HTML block: Difference between revisions
From MoodleDocs
- Managing blocks
- Block settings
- Activities
- Admin bookmarks
- Blog menu
- Blog tags
- Calendar
- Comments
- Community finder
- Course completion status
- Course overview
- Course/site description
- Courses
- Flickr
- HTML
- Latest news
- Login
- Logged in user
- Main menu
- Mentees
- Messages
- My private files
- Navigation
- Network servers
- Online users
- People
- Quiz results
- Random glossary entry
- Recent activity
- Recent blog entries
- Remote RSS feeds
- Search forums
- Section links
- Self completion
- Settings
- Social activities
- Tags
- Upcoming events
- Youtube
- Blocks FAQ
Mary Cooch (talk | contribs) (added screenshot) |
Helen Foster (talk | contribs) (copying recent changes from 22 wiki) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Blocks}} | {{Blocks}} | ||
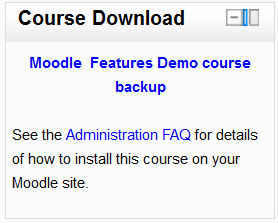
A '''HTML block''' is a standard block used to add text or images on a site or course page. The title bar can be left blank. | |||
[[File:Htmlblockexample.png]] | |||
[[ | The block is flexible and can incorporate a variety of functions and uses in the content area. It has the standard Moodle [[Text editor]] for formatting text, adding images or creating links, switching to code view and allows any valid HTML markup to be used. This enables [[Multimedia plugins|embedding video]], [[Audio in Moodle|sounds]], [[Flash]], and other files which can add unique elements to a course or site page. | ||
[[fr:Bloc HTML]] | [[fr:Bloc HTML]] | ||
[[de: | [[de:Textblock]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:11, 4 January 2012
A HTML block is a standard block used to add text or images on a site or course page. The title bar can be left blank.
The block is flexible and can incorporate a variety of functions and uses in the content area. It has the standard Moodle Text editor for formatting text, adding images or creating links, switching to code view and allows any valid HTML markup to be used. This enables embedding video, sounds, Flash, and other files which can add unique elements to a course or site page.