Development:Process: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This document summarises the various development processes used in developing Moodle. There are four main processes that overlap. | |||
Here are some terms we'll use in this document: | Here are some terms we'll use in this document: | ||
* STABLE = the next stable minor version of Moodle (eg 2.0.1, 2.0.2 ... etc) | * STABLE = the next stable minor version of Moodle (eg 2.0.1, 2.0.2 ... etc) | ||
* | * STABLE backlog = the queue of bugs to be fixed in STABLE (eg 2.0.x) | ||
* DEV = the next major version of Moodle (eg 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 ... etc) | * DEV = the next major version of Moodle (eg 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 ... etc) | ||
* | * DEV backlog = everything to be looked at for upcoming major versions (eg 2.X) | ||
==Integration workflow in the tracker== | |||
The Moodle tracker keeps track of the status of all bug fixes and new features. | |||
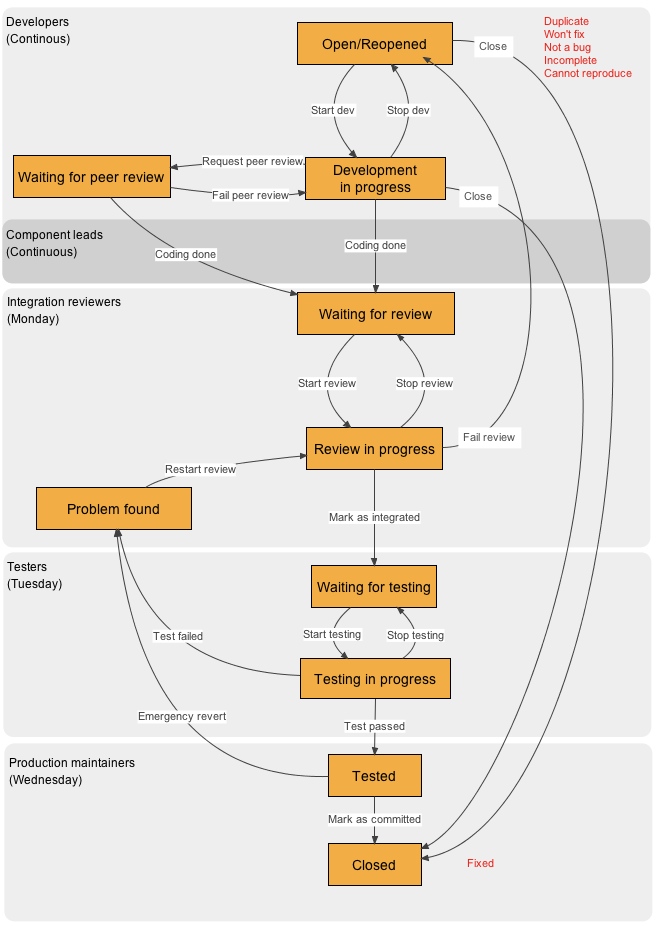
We use a workflow that ensures that new code receives multiple reviews by different people before it is included into the core Moodle code. | |||
[[Image:Workflow.jpg]] | |||
A number of roles make this work: | |||
===Users=== | |||
Users report bugs and make feature requests directly in the tracker, by creating new issues with a summary and a description. | |||
===Developers=== | |||
Developers work on the issues in the tracker to specify solutions and write code that implements these solutions. They will often ask other developers to "peer review" their code in the early stages to avoid problems later on. | |||
While many of the developers work for Moodle.com, a large number are part of the global development community around Moodle. | |||
===Component leads=== | |||
Component leads are developers with some responsibility for particular components (plugins or modules) in Moodle. They have the authority to decide that a particular fix is suitable and complete enough to be considered for integration in Moodle core, by adding their git branches to the integration queue. This can happen at any time. | |||
===Integrators=== | |||
On Monday of each week, the integration team (a small team of senior developers employed by Moodle HQ) conducts a code-level review of all issues in the integration queue. This is often called the "pull" process. If the fix is judged appropriate they will integrate the code into our git integration repository for further testing and it gets added to the testing queue. | |||
If they find problems they reject the issue and send it back to the developer for further work. | |||
== | ===Testers=== | ||
On Tuesday each week, testers look at all the issues in the testing queue, trying each fix and feature to make sure that it does actually fix the problem it was supposed to, and that there are no regressions. | |||
If they find problems they reject the issue and integrators may remove it from the integration repository and push it back to the developer for further work. | |||
=== | ===Committers=== | ||
On Wednesday each week, committers merge all the issues that passed testing into the git production repository, and it becomes available for use on production systems via git, cvs, and download packages. | |||
==Stable maintenance cycles== | |||
Moodle releases regular updates of the stable version of the software to fix bugs and other issues. Releases like 2.0.1, 2.0.2, 2.0.3 etc only include fixes based on the latest major release (2.0) and never any significant new features or database changes. | |||
At Moodle HQ there is a team of developers using a SCRUM-based process to work on these releases. | |||
===Triage team=== | |||
Triagers evaluate new issues, making sure that they are labelled correctly. One of the most important jobs they do is to identify issues that should be fixed in the stable branch. These are added to the STABLE backlog with a priority ranging from "Trivial" up to "Blocker". | |||
Other larger issues go into the DEV backlog for consideration as part of the next major release. | |||
===Scrum team=== | |||
