Groupings: diferència entre les revisions
m (removing new features template) |
|||
| (14 revisions intermèdies per 3 usuaris que no es mostren) | |||
| Línia 1: | Línia 1: | ||
{{Grouping users}} | {{Grouping users}} | ||
NOTE: if you want to show resources just to one group and not another, | If you want to make an activity (such as an assignment or a quiz) visible to only one set of users within a course, you need first to put the users into a [[Groups|group]] and then put them into a grouping. A single grouping can house one group or several groups. | ||
If you assign an activity to a grouping then only the group/grouping that is selected will be able to see and do the activity. It will be invisible to other groups or groupings. | |||
NOTE: if you want to show resources (such as a folder or webpage) to just to one group and not another, see [[Available for group members only]]. | |||
==Adding groups to a grouping== | ==Adding groups to a grouping== | ||
To add groups to a grouping: | To add groups to a grouping: | ||
*In your course, click Settings>Users>Groups. | *In your course, click ''Settings > Course administration > Users > Groups''. | ||
*Click the groupings tab | *Click the groupings tab: | ||
[[File:Groupingstabs.png]] | [[File:Groupingstabs.png]] | ||
*If necessary, create a new grouping by clicking the create grouping button on the groupings page. | |||
An optional grouping ID number (an advanced setting) may be added for matching the grouping against external systems. Grouping ID numbers are not displayed anywhere on the site. Within a course, all grouping ID numbers must be unique. Thus it's not possible to create a grouping with a duplicate grouping ID number. | |||
*Click the "Show groups in grouping" people icon in the edit column: | |||
[[File:Showgroupsingroupings2.png]] | |||
*On the add/remove groups page, select the group(s) you want to add to the grouping from the "Potential members" list. | |||
*Click the arrow button that points towards the "Existing members" list. | |||
[[File:Addremovegroupings.png]] | |||
*Click the "Back to groupings" button. The group(s) you added to the grouping will now be listed in the table on the groupings page. | |||
Existing groupings can be edited and/or deleted using the appropriate icons in the edit column of the table on the groupings page. | Existing groupings can be edited and/or deleted using the appropriate icons in the edit column of the table on the groupings page. | ||
| Línia 24: | Línia 34: | ||
#Follow the settings link in the course administration block. | #Follow the settings link in the course administration block. | ||
#In the groups section in the | #In the groups section in the course settings, select the default grouping. | ||
The default grouping is used on the Participants page. | The default grouping is used on the Participants page. | ||
| Línia 30: | Línia 40: | ||
==Selecting grouping in activity== | ==Selecting grouping in activity== | ||
To use a particular grouping in an activity: | To use a particular grouping in an activity: | ||
*In the "edit settings" link of the Settings block for the activity, click the "Show advanced" button in the common module settings section. | |||
*Ensure that the group mode is set to separate or visible groups. | |||
*Select the grouping from the grouping dropdown menu. | |||
*Check the "Available for group members only" box. | |||
[[File:Setyourgrouping.png]] | |||
*Click the "Save changes" button at the bottom of the page. | |||
Students will only see the activities they have been assigned to. Teachers will see the name of the grouping in brackets after the activity name on the course page. A count of activities assigned to each grouping is kept on the groupings page. | |||
Please note that the grouping option appears by default only in activities that support group modes | Please note that the grouping option appears by default only in activities that support group modes. If you enable ''Available for group members only'' you will be able to assign resources to specific groups also. | ||
==Restricting a whole topic to a grouping== | |||
There is a dropdown setting in each topic summary which allows you to select a particular grouping for that topic section. To enable this setting, you need to enable both [[Conditional activities]] and [[Available for group members only]] | |||
[[File:topicgrouping.gif]] | |||
==Examples of groupings== | |||
==Examples of groupings== | ==Examples of groupings== | ||
It sometimes helps to think of a grouping as a [http://en.memory-alpha.org/wiki/Cloaking_device| Romulan cloaking device] Those groups inside it know of their existence but other groups within the course cannot see them. | |||
===Example 1: Differentiation=== | |||
*You have course on Macbeth shared by three teachers. The activities and resources are mostly the same and used by all three classes. | |||
*However, Mr Brown’s class are a higher ability and so are set some extension assignments that must not be seen by Mrs Smith’s class who are of a lower ability. Mrs Smith’s class need some extra assistance and are set some activities which are too easy for Mr Brown's students. Ms Black’s class are middle ability and can cope with some of the higher tasks but also benefit from some of the supportive tasks Mrs Smith uses. | |||
