WebDAV repository: Difference between revisions
Tomaz Lasic (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Mary Cooch (talk | contribs) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Repositories}} | {{Repositories}} | ||
Web-based Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV) is a set of methods based on the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) that facilitates collaboration between users in editing and managing documents and files stored on World Wide Web servers. | Web-based Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV) is a set of methods based on the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) that facilitates collaboration between users in editing and managing documents and files stored on World Wide Web servers. | ||
A WebDAV repository can be enabled by | A WebDAV repository can be enabled by a site administrator in ''Administration > Site administration > Plugins > Repositories > Manage repositories''. | ||
==WebDAV configuration== | |||
After enabling the WebDAV repository, a repository instance can be created in ''Administration > Site administration > Plugins > Repositories > WebDAV repository''. | |||
[[Image:Webdav config.png | [[Image:Webdav config.png]] | ||
===Options=== | ===Options=== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 25: | ||
WebDAV server password: HTTP Basic authentication password | WebDAV server password: HTTP Basic authentication password | ||
For example, if you are going to add a webdav server at http://webdavserver.tld/path/to/dir, you should use following options: | |||
For example, if you are going to | |||
WebDAV type: HTTP | WebDAV type: HTTP | ||
WebDAV Server: webdavserver.tld | WebDAV Server: webdavserver.tld | ||
== Configuring WebDAV on Microsoft Windows Server 2003 R2 (Service Pack 2), IIS V6.0 == | |||
=== Configure Windows Server 2003 === | |||
First we need to install WebDAV on the server. ''Note:'' when you promote a basic Windows Server 2003 installation to an application server, it installs various IIS 6 components but WebDAV isn’t one of them. | |||
==== Install and Enable WebDAV on the Server ==== | |||
To install WebDAV on the IIS 6 machine, use Add or Remove Programs in Control Panel and run the Windows Components Wizard. You can find WebDAV under '''Application Server -> Internet Information Services -> World Wide Web Service -> WebDAV Publishing'''. | |||
Once WebDAV is installed it needs to be enabled. Check the WebDAV option under the Web Service Extensions node in IIS Manager. | |||
=== Configure IIS === | |||
Configuring a new virtual directory in IIS is a two-step process: | |||
#Create a new virtual directory using the Virtual Directory wizard | |||
#Configure the access permissions on the new virtual directory | |||
==== Create New Virtual Directory ==== | |||
#Open IIS and right-click on your Moodle website. Select '''New -> Virtual Directory'''... from the pop-up menu.<br />[[Image:New_virtual_directory.png|200 px|Menu option required for creating new virtual directory]] | |||
#Select '''New -> Virtual directory...''' from the pop-up menu. The '''Create New Virtual Directory Wizard''' is displayed.<br />[[Image:Wizard_intro.png|200 px|IIS Virtual Directory Creation Wizard]] | |||
#Call the new virtual directory '''Moodledata'''.<br />[[Image:Name_directory.png|200 px|alt text]] | |||
#Specify the path to the Moodledata directory.<br />[[Image:Choose_path.png|200 px|Choosing path to folder on server]] | |||