Every three weeks, the Stable Scrum team takes a number of the most urgent issues from the STABLE backlog (approx 30, but it varies) and starts working on solving them. The team meets daily to discuss solutions and progress, as well as conducting peer reviews of code. The team has a "Scrum master" to help everyone stay organised and to "unblock" any barriers to progress. Everything is documented publically in the tracker. | |||
Whenever a solution for an issue is finished, it is submitted into to the standard integration workflow process described above. | |||
== | ==Major release cycles== | ||
Since Moodle 2.0, we have a policy of release major versions (eg 2.1, 2.2) every six months: in June and December. | |||
Each release can be different, but generally the cycles work like this: | |||
===Define roadmap=== | |||
The product owner (Martin Dougiamas) defines the likely roadmap based on community wishes, third-party developments and important issues within the existing code. The DEV backlog is also a factor. | |||
Sometimes these might be based on earlier features, sometimes they may be evauluating something developed by a third party, sometimes it might be something completely new. | |||
===Development team=== | |||
The DEV team (employed at Moodle HQ) work on major new features one or two at a time. The aim is always to try and finish things completely before moving on to the next features, as this helps to avoid delays in delivering a release on time. | |||
All this code goes through the standard weekly integration workflow described above. | |||
===QA Team=== | |||
Finally, in the last month before the release, a feature freeze is called (no new features can be added) and our QA team performs a full functional test of Moodle features (manually, one at a time) to make sure there are no regressions caused by new features. | |||
The current list of functional tests is listed in the tracker in the [http://tracker.moodle.org/browse/MDLQA-1 MDLQA project]. This list of tests is extended on every release to include new developments. | |||
== | ==New feature development== | ||
Major new features in Moodle usually should go through the following process. | |||
===Specification=== | |||
The developer should create a detailed spec (here in Moodle Docs) outlining their goals for the development and their design for meeting those goals. The more detail the better. | |||
You should also create an issue in the tracker (linking to your docs) to keep track of the project status. | |||
=== | ===Community consultation=== | ||
Get the community involved in looking at the spec to see if it meets their needs and to get further feedback. The forums on moodle.org are good for this, but you could also blog/tweet about it etc. | |||
You probably also want to talk with HQ core developers to make sure the ideas make sense, and possibly get some review on database design, architecture and so on. | |||
===Develop the code using git=== | |||
Develop your code on an open git repository, like github.com. That enables people to see your code and to help you as it develops. Testers and early adopters also have the opportunity to try it early in the process and give you more valuable feedback. | |||
It is essential that your code follows the [[Development:Coding|Moodle Coding Guide]] | |||
== | ===Submit the code for integration=== | ||
This is much the same as for any Moodle code. See the information about the integration workflow above. | |||
[[Category:Developer|Process]] | |||
[[Category:Quality Assurance]] | |||
[[Category:Git]] | [[Category:Git]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:32, 27 April 2011
This document summarises the various development processes used in developing Moodle. There are four main processes that overlap.
Here are some terms we'll use in this document:
- STABLE = the next stable minor version of Moodle (eg 2.0.1, 2.0.2 ... etc)
- STABLE backlog = the queue of bugs to be fixed in STABLE (eg 2.0.x)
- DEV = the next major version of Moodle (eg 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 ... etc)
- DEV backlog = everything to be looked at for upcoming major versions (eg 2.X)
Integration workflow in the tracker
The Moodle tracker keeps track of the status of all bug fixes and new features.
We use a workflow that ensures that new code receives multiple reviews by different people before it is included into the core Moodle code.
A number of roles make this work:
Users
Users report bugs and make feature requests directly in the tracker, by creating new issues with a summary and a description.
Developers
Developers work on the issues in the tracker to specify solutions and write code that implements these solutions. They will often ask other developers to "peer review" their code in the early stages to avoid problems later on.
While many of the developers work for Moodle.com, a large number are part of the global development community around Moodle.
Component leads
Component leads are developers with some responsibility for particular components (plugins or modules) in Moodle. They have the authority to decide that a particular fix is suitable and complete enough to be considered for integration in Moodle core, by adding their git branches to the integration queue. This can happen at any time.
Integrators
On Monday of each week, the integration team (a small team of senior developers employed by Moodle HQ) conducts a code-level review of all issues in the integration queue. This is often called the "pull" process. If the fix is judged appropriate they will integrate the code into our git integration repository for further testing and it gets added to the testing queue.
If they find problems they reject the issue and send it back to the developer for further work.
Testers
On Tuesday each week, testers look at all the issues in the testing queue, trying each fix and feature to make sure that it does actually fix the problem it was supposed to, and that there are no regressions.
If they find problems they reject the issue and integrators may remove it from the integration repository and push it back to the developer for further work.
Committers
On Wednesday each week, committers merge all the issues that passed testing into the git production repository, and it becomes available for use on production systems via git, cvs, and download packages.
Stable maintenance cycles
Moodle releases regular updates of the stable version of the software to fix bugs and other issues. Releases like 2.0.1, 2.0.2, 2.0.3 etc only include fixes based on the latest major release (2.0) and never any significant new features or database changes.
At Moodle HQ there is a team of developers using a SCRUM-based process to work on these releases.
Triage team
Triagers evaluate new issues, making sure that they are labelled correctly. One of the most important jobs they do is to identify issues that should be fixed in the stable branch. These are added to the STABLE backlog with a priority ranging from "Trivial" up to "Blocker".
Other larger issues go into the DEV backlog for consideration as part of the next major release.
Scrum team
Every three weeks, the Stable Scrum team takes a number of the most urgent issues from the STABLE backlog (approx 30, but it varies) and starts working on solving them. The team meets daily to discuss solutions and progress, as well as conducting peer reviews of code. The team has a "Scrum master" to help everyone stay organised and to "unblock" any barriers to progress. Everything is documented publically in the tracker.
Whenever a solution for an issue is finished, it is submitted into to the standard integration workflow process described above.
Major release cycles
Since Moodle 2.0, we have a policy of release major versions (eg 2.1, 2.2) every six months: in June and December.
Each release can be different, but generally the cycles work like this:
Define roadmap
The product owner (Martin Dougiamas) defines the likely roadmap based on community wishes, third-party developments and important issues within the existing code. The DEV backlog is also a factor.
Sometimes these might be based on earlier features, sometimes they may be evauluating something developed by a third party, sometimes it might be something completely new.
Development team
The DEV team (employed at Moodle HQ) work on major new features one or two at a time. The aim is always to try and finish things completely before moving on to the next features, as this helps to avoid delays in delivering a release on time.
All this code goes through the standard weekly integration workflow described above.
QA Team
Finally, in the last month before the release, a feature freeze is called (no new features can be added) and our QA team performs a full functional test of Moodle features (manually, one at a time) to make sure there are no regressions caused by new features.
The current list of functional tests is listed in the tracker in the MDLQA project. This list of tests is extended on every release to include new developments.
New feature development
Major new features in Moodle usually should go through the following process.
Specification
The developer should create a detailed spec (here in Moodle Docs) outlining their goals for the development and their design for meeting those goals. The more detail the better.
You should also create an issue in the tracker (linking to your docs) to keep track of the project status.
Community consultation
Get the community involved in looking at the spec to see if it meets their needs and to get further feedback. The forums on moodle.org are good for this, but you could also blog/tweet about it etc.
You probably also want to talk with HQ core developers to make sure the ideas make sense, and possibly get some review on database design, architecture and so on.
Develop the code using git
Develop your code on an open git repository, like github.com. That enables people to see your code and to help you as it develops. Testers and early adopters also have the opportunity to try it early in the process and give you more valuable feedback.
It is essential that your code follows the Moodle Coding Guide
Submit the code for integration
This is much the same as for any Moodle code. See the information about the integration workflow above.