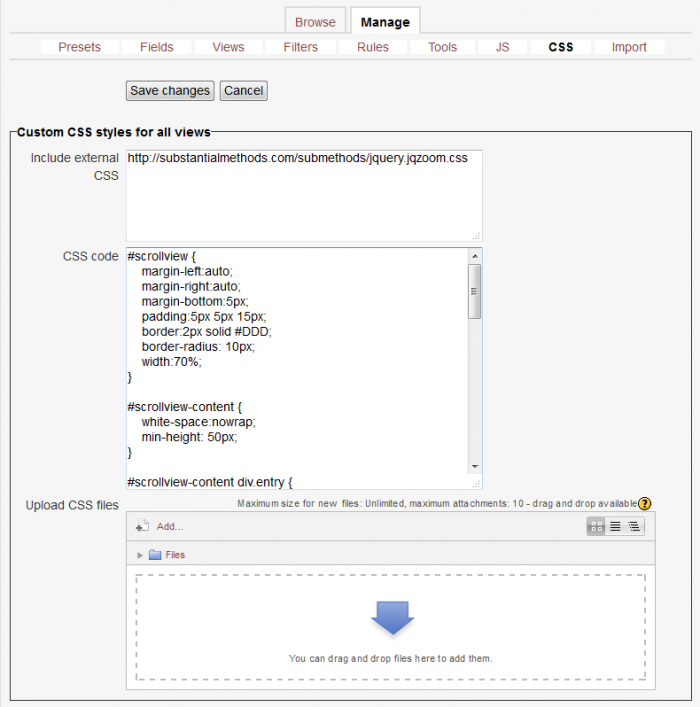
CSS
You can use CSS to manipulate the layout and styles of entries and content in any of the Dataform views. Any html element in the designated view, that has an id or a CSS class can be assigned specialized styles by including the style definitions in the CSS tab.
The Dataform allows you to add CSS in the CSS tab in three ways:
- Include external CSS - You can specify a list of urls to external CSS files and these files will be loaded to the Dataform view page.
- CSS code - You can enter CSS definitions directly.
- Upload CSS files - You can upload CSS files into the Dataform files area in Moodle's file system. These files become part of the Dataform instance to which they are uploaded and are included in Dataform presets and backups.
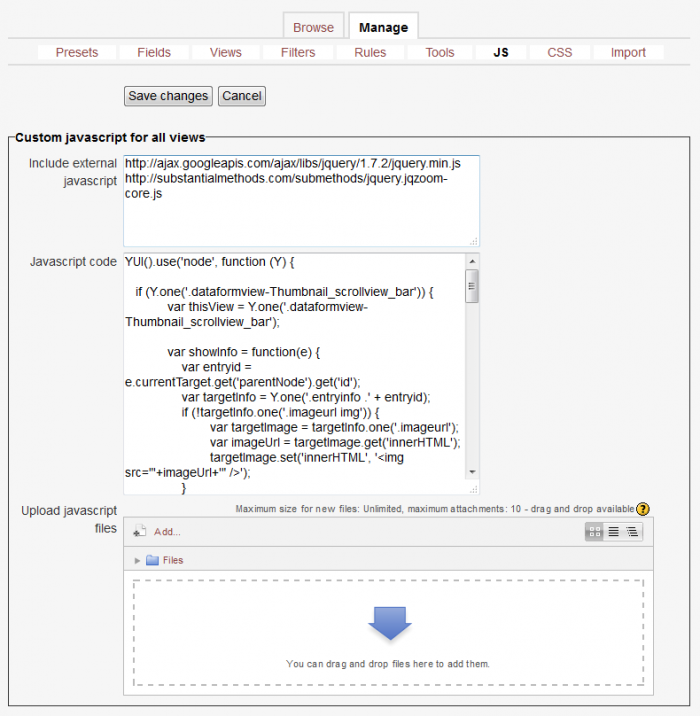
Javascript
You can use javascript to manipulate the way entries are displayed and behave in any of the Dataform views. Any html element in the designated view, that has an id or a css class can be accessed and manipulated by javascript.
The Dataform allows you to add javascript in three ways:
- Include external javascript - You can specify a list of urls to external javascript files and these files will be loaded to the Dataform view page.
- Javascript code - You can enter javascript code directly. This is usually required in addition to including javascript files so as to apply the desired effects to particular views or particular items in views.
- Upload javascript files - You can upload javascript files into the Dataform files area in Moodle's file system. These files become part of the Dataform instance to which they are uploaded and are included in Dataform presets and backups.
Tools
TBC
Setting permissions
TBC