Groupings would allow all three teachers to share the course and yet direct activities to specific classes: | |||
#''3000 word in-depth assignment'' - only for Class Brown. The class is added to the grouping “Class Brown” and the assignment is set to the “Class Brown” grouping. Only these students will see it. | |||
#''Basic Shakespeare vocabulary'' –a page only for Class Smith. The class is added to the grouping “Class Smith” and the page is set to the "Class Smith" grouping (See [[Available for group members only]] for resources) Only the students with special educational needs will see it. | |||
#''Quiz on the main protagonists'' –suitable for Class Brown (high ability) but offered to Class Black also to extend their learning. Both classes are added to a grouping “ClassBrownBlack” and the quiz is set to the "ClassBrownBlack" grouping. These two classes will see the quiz but Mrs Smiths’s will not. | |||
===Example 2: Mandatory and optional modules=== | |||
*A university has a mandatory module of work ''FS32'' and two optional modules ''FS33'' and ''FS34'' within a single Moodle course. So all students must complete FS32 and then choose either one of the other two options. Once students have signed up to one of the optional modules they are not allowed to view the contents of the other module. | |||
*Three groups may be made: group FS32 including all students on the course; group FS33 including only those who have signed up for this optional module, and group FS34 including only those who have signed up for the other optional module. | |||
#Nothing needs to be done with the activities in the mandatory module FS32 as all students need to access them. The activities can be set to separate or visible groups but no grouping is necessary. | |||
# In order for only those students who signed up for optional modules FS33 and FS34 to view them, "Group FS33" needs to be put into "Grouping FS33". and "Group FS32" needs to be put into "Grouping FS34" | |||
#. The activities in each of the two optional modules can then be assigned to the respective groupings. With Moodle 2.3 it is possible to allocate whole course sections to groupings so it might be useful to add the activities to a particular course section to save administrative time. | |||
==One way to visualise groupings== | |||
Olympic metaphor: at the Olympics, there are different sports (gymnastics, swimming, track) and many countries. There are two ways to think of an Olympian athlete: by the sport they compete in, and by their nationality. To be part of the United States Olympic Team, you must first be a swimmer, a gymnast, or a runner. You cannot be in the US Team without first being an athlete in a specific sport. The sport is your group. Your country is your grouping. You must belong to a group before joining a grouping. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Línia 48: | Línia 92: | ||
*[[Groupings FAQ]] | *[[Groupings FAQ]] | ||
*Using Moodle [http://moodle.org/mod/forum/discuss.php?d=131905 Moodle Groups vs. Groupings] forum discussion including youtube video showing how to set up groupings | *Using Moodle [http://moodle.org/mod/forum/discuss.php?d=131905 Moodle Groups vs. Groupings] forum discussion including youtube video showing how to set up groupings | ||
[[fr:Groupements]] | [[fr:Groupements]] | ||
Revisió de 16:12, 6 nov 2012
If you want to make an activity (such as an assignment or a quiz) visible to only one set of users within a course, you need first to put the users into a group and then put them into a grouping. A single grouping can house one group or several groups.
If you assign an activity to a grouping then only the group/grouping that is selected will be able to see and do the activity. It will be invisible to other groups or groupings.
NOTE: if you want to show resources (such as a folder or webpage) to just to one group and not another, see Available for group members only.
Adding groups to a grouping
To add groups to a grouping:
- In your course, click Settings > Course administration > Users > Groups.
- Click the groupings tab:
- If necessary, create a new grouping by clicking the create grouping button on the groupings page.
An optional grouping ID number (an advanced setting) may be added for matching the grouping against external systems. Grouping ID numbers are not displayed anywhere on the site. Within a course, all grouping ID numbers must be unique. Thus it's not possible to create a grouping with a duplicate grouping ID number.
- Click the "Show groups in grouping" people icon in the edit column:
- On the add/remove groups page, select the group(s) you want to add to the grouping from the "Potential members" list.
- Click the arrow button that points towards the "Existing members" list.
- Click the "Back to groupings" button. The group(s) you added to the grouping will now be listed in the table on the groupings page.
Existing groupings can be edited and/or deleted using the appropriate icons in the edit column of the table on the groupings page.
Setting the default grouping
Once some groupings have been created, a default grouping for course activities and resources may be set.