#Ensure the new virtual directory has '''Read''', '''Write''' and '''Browse''' permissions.<br />[[Image:Directory_permissions.png|200 px|Specifying directory permissions]] | |||
#Press the Finish button to create the new virtual directory. | |||
==== Configuring Virtual Directory Properties ==== | |||
#Right-click on the new virtual directory and select Properties from the pop-up menu.<br />[[Image:Check_properties.png|200 px|Checking new virtual directory properties]] | |||
#Ensure that '''Read''', '''Write''', '''Directory browsing''', and '''Log visits''' are checked. Ensure '''Index this resource''' is unchecked.<br />[[Image:Properties_view.png|200 px|Virtual directory properties correctly configured]] | |||
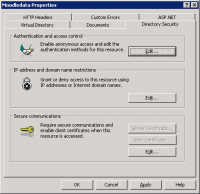
#Click on the '''Directory Security''' tab and press the '''Authentication and access control''' Edit... button<br />[[Image:Authentication_tab.png|200 px|Directory Security authentication and access control]] | |||
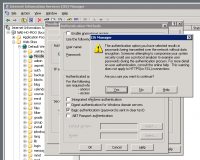
#Authenticated access configuration will depend on your needs. Basic access will require you to uncheck '''Enable anonymous access''' and check '''Basic authentication (password is sent in clear text)'''. You may get a warning about security:<br />[[Image:Authentication_warn.png|200 px|Directory security warning]] | |||
#Your new virtual directory is ready for testing.<br />[[Image:Final_view.png|200 px|New virtual directory ready for use]] | |||
=== Testing WebDAV on Windows XP === | |||
WebDAV needs to be enabled on any client machines that will be used to create and manage content for Moodle. Windows XP has a built-in WebDAV client service that needs to be enabled: | |||
#Open the '''Services''' console under '''Administrative Tools''' and find the '''WebClient''' service. | |||
#Double-click on this service to open its '''Properties''' sheet. | |||
#Change the '''Startup Type''' to ''Automatic'', then click the Start button to start the service. | |||
''Note:'' Internet Explorer 8.0 no longer supports web folders. See [http://blogs.msdn.com/b/askie/archive/2009/03/20/open-as-web-folder-not-in-the-internet-explorer-8-file-open-dialog.aspx this blog post from David Conner] for details. Instead, you will need to map a network drive (instructions on mapping a network drive are also given in David's blog post). | |||
WebDAV path: /path/to/dir/ | WebDAV path: /path/to/dir/ | ||
==Repository permissions== | |||
This repository is accessible by default to administrators, course creators, teachers, editing teachers and managers, but not to guests or students. This [[Capabilities/repository/webdav:view|capability]] can be changed to control access to users with specific roles. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 84: | ||
* MDL-22663 | * MDL-22663 | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Site administration]] | ||
[[de:WebDAV Repository]] | [[de:WebDAV Repository]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:17, 12 May 2014
Web-based Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV) is a set of methods based on the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) that facilitates collaboration between users in editing and managing documents and files stored on World Wide Web servers.
A WebDAV repository can be enabled by a site administrator in Administration > Site administration > Plugins > Repositories > Manage repositories.
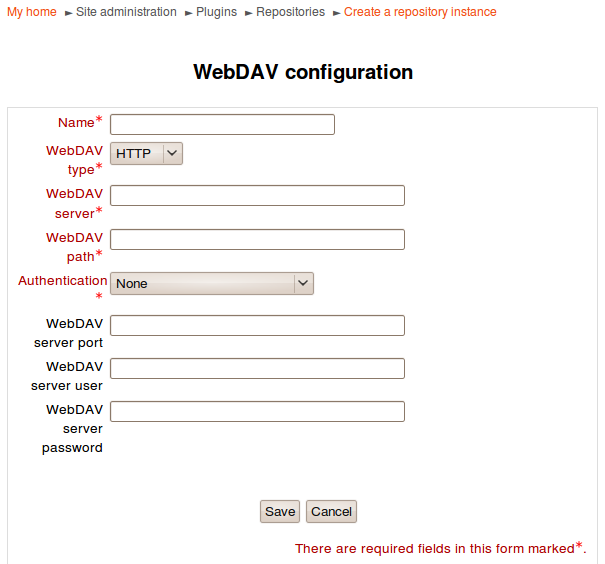
WebDAV configuration
After enabling the WebDAV repository, a repository instance can be created in Administration > Site administration > Plugins > Repositories > WebDAV repository.
Options
WebDAV type: Choose from HTTP or HTTPS connection
WebDAV server: The server name
WebDAV path: The path to webdav directory
Authentication: We currently only support HTTP Basic Authentication
WebDAV server port: The webdav server port
WebDAV server user: HTTP Basic authentication username
WebDAV server password: HTTP Basic authentication password
For example, if you are going to add a webdav server at http://webdavserver.tld/path/to/dir, you should use following options: WebDAV type: HTTP WebDAV Server: webdavserver.tld
Configuring WebDAV on Microsoft Windows Server 2003 R2 (Service Pack 2), IIS V6.0
Configure Windows Server 2003
First we need to install WebDAV on the server. Note: when you promote a basic Windows Server 2003 installation to an application server, it installs various IIS 6 components but WebDAV isn’t one of them.
Install and Enable WebDAV on the Server
To install WebDAV on the IIS 6 machine, use Add or Remove Programs in Control Panel and run the Windows Components Wizard. You can find WebDAV under Application Server -> Internet Information Services -> World Wide Web Service -> WebDAV Publishing.
Once WebDAV is installed it needs to be enabled. Check the WebDAV option under the Web Service Extensions node in IIS Manager.
Configure IIS
Configuring a new virtual directory in IIS is a two-step process:
- Create a new virtual directory using the Virtual Directory wizard
- Configure the access permissions on the new virtual directory
Create New Virtual Directory
- Open IIS and right-click on your Moodle website. Select New -> Virtual Directory... from the pop-up menu.
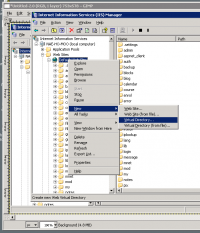
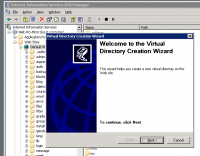
- Select New -> Virtual directory... from the pop-up menu. The Create New Virtual Directory Wizard is displayed.
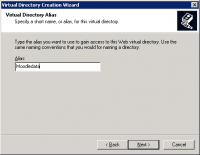
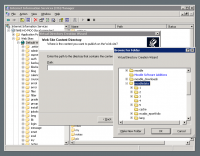
- Call the new virtual directory Moodledata.
- Specify the path to the Moodledata directory.
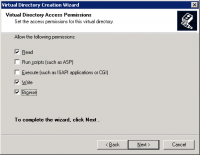
- Ensure the new virtual directory has Read, Write and Browse permissions.
- Press the Finish button to create the new virtual directory.
Configuring Virtual Directory Properties
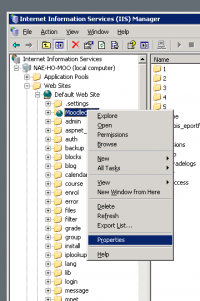
- Right-click on the new virtual directory and select Properties from the pop-up menu.
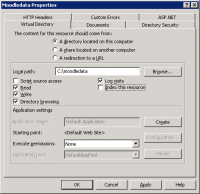
- Ensure that Read, Write, Directory browsing, and Log visits are checked. Ensure Index this resource is unchecked.
- Click on the Directory Security tab and press the Authentication and access control Edit... button
- Authenticated access configuration will depend on your needs. Basic access will require you to uncheck Enable anonymous access and check Basic authentication (password is sent in clear text). You may get a warning about security:
- Your new virtual directory is ready for testing.
Testing WebDAV on Windows XP
WebDAV needs to be enabled on any client machines that will be used to create and manage content for Moodle. Windows XP has a built-in WebDAV client service that needs to be enabled:
- Open the Services console under Administrative Tools and find the WebClient service.
- Double-click on this service to open its Properties sheet.
- Change the Startup Type to Automatic, then click the Start button to start the service.
Note: Internet Explorer 8.0 no longer supports web folders. See this blog post from David Conner for details. Instead, you will need to map a network drive (instructions on mapping a network drive are also given in David's blog post).
WebDAV path: /path/to/dir/
Repository permissions
This repository is accessible by default to administrators, course creators, teachers, editing teachers and managers, but not to guests or students. This capability can be changed to control access to users with specific roles.