Using web services
Template:Moodle 2.0This document explains how an administrator set up a web service for ordinary users. It is useful if you want many user to access a service. All user will have a specific and unique security key (also known as "token") to access the service.
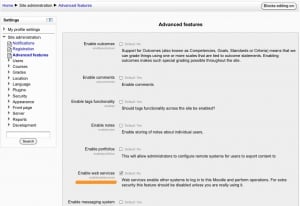
Enable web service feature
For security reasons, web services should only be enabled if you intend to make use of it.
Settings block > Site Administration > Advanced features
Check Enable web services option and Save Changes
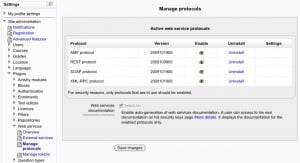
Enable a protocol
In this step you will enable some web service protocols. Usually external applications that users wish to use should dictate which protocols are enabled.
Settings block > Site Administration > Plugins > Web services > Manage protocols
Enable the desired protocol (SOAP, REST, XMLRPC, AMF, ...)
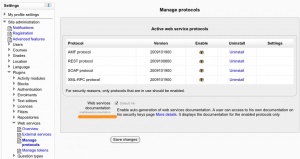
Enable the web service function documentation
On the 'Manage protocols' page you can also enable the web service function documentation. If this documentation is enabled, the user specific web service descriptions will be available to each user. This option is mainly useful to web service client developers.
.
Create a service
There is no such thing as a default web service in Moodle, so anyone looking for one (or for a list of available services) may get rather confused. Instead, you must create a custom service.
Creating a custom service does not mean you are really creating an entirely new web service yourself. You don't have to program anything. Instead, a 'custom web service' just lets you select which of the standard web service functions are available via that service.
This allows you to enable only the specific functions that you need to expose, therefore increasing security.
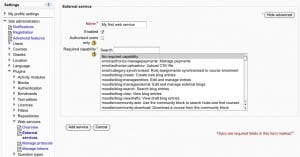
Settings block > Site Administration > Plugins > Web services > External Services Click on Add new custom service
The Add a service page should be displayed.
- "Authorised users": if enabled, you will need to select the authorised users manually. Otherwise all Moodle users are allowed, at the condition they have the right permissions
- required capability: if enabled, any user accessing the web service will be checked against this selected capability. It is just an additional and optional security layer for your own usage.
Enter a name and check enable Uncheck "Authorised users" and required capability Click on Add service
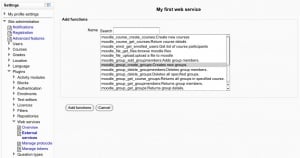
Add functions to the service
Add functions to the service.jpg|thumb]]At this moment your service is empty and doesn't do much. You want to add some web service function to it. Your choice will be dictated by what you allow the external application to do. For now you are going to select 'Create group' function for the only reason that it is the function used as example to create a web service client.
Click Add functions link, Select a 'create group' function and click Add functions button
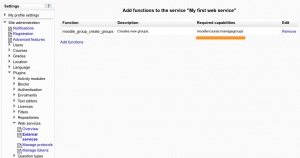
You should be back to the service function list. Next to each function you can see a 'Required capabilies' field. Users need these capabilities to run each function. However there is some exception. Sometimes a function use case could not require the entire capability list. The only way to be 100% sure is to read the web service function documentation (even though they are currently not indicated see MDL-XXX). Core developers try to keep capability names clear enough that it should straight forward for administrator to guess it right.
.
Enable capabilities to users
The last step, and probably the trickiest, is to grant the right permission to the users. They would need the following capabilities:
- "moodle/webservice:createtoken" capability to the users
- "webservice/rest:use, webservice/soap:use, webservice/xmlrpc:use, webservice/amf:use" matching the enabled protocols.
- the required capabilities by the web service functions. These required capabilities are listed when you add a function to the service.
For more information about roles and capabilities, read the Manage roles documentation.
Once done, the web service should be set up. The user can retrieve his/her personal security key and copy it in an external application.