- Follow the settings link in the course administration block.
- In the groups section in the course settings, select the default grouping.
The default grouping is used on the Participants page.
Selecting grouping in activity
To use a particular grouping in an activity:
- In the "edit settings" link of the Settings block for the activity, click the "Show advanced" button in the common module settings section.
- Ensure that the group mode is set to separate or visible groups.
- Select the grouping from the grouping dropdown menu.
- Check the "Available for group members only" box.
- Click the "Save changes" button at the bottom of the page.
Students will only see the activities they have been assigned to. Teachers will see the name of the grouping in brackets after the activity name on the course page. A count of activities assigned to each grouping is kept on the groupings page.
Please note that the grouping option appears by default only in activities that support group modes. If you enable Available for group members only you will be able to assign resources to specific groups also.
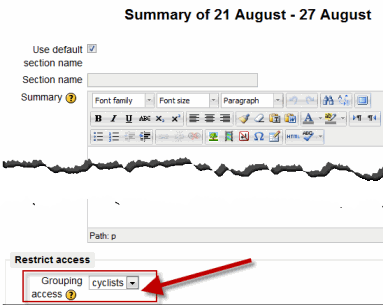
Restricting a whole topic to a grouping
There is a dropdown setting in each topic summary which allows you to select a particular grouping for that topic section. To enable this setting, you need to enable both Conditional activities and Available for group members only
Examples of groupings
Examples of groupings
It sometimes helps to think of a grouping as a Romulan cloaking device Those groups inside it know of their existence but other groups within the course cannot see them.
Example 1: Differentiation
- You have course on Macbeth shared by three teachers. The activities and resources are mostly the same and used by all three classes.
- However, Mr Brown’s class are a higher ability and so are set some extension assignments that must not be seen by Mrs Smith’s class who are of a lower ability. Mrs Smith’s class need some extra assistance and are set some activities which are too easy for Mr Brown's students. Ms Black’s class are middle ability and can cope with some of the higher tasks but also benefit from some of the supportive tasks Mrs Smith uses.
Groupings would allow all three teachers to share the course and yet direct activities to specific classes:
- 3000 word in-depth assignment - only for Class Brown. The class is added to the grouping “Class Brown” and the assignment is set to the “Class Brown” grouping. Only these students will see it.
- Basic Shakespeare vocabulary –a page only for Class Smith. The class is added to the grouping “Class Smith” and the page is set to the "Class Smith" grouping (See Available for group members only for resources) Only the students with special educational needs will see it.
- Quiz on the main protagonists –suitable for Class Brown (high ability) but offered to Class Black also to extend their learning. Both classes are added to a grouping “ClassBrownBlack” and the quiz is set to the "ClassBrownBlack" grouping. These two classes will see the quiz but Mrs Smiths’s will not.
Example 2: Mandatory and optional modules
- A university has a mandatory module of work FS32 and two optional modules FS33 and FS34 within a single Moodle course. So all students must complete FS32 and then choose either one of the other two options. Once students have signed up to one of the optional modules they are not allowed to view the contents of the other module.
- Three groups may be made: group FS32 including all students on the course; group FS33 including only those who have signed up for this optional module, and group FS34 including only those who have signed up for the other optional module.
- Nothing needs to be done with the activities in the mandatory module FS32 as all students need to access them. The activities can be set to separate or visible groups but no grouping is necessary.
- In order for only those students who signed up for optional modules FS33 and FS34 to view them, "Group FS33" needs to be put into "Grouping FS33". and "Group FS32" needs to be put into "Grouping FS34"
- . The activities in each of the two optional modules can then be assigned to the respective groupings. With Moodle 2.3 it is possible to allocate whole course sections to groupings so it might be useful to add the activities to a particular course section to save administrative time.
One way to visualise groupings
Olympic metaphor: at the Olympics, there are different sports (gymnastics, swimming, track) and many countries. There are two ways to think of an Olympian athlete: by the sport they compete in, and by their nationality. To be part of the United States Olympic Team, you must first be a swimmer, a gymnast, or a runner. You cannot be in the US Team without first being an athlete in a specific sport. The sport is your group. Your country is your grouping. You must belong to a group before joining a grouping.
See also
- Available for group members only
- Groupings FAQ
- Using Moodle Moodle Groups vs. Groupings forum discussion including youtube video showing how to set up groupings