Scheduled tasks: Difference between revisions
(→Managing scheduled tasks: Changed \ to / in paths, URL to HTTPS) |
Helen Foster (talk | contribs) (→Format for scheduling tasks: Default: R meaning (thanks to David Mu)) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Server settings}} | {{Server settings}} | ||
==Managing scheduled tasks== | ==Managing scheduled tasks== | ||
An administrator can schedule routine tasks very precisely from ''Administration > Site administration > Server > Scheduled tasks.'' | An administrator can schedule routine tasks very precisely from ''Administration > Site administration > Server > Tasks > Scheduled tasks.'' | ||
Note that you still need to run the [[Cron|cron scripts]] (admin/cli/cron.php or https://yoursite/admin/cron.php) at regular intervals. It is recommended that the cron is run every minute. | Note that you still need to run the [[Cron|cron scripts]] (admin/cli/cron.php or https://yoursite/admin/cron.php) at regular intervals. It is recommended that the cron is run every minute. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
1 is every Monday or every January | 1 is every Monday or every January | ||
2,5 is the second and 5th of the month, or February and May, or Tuesday and Friday. | 2,5 is the second and 5th of the month, or February and May, or Tuesday and Friday. | ||
Default: R means that a random value is picked when saving changes. This helps to distribute tasks more equally instead of running too many of them on the hour, midnight etc. | |||
==Fail delay== | ==Fail delay== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:26, 30 April 2021
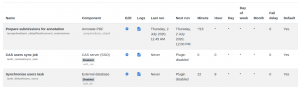
Managing scheduled tasks
An administrator can schedule routine tasks very precisely from Administration > Site administration > Server > Tasks > Scheduled tasks.
Note that you still need to run the cron scripts (admin/cli/cron.php or https://yoursite/admin/cron.php) at regular intervals. It is recommended that the cron is run every minute.
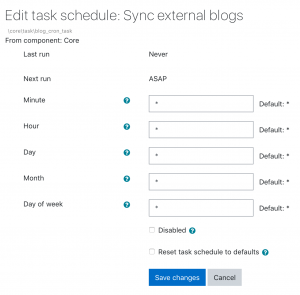
Clicking the edit icon allows the administrator to specify the minute/hour/day/month or day of the week the task is to be run. It is also possible to reset the task to its default setting or disable it completely.
The column 'Next run' provides information on whether a plugin or a task is disabled (as well as the date that a task will next run).
Format for scheduling tasks
When typing into the fields, the format is the same as for Unix cron. Examples are as follows and are according to which field you are editing:
* is every minute, hour, day, month */2 is every two minutes, every two hours or every second day 2-10 is every minute between two and ten past the hour or every hour between 2 and 10 am 0 is every Sunday 1 is every Monday or every January 2,5 is the second and 5th of the month, or February and May, or Tuesday and Friday.
Default: R means that a random value is picked when saving changes. This helps to distribute tasks more equally instead of running too many of them on the hour, midnight etc.
Fail delay
If you're trying to debug a cron task, you may notice the Fail Delay becomes populated with a number. This is the time in seconds the cron will delay running the task. To sidestep this problem for development purposes, take a look at the Scheduled Tasks section here: Administration_via_command_line#Scheduled_tasks.
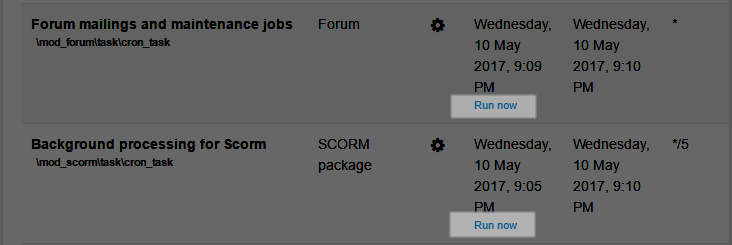
Running individual tasks
To be able to run individual scheduled tasks via 'Run now' links on the scheduled tasks page, 'Allow 'Run now' for scheduled tasks' (tool_task | enablerunnow) in Site administration / Security / Site security settings should be enabled AND 'Path to PHP CLI' (pathtophp) in Site administration / Server / System paths should be set.
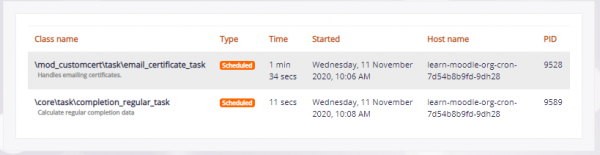
Tasks running now
Currently running tasks may be viewed from Site administration > Server > Tasks >Tasks running now
Launching a task from CLI
You can also launch individual task from Command Line Interface (see Administration via command line).