Development:Language API: Difference between revisions
David Mudrak (talk | contribs) (New page: ''This is a draft of Language API proposal that should define data structures and API to manipulate Moodle lang files.'' [[Image:lang_api_classes.png|thumb|UML diagram of Language API cla...) |
David Mudrak (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''This is a draft of | ''This is a draft of a document that should define data structures and API to manipulate Moodle lang files.'' | ||
==Motivation== | |||
Moodle uses its own mechanism of translated strings and files storage. Other ways of handling localization files are sometimes requested. Some translators want to use gettext library (which is using .po files), some might want to export Moodle strings into custom format (eg. XML) to translate them with an external tool and import them back to Moodle. The Moodle Language API should enable to write additional plugins of strings and help files storage. | |||
==Language pack URL== | |||
The type of API implementation is selected automatically acording to URL scheme. Currently, only "internal" plugin is supported which represents the traditional way of lang packs handling. Such pack should be referenced as | |||
internal://localhost/full/path/to/the/pack | |||
Other language pack repositories might be references as e.g.: | |||
cvs://username:password@cvs.moodle.org/lang/cs_utf8 | |||
gettext://localhost/full/path/to/the/pack | |||
xml://localhost/full/path/to/the/pack | |||
==API usage examples== | |||
Basic usage scenario - get a translated string: | |||
$lang_path = $CFG->dataroot."/lang/".current_language(); | |||
$lang_repo = lang_pack_factory("internal://localhost/".$lang_path); | |||
$string = $lang_repo->get_raw_string('identifier', 'module'); | |||
Save a customized string translation: | |||
$lang_path = $CFG->dataroot."/lang/".current_language()."_local"; | |||
$lang_repo = lang_pack_factory("internal://localhost/".$lang_path); | |||
$lang_repo->save_string('identifier', 'module', $translation); | |||
Commit translation into moodle.org repository: | |||
$lang_repo = lang_pack_factory("cvs://${username}:${password}@cvs.moodle.org/lang/{$langcode}"); | |||
$lang_repo->save_module($module, $comment); | |||
==Language API implementations== | |||
[[Image:lang_api_classes.png|thumb|UML diagram of Language API classes]] | [[Image:lang_api_classes.png|thumb|UML diagram of Language API classes]] | ||
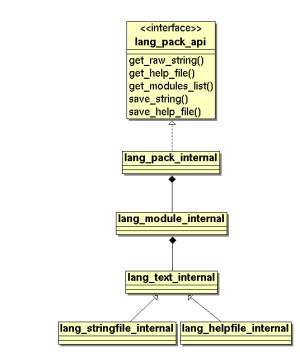
The Language API is defined as interface. Every plugin must implement this interface. The internal plugin (representing traditional way) will be implemented first. | |||
===Internal=== | |||
The internal plugin is defined as | |||
class lang_pack_internal implements lang_pack_api {...} | |||
; | The internal plugin will use sevaral classes: | ||
; | |||
; lang_pack_internal : This represents the whole pack. It is implemented as a directory - e.g. $CFG->dirroot/lang/en_utf8 or $CFG->dataroot/lang/cs_utf8 etc. | |||
; lang_pack_internal_module : represents a single module of a given pack, defines the sub-context of translated texts. It is implemented as a file - e.g. moodle.php or qtype_multichoice.php. | |||
; lang_pack_internal_text : represents a single unit of text (word, sentence or whole page) that can be translated and then used in the UI. It is either one $string[] definition or a help file content. | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Development:Places to search for lang strings]]. | * [[Development:Places to search for lang strings]]. | ||
Revision as of 11:45, 18 November 2008
This is a draft of a document that should define data structures and API to manipulate Moodle lang files.
Motivation
Moodle uses its own mechanism of translated strings and files storage. Other ways of handling localization files are sometimes requested. Some translators want to use gettext library (which is using .po files), some might want to export Moodle strings into custom format (eg. XML) to translate them with an external tool and import them back to Moodle. The Moodle Language API should enable to write additional plugins of strings and help files storage.
Language pack URL
The type of API implementation is selected automatically acording to URL scheme. Currently, only "internal" plugin is supported which represents the traditional way of lang packs handling. Such pack should be referenced as
internal://localhost/full/path/to/the/pack
Other language pack repositories might be references as e.g.:
cvs://username:password@cvs.moodle.org/lang/cs_utf8 gettext://localhost/full/path/to/the/pack xml://localhost/full/path/to/the/pack
API usage examples
Basic usage scenario - get a translated string:
$lang_path = $CFG->dataroot."/lang/".current_language();
$lang_repo = lang_pack_factory("internal://localhost/".$lang_path);
$string = $lang_repo->get_raw_string('identifier', 'module');
Save a customized string translation:
$lang_path = $CFG->dataroot."/lang/".current_language()."_local";
$lang_repo = lang_pack_factory("internal://localhost/".$lang_path);
$lang_repo->save_string('identifier', 'module', $translation);
Commit translation into moodle.org repository:
$lang_repo = lang_pack_factory("cvs://${username}:${password}@cvs.moodle.org/lang/{$langcode}");
$lang_repo->save_module($module, $comment);
Language API implementations
The Language API is defined as interface. Every plugin must implement this interface. The internal plugin (representing traditional way) will be implemented first.
Internal
The internal plugin is defined as
class lang_pack_internal implements lang_pack_api {...}
The internal plugin will use sevaral classes:
- lang_pack_internal
- This represents the whole pack. It is implemented as a directory - e.g. $CFG->dirroot/lang/en_utf8 or $CFG->dataroot/lang/cs_utf8 etc.
- lang_pack_internal_module
- represents a single module of a given pack, defines the sub-context of translated texts. It is implemented as a file - e.g. moodle.php or qtype_multichoice.php.
- lang_pack_internal_text
- represents a single unit of text (word, sentence or whole page) that can be translated and then used in the UI. It is either one $string[] definition or a help file